Premium Only Content
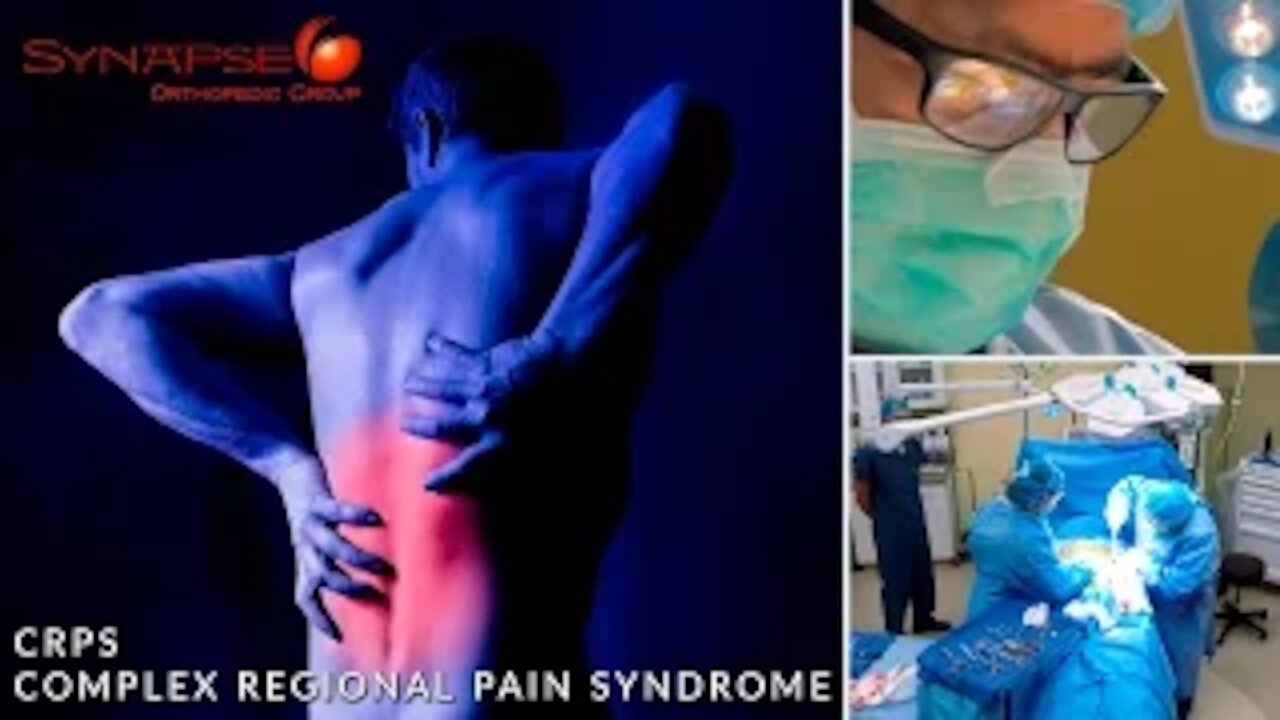
CRPS - Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
No one should have to live with chronic pain. Synapse Orthopedic Group's Jonathan Kohan is a Board Certified Anesthesiologist and specialist in Pain Management.
Call us to schedule an appointment: (818) 788-2400
Locations in Pomona, Sherman Oaks, and Los Angeles
Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a chronic pain condition most often affecting one of the limbs (arms, legs, hands, or feet), usually after an injury or trauma to that limb. CRPS is believed to be caused by damage to, or malfunction of, the peripheral and central nervous systems. The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system involves nerve signaling from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. CRPS is characterized by prolonged or excessive pain and mild or dramatic changes in skin color, temperature, and/or swelling in the affected area.
There are two similar forms, called CRPS-I and CRPS-II, with the same symptoms and treatments. CRPS-II (previously called causalgia) is the term used for patients with confirmed nerve injuries. Individuals without confirmed nerve injury are classified as having CRPS-I (previously called reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome). Some research has identified evidence of nerve injury in CRPS-I, so the validity of the two different forms is being investigated.
CRPS symptoms vary in severity and duration. Studies of the incidence and prevalence of the disease show that most cases are mild and individuals recover gradually with time. In more severe cases, individuals may not recover and may have long-term disability.
Anyone can get CRPS. It can strike at any age and affects both men and women, although it is much more common in women. The average age of affected individuals is about age 40. CRPS is rare in the elderly. Children do not get it before age 5 and only very rarely before age 10, but it is not uncommon in teenagers.
For more information please visit our website at: http://www.synapsedoctor.com
You can also follow our social media pages at:
http://www.facebook.com/synapsedoctor
http://www.instagram.com/synapsedoctor
http://www.twitter.com/synapsedoctor
-
 2:36
2:36
KMGH
5 years agoPatrick Boland finds way to help others suffering from Complex Regional Pain Syndrome through his nonprofit
43 -
 0:19
0:19
ajrassam
4 years agoIrvine regional park
34 -
 1:42
1:42
Amuso Athletics
4 years agoLandmine Complex #1
25 -
 5:10
5:10
levihatton
4 years agoStockholm Syndrome - Muse Drum Cover
2563 -
 3:57
3:57
PsychicFocus
4 years agoPsychic Focus on Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome
34 -
 2:23
2:23
Rabiddugg
4 years agoRecurrent Complex (Cinematic Showcase
14 -
 1:06
1:06
Webbtime
4 years agoThe Villages Eisenhower Regional Recreation Center
65 -
 1:38:45
1:38:45
Steven Crowder
4 hours agoAI Celebs Just Scammed Women out of Millions & Premium Interview w/ Patrick Christys
201K165 -
 43:48
43:48
The Mel K Show
3 hours agoMORNINGS WITH MEL K -This Labor Day Celebrate Liberty, Freedom & Family! 8-29-25
14.2K4 -
 59:02
59:02
The Shannon Joy Show
4 hours ago🔥🔥The Butchers At Hilo Benioff Hospital Hawaii - Mom Subjected To Forced C-Section & Abuse🔥🔥
20.1K3