Premium Only Content
THIS CAN SAVE YOUR LIFE || WATCH THIS FRIST THING IN THE MORNING
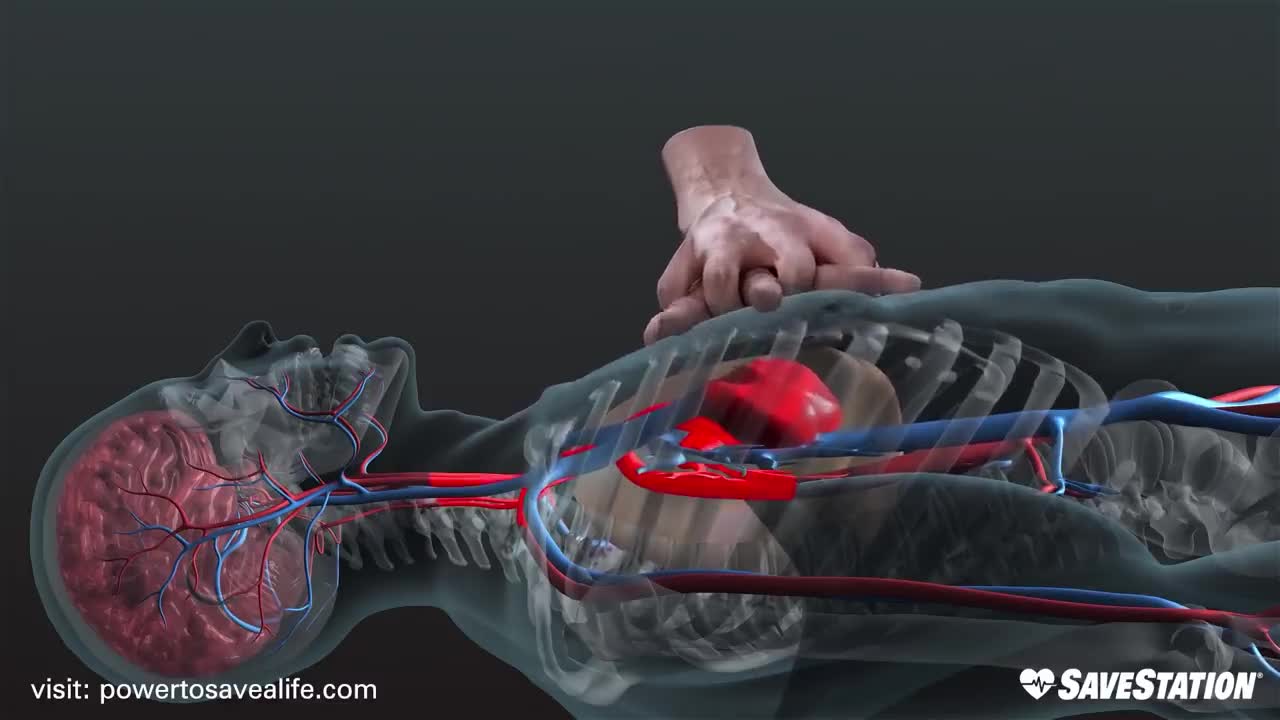
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It is recommended in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations.
CPR involves chest compressions for adults between 5 cm (2.0 in) and 6 cm (2.4 in) deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation). Current recommendations place emphasis on early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for untrained rescuers. In children, however, only doing compressions may result in worse outcomes because, in children, the problem normally arises from respiratory, rather than cardiac, problems. Chest compression to breathing ratios is set at 30 to 2 in adults.
CPR alone is unlikely to restart the heart. Its main purpose is to restore the partial flow of oxygenated blood to the brain and heart. The objective is to delay tissue death and to extend the brief window of opportunity for a successful resuscitation without permanent brain damage. Administration of an electric shock to the subject's heart, termed defibrillation, is usually needed in order to restore a viable, or "perfusing", heart rhythm. Defibrillation is effective only for certain heart rhythms, namely ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, rather than asystole or pulseless electrical activity, which usually require the treatment of underlying conditions to restore cardiac function. Early shock, when appropriate, is recommended. CPR may succeed in inducing a heart rhythm that may be shockable. In general, CPR is continued until the person has a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) or is declared dead.
-
 0:51
0:51
Chrisfocused
3 years agoA must watch | 8 things that can your life forever
66 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Man in America
23 hours agoPfizer Has Been Caught RED HANDED w/ Dr. Chris Flowers
1,420 watching -
 2:24:15
2:24:15
Slightly Offensive
6 hours ago $1.18 earnedAttempted ASSASSINATION of Nick J Fuentes LEAVES 1 DEAD! | Guest: Mel K & Breanna Morello
16.7K11 -
 1:43:08
1:43:08
Roseanne Barr
6 hours ago $2.96 earned"Ain't Nobody Good" with Jesse Lee Peterson | The Roseanne Barr Podcast #79
55.5K27 -

The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
3 hours agoTrump Should Sue Billionaire Governor JB Pritzker for Calling Him a Rapist | The StoneZONE
31.1K3 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Flyover Conservatives
21 hours agoAmerica’s Psychiatrist Speaks Out: Are We Greenlighting Violence? - Dr. Carole Lieberman | FOC Show
740 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
LittleSaltyBear
4 hours ago $0.32 earnedNecromancing Path of Exile 2 4K
325 watching -
 3:51:34
3:51:34
Akademiks
4 hours agoJay Z War against Diddy Accuser Lawyer GOES CRAZY! Lil Baby Speaks OUT! Cardi v Offset? Bhad Bhabie?
73.9K5 -
 1:15:42
1:15:42
Josh Pate's College Football Show
5 hours ago $0.16 earnedCFP Changes Coming | Transfer Portal Intel | Games Of The Year | Head Coaches Set To Elevate
21.4K -
 1:21:17
1:21:17
Donald Trump Jr.
8 hours agoWhat are These Mystery Drones? Plus Inside the Swamp’s CR. Interview with Lue Elizondo | TRIGGERED Ep.200
116K114