Premium Only Content
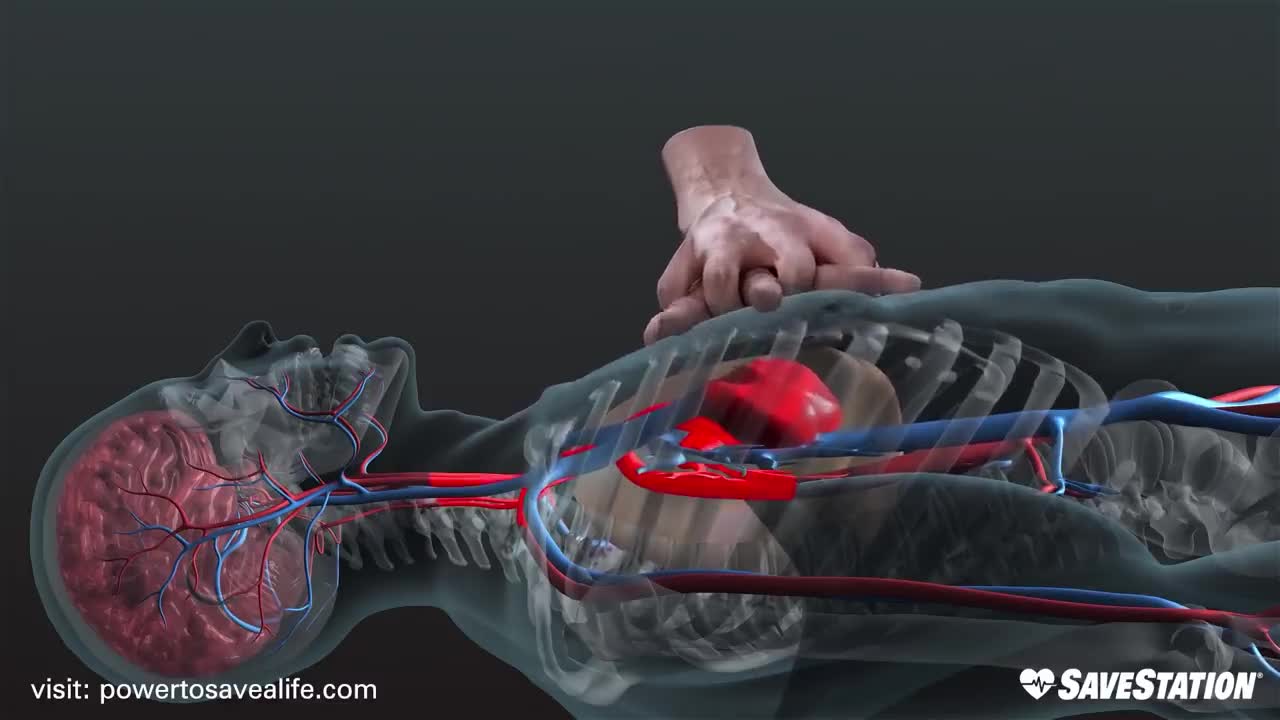
THIS CAN SAVE YOUR LIFE || WATCH THIS FRIST THING IN THE MORNING
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It is recommended in those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations.
CPR involves chest compressions for adults between 5 cm (2.0 in) and 6 cm (2.4 in) deep and at a rate of at least 100 to 120 per minute. The rescuer may also provide artificial ventilation by either exhaling air into the subject's mouth or nose (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) or using a device that pushes air into the subject's lungs (mechanical ventilation). Current recommendations place emphasis on early and high-quality chest compressions over artificial ventilation; a simplified CPR method involving only chest compressions is recommended for untrained rescuers. In children, however, only doing compressions may result in worse outcomes because, in children, the problem normally arises from respiratory, rather than cardiac, problems. Chest compression to breathing ratios is set at 30 to 2 in adults.
CPR alone is unlikely to restart the heart. Its main purpose is to restore the partial flow of oxygenated blood to the brain and heart. The objective is to delay tissue death and to extend the brief window of opportunity for a successful resuscitation without permanent brain damage. Administration of an electric shock to the subject's heart, termed defibrillation, is usually needed in order to restore a viable, or "perfusing", heart rhythm. Defibrillation is effective only for certain heart rhythms, namely ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia, rather than asystole or pulseless electrical activity, which usually require the treatment of underlying conditions to restore cardiac function. Early shock, when appropriate, is recommended. CPR may succeed in inducing a heart rhythm that may be shockable. In general, CPR is continued until the person has a return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) or is declared dead.
-
 0:51
0:51
Chrisfocused
3 years agoA must watch | 8 things that can your life forever
66 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Grant Stinchfield
37 minutes agoDemocrats Try to Turn California Into Predator Playground with Proposed "Child Predator Dream Bill"
184 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Rebel News
1 hour agoCdn troops in Ukraine? Poilievre backs self-defence, Hamas thugs cancel Ottawa Pride | Rebel Roundup
341 watching -
 DVR
DVR
Neil McCoy-Ward
1 hour ago⚠️ OUTRAGE! What They Just Announced For YOUR HOME!!! 🚨
3.82K -
 LIVE
LIVE
IrishBreakdown
2 hours agoNotre Dame and Miami Set To Reignite Intense Rivalry
813 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Charlie Kirk Show
1 hour agoChicago Next! + The Blue Slip Problem | Sen. Tuberville, Alex Clark | 8.25.2025
3,151 watching -
 1:20:52
1:20:52
Benny Johnson
3 hours ago🚨Trump LIVE Now: Signs Executive Order ENDING Cashless Bail | Dem Cities PANIC, Which City NEXT?...
39K30 -
 1:31:26
1:31:26
The White House
4 hours agoPresident Trump Signs Executive Orders, Aug. 25, 2025
40.8K17 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Mel K Show
2 hours agoMORNINGS WITH MEL K - Starving the Globalist Funded Color Revolution in America 8-25-25
777 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Shannon Joy Show
3 hours ago🔥🔥Stressflation Incoming - Coffee Up 25% Veggies Up 40% As Trumps Tariff Taxes Detonate On American Families.🔥🔥
178 watching