Premium Only Content
5 Drug Binding Receptors
Receptor is a macromolecule in the membrane or inside the cell that specifically (chemically) bind a ligand (drug). The binding of a drug to receptor depends on types of chemical bounds that can be established between drug and receptor. The strength of this chemical bonds (covalent, ionic, hydrogen, hydrophobic) determine the degree of affinity of ligand to receptor. Ligands (drugs) that attracted the receptors may be classified as agonists or antagonists. Agonists produce the biological response as a results of receptor –ligand interactions therefore agonists posses efficacy. On the contrary antagonists did not provoke any biological activity after binding to its receptor.
There are different types of receptors :
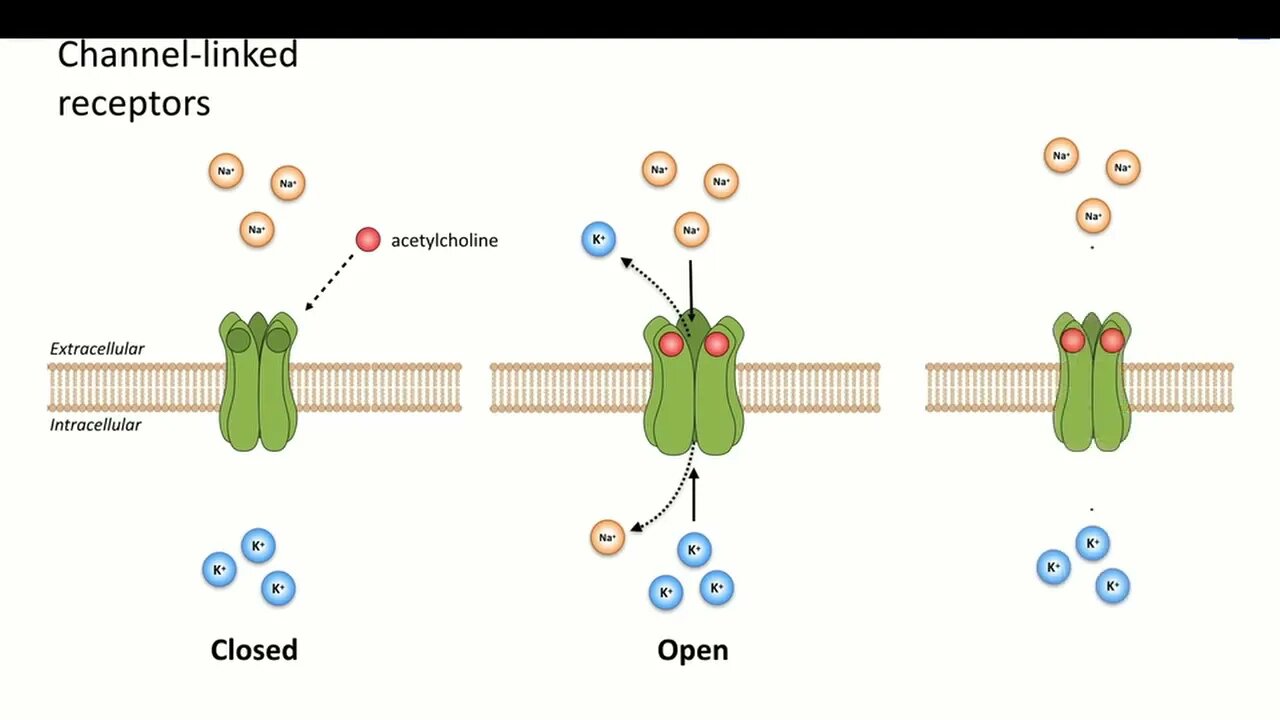
Transmembrane ion-channels receptors
Transmembrane G-protein-coupled receptors
Transmembrane receptors with cytosolic domain
Intracellular (cytoplasm or nucleus) receptors
-
 4:17
4:17
Whisperingpinesstudio
2 years agoBinding demons?
15 -
 38:03
38:03
DOUBLE EAGLES MINISTRY
2 years agoBinding the Strongman
43 -
 19:48
19:48
General Gaming
2 years agobinding of isaac
16 -
 2:32:53
2:32:53
braggaboom gaming channel
2 years agoBinding of Isaac Shenanigans
2 -
 2:20:07
2:20:07
braggaboom gaming channel
2 years agoBinding of Isaac Shenanigans
2 -
 4:06:59
4:06:59
braggaboom gaming channel
2 years agoBinding of Isaac Shenanigans
2 -
 5:06:15
5:06:15
braggaboom gaming channel
2 years agoBinding of Isaac Shenanigans
1 -
 7:05:05
7:05:05
The Mad Reviewer Kyouma
2 years agoFire Emblem The Binding Blade Movie
15 -
 13:27
13:27
Clownfish TV
16 hours agoSydney Sweeney Backlash BACKFIRES! American Eagle Stock UP 38%! | Clownfish TV
42.7K12 -
 18:55
18:55
AndresRestart
16 hours ago $0.84 earnedSomething Key We Keep Missing About Metroid Prime 4 Beyond...
18.5K1