Premium Only Content
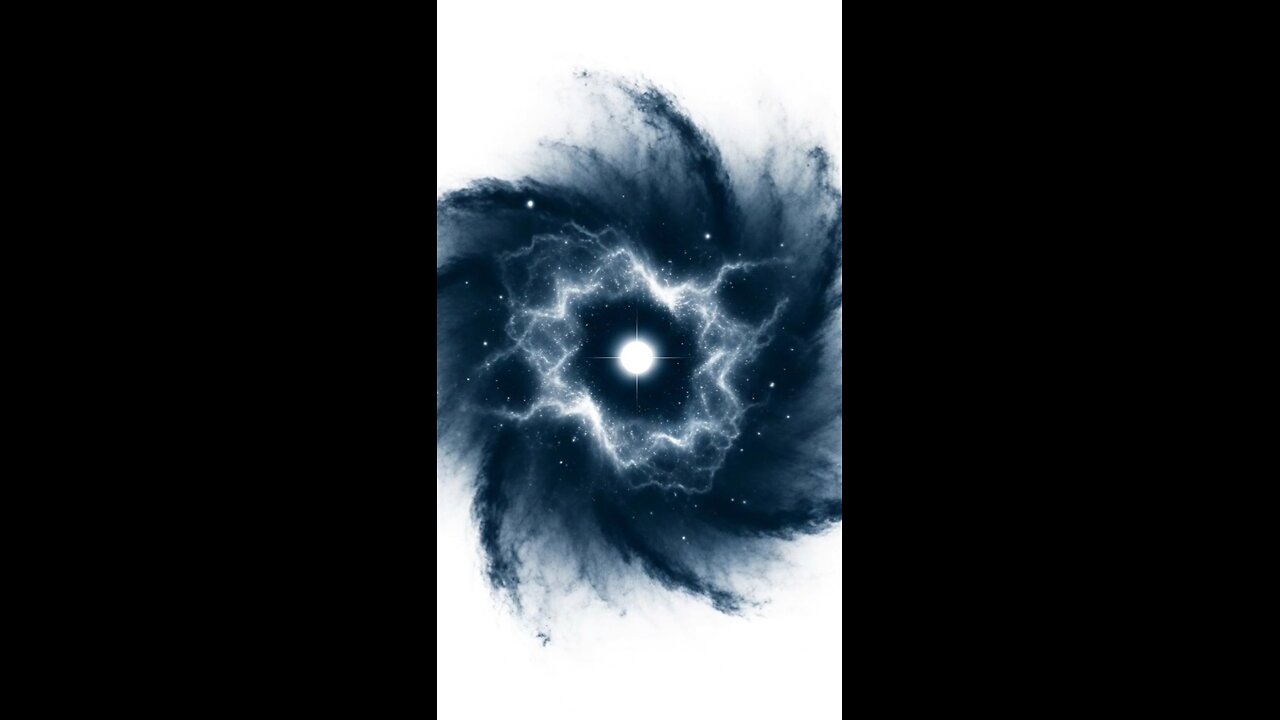
Stellar Birth
Stars are born within cold, dense molecular clouds—regions rich in hydrogen molecules (H₂), helium, and trace amounts of elements like carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Gravitational instabilities, often triggered by shockwaves from nearby supernovae or galactic collisions, cause parts of these clouds to collapse.
As the gas contracts, gravitational energy converts to thermal energy, heating the core.
Chemical processes within the collapsing protostar include molecular hydrogen dissociation and ionization of atoms, which regulate temperature and pressure.
When core temperatures exceed about 10 million Kelvin, nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium begins, marking the birth of a main-sequence star and releasing vast amounts of energy that counterbalance further collapse.
-
 2:49:26
2:49:26
Laura Loomer
6 hours agoEP145: Trump Makes BOMBSHELL Autism Announcement
40.2K18 -
 6:14:04
6:14:04
SpartakusLIVE
7 hours agoEXPLOSIVE $400+ 2v2 Tuesday has viewers GLUED to the screen
54.4K1 -
 3:19:06
3:19:06
GrimmHollywood
6 hours ago🔴LIVE • GRIMM'S TUESDAY FRIGHT NIGHT • STARRING GRIMM HOLLYWOOD • NO, I'M NOT HUMAN PART 1 •
34.5K2 -
 1:21:01
1:21:01
Flyover Conservatives
13 hours agoAI Encouraged Suicide: The Global Experiment on Our Kids - Joe Allen | FOC Show
46.7K4 -
 1:07:40
1:07:40
Glenn Greenwald
8 hours agoTucker Carlson on Charlie Kirk Assassination Fallout, Free Speech, Foreign Policy, and the Reaction to his Kirk Remarks | SYSTEM UPDATE #520
183K135 -
 14:22
14:22
Robbi On The Record
2 days ago $2.23 earnedGen Z’s Narcissism Obsession: Why Everyone’s a “Psychologist”
45.3K14 -
 8:15:08
8:15:08
GritsGG
9 hours agoQuad Win Streaks!🫡 Most Wins in WORLD! 3600+
62.5K2 -
 1:09:28
1:09:28
Sarah Westall
6 hours agoCan the World Be This Strange? The Nature of Our Reality w/ Darius J Wright
41.6K4 -
 1:58:20
1:58:20
megimu32
6 hours agoOn The Subject: Friends | 31 Years of the Sitcom That Defined a Generation
38.8K5 -
 30:00
30:00
BEK TV
1 day agoCounter Culture Mom
12.3K