Premium Only Content
REDUCE STRESS AND SLEEP BETTER! IN YOUR OWN BED!!!
Reduce stress and sleep better with this simple technique !❤️
This position provides a nice inversion for the head, neck and shoulders! By hanging your head in this inverted position, gravity is working to pull your head and spine into alignment and taking the pressure off your muscles and nerves, improving cervical pain. Increased blood flow is also a massive benefit here!
NOTES:
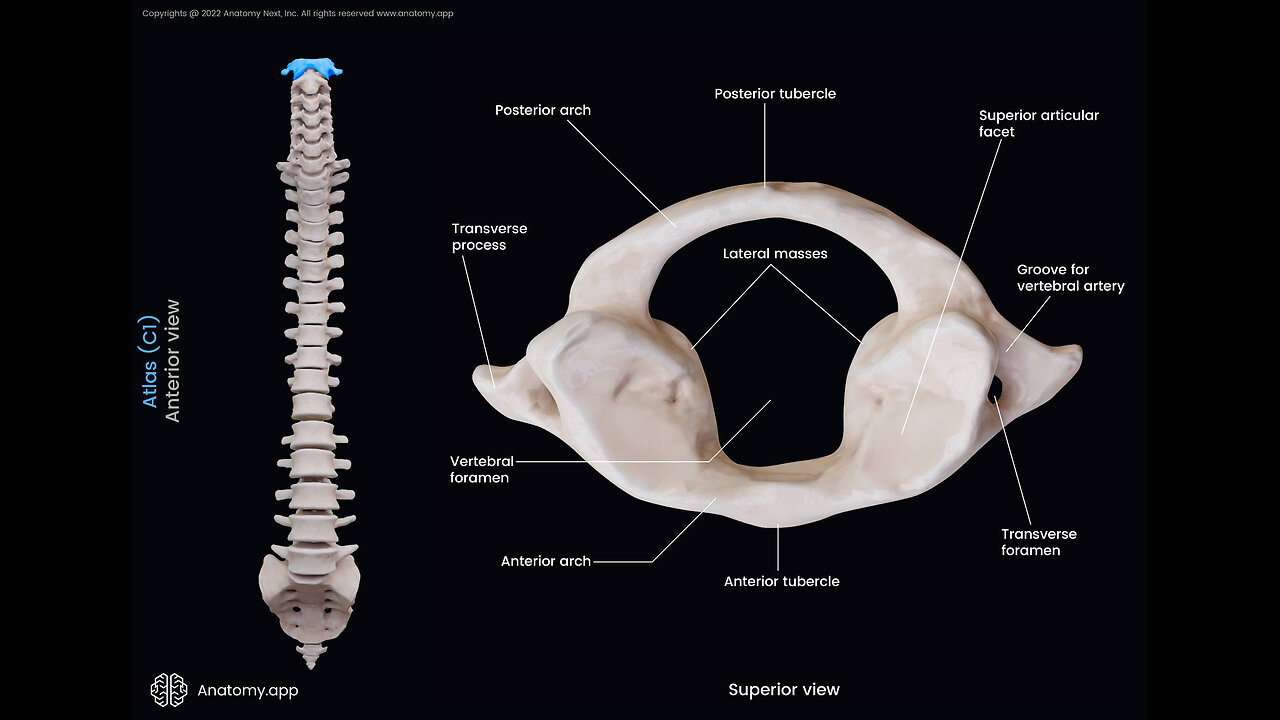
The human vertebral or spinal column can be divided into the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines. The cervical spine includes the first 7 vertebrae following the skull down the upper back. The atlas is the first of these 7 cervical vertebrae and is also referred to as the 1st cervical vertebrae or C1.
Its name derives from the Greek God Atlas, famous in mythologies for being condemned to bear the weight of the Earth on his shoulders for eternity. Similarly, the atlas supports the weight of the skull or the globe-like cranium.
As mentioned above, the atlas is the first vertebral bone, located between the skull base and the axis (C2), the second cervical vertebrae.
As it is the first bone of the vertebral column, the atlas is the point of connection between the skull and the spine. In addition to supporting the weight of the skull, the small bone also controls the head’s range of motion. The atlas forms a number of articulations and serves as the point of attachment for several muscles and ligaments that are instrumental to all head movements.
Anatomy
The atlas is a thin ring-shaped bone that does not resemble the typical vertebrae, thus being classified as an atypical vertebra. It is the most delicate of all the 7 cervical vertebrae and lacks a vertebral body and spinous process. Instead, it comprises an anterior and posterior arch and a lateral mass.
Anterior Arch
It is the bony band that forms the anterior part of the atlas’s ring. There is a bony prominence or tubercle at the front of the bone, known as the anterior tubercle, where the anterior longitudinal ligament attaches.
The smooth circular facet on its posterior surface articulates with the dens or odontoid process of the axis, forming the median atlantoaxial joint. It is a pivot joint that allows the rotational movements of the head, such as when you shake your head to say ‘no.’
The anterior atlanto-occipital membrane attaches to its upper border. In contrast, the lower border is the attachment point for the anterior atlantoaxial membrane.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
We Like Shooting
13 hours agoWe Like Shooting 638 (Gun Podcast)
137 watching -
 46:09
46:09
MattMorseTV
2 hours ago $12.61 earned🔴Bondi just DROPPED the BALL... BIG TIME.🔴
8.69K62 -
 23:57
23:57
Jasmin Laine
5 hours agoCarney SNAPS at Reporters—MOCKS Trump and it BACKFIRES IMMEDIATELY
4.06K18 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Sarah Westall
2 hours agoDo Near Death Experiences Provide a Glimpse into Reality? w/ Darius Wright
204 watching -
 49:36
49:36
Barry Cunningham
3 hours agoMUST SEE: PAM BONDI AND KAROLINE LEAVITT MAKE REMARKS! | AND MORE NEWS!
92.4K24 -
 41:11
41:11
Donald Trump Jr.
22 hours agoMaking America Affordable Again, Interview with Economist Steve Moore | TRIGGERED Ep.294
119K97 -
 1:02:43
1:02:43
BonginoReport
4 hours agoThe Insane Proposal That Will Ruin Elections FOREVER - Nightly Scroll w/ Hayley Caronia (Ep.184)
53.6K45 -
 16:56
16:56
T-SPLY
6 hours agoTennessee Lawmaker Running For Congress Admits To "Bullying" ICE Vehicles
10.4K10 -
 13:09:46
13:09:46
LFA TV
1 day agoLIVE & BREAKING NEWS! | MONDAY 11/24/25
171K23 -
 1:44:50
1:44:50
Mike Mac - Say Something
1 day agoSay Something Beyond W/MikeMac: DR. HEATH - Ep.15
21.9K