Premium Only Content
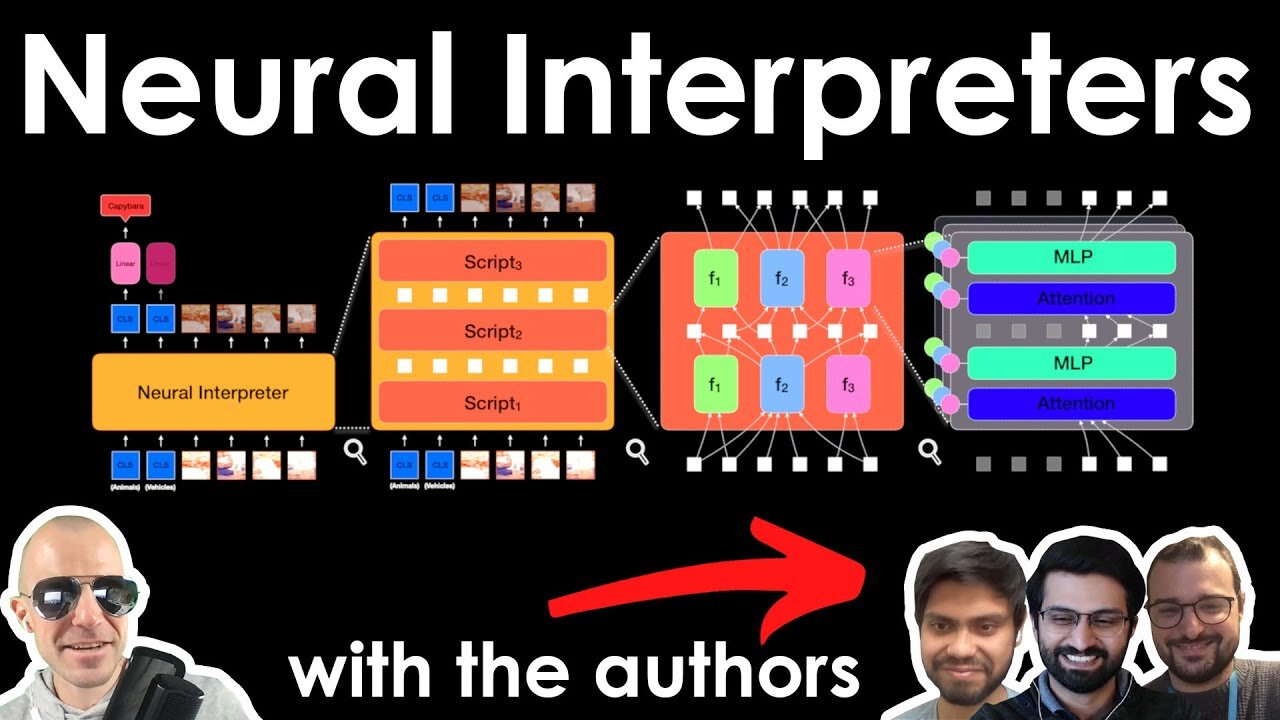
Dynamic Inference with Neural Interpreters (w/ author interview)
#deeplearning #neuralinterpreter #ai
This video includes an interview with the paper's authors!
What if we treated deep networks like modular programs? Neural Interpreters divide computation into small modules and route data to them via a dynamic type inference system. The resulting model combines recurrent elements, weight sharing, attention, and more to tackle both abstract reasoning, as well as computer vision tasks.
OUTLINE:
0:00 - Intro & Overview
3:00 - Model Overview
7:00 - Interpreter weights and function code
9:40 - Routing data to functions via neural type inference
14:55 - ModLin layers
18:25 - Experiments
21:35 - Interview Start
24:50 - General Model Structure
30:10 - Function code and signature
40:30 - Explaining Modulated Layers
49:50 - A closer look at weight sharing
58:30 - Experimental Results
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.06399
Guests:
Nasim Rahaman: https://twitter.com/nasim_rahaman
Francesco Locatello: https://twitter.com/FrancescoLocat8
Waleed Gondal: https://twitter.com/Wallii_gondal
Abstract:
Modern neural network architectures can leverage large amounts of data to generalize well within the training distribution. However, they are less capable of systematic generalization to data drawn from unseen but related distributions, a feat that is hypothesized to require compositional reasoning and reuse of knowledge. In this work, we present Neural Interpreters, an architecture that factorizes inference in a self-attention network as a system of modules, which we call \emph{functions}. Inputs to the model are routed through a sequence of functions in a way that is end-to-end learned. The proposed architecture can flexibly compose computation along width and depth, and lends itself well to capacity extension after training. To demonstrate the versatility of Neural Interpreters, we evaluate it in two distinct settings: image classification and visual abstract reasoning on Raven Progressive Matrices. In the former, we show that Neural Interpreters perform on par with the vision transformer using fewer parameters, while being transferrable to a new task in a sample efficient manner. In the latter, we find that Neural Interpreters are competitive with respect to the state-of-the-art in terms of systematic generalization
Authors: Nasim Rahaman, Muhammad Waleed Gondal, Shruti Joshi, Peter Gehler, Yoshua Bengio, Francesco Locatello, Bernhard Schölkopf
Links:
TabNine Code Completion (Referral): http://bit.ly/tabnine-yannick
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/yannickilcher
Twitter: https://twitter.com/ykilcher
Discord: https://discord.gg/4H8xxDF
BitChute: https://www.bitchute.com/channel/yann...
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/ykilcher
BiliBili: https://space.bilibili.com/2017636191
If you want to support me, the best thing to do is to share out the content :)
If you want to support me financially (completely optional and voluntary, but a lot of people have asked for this):
SubscribeStar: https://www.subscribestar.com/yannick...
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/yannickilcher
Bitcoin (BTC): bc1q49lsw3q325tr58ygf8sudx2dqfguclvngvy2cq
Ethereum (ETH): 0x7ad3513E3B8f66799f507Aa7874b1B0eBC7F85e2
Litecoin (LTC): LQW2TRyKYetVC8WjFkhpPhtpbDM4Vw7r9m
Monero (XMR): 4ACL8AGrEo5hAir8A9CeVrW8pEauWvnp1WnSDZxW7tziCDLhZAGsgzhRQABDnFy8yuM9fWJDviJPHKRjV4FWt19CJZN9D4n
-
 1:54
1:54
Damon Imani
3 days agoDamon Left The View SPEECHLESS on Marriage And Government Overreach
6568 -
 4:09
4:09
Memology 101
13 hours ago"Journalist" REPEATEDLY tries and FAILS to bait John Fetterman into calling Trump an "AUTOCRAT"
47110 -
 58:02
58:02
Dialogue works
2 days ago $3.44 earnedMatthew Hoh: Ukraine’s Army Is COLLAPSING Everywhere!
16.2K11 -
 17:24
17:24
Nate The Lawyer
1 day ago $1.98 earnedBREAKING: NEW Scientific Evidence Shows Men Are Better in Sports Than Women
9.26K12 -
 29:43
29:43
Code Blue Cam
1 day agoHow Missing Dipping Sauce Turned into a Felony Arrest
11.3K11 -
 16:19
16:19
BlaireWhite
2 days agoWoman Confronts "Trans Woman" In Locker Room: Gold's Gym Scandal
11.9K10 -
 2:15:40
2:15:40
Side Scrollers Podcast
20 hours agoWTF Happened to Call of Duty?! + Ubisoft’s MAJOR F Up + Vtuber HIT LIST + More | Side Scrollers
64.9K16 -
 18:31
18:31
Nikko Ortiz
16 hours agoKaren You Need A Shower...
12.5K12 -
 9:47
9:47
MattMorseTV
17 hours ago $15.77 earnedDemocrats CAUGHT in $15,000,000 LIE.
23.6K41 -
 43:24
43:24
ThisIsDeLaCruz
19 hours ago $1.97 earnedWhat Fans Never Knew About Falling In Reverse’s Guitarist
10.8K