Premium Only Content
This video is only available to Rumble Premium subscribers. Subscribe to
enjoy exclusive content and ad-free viewing.
Central Limits
4 months ago
14
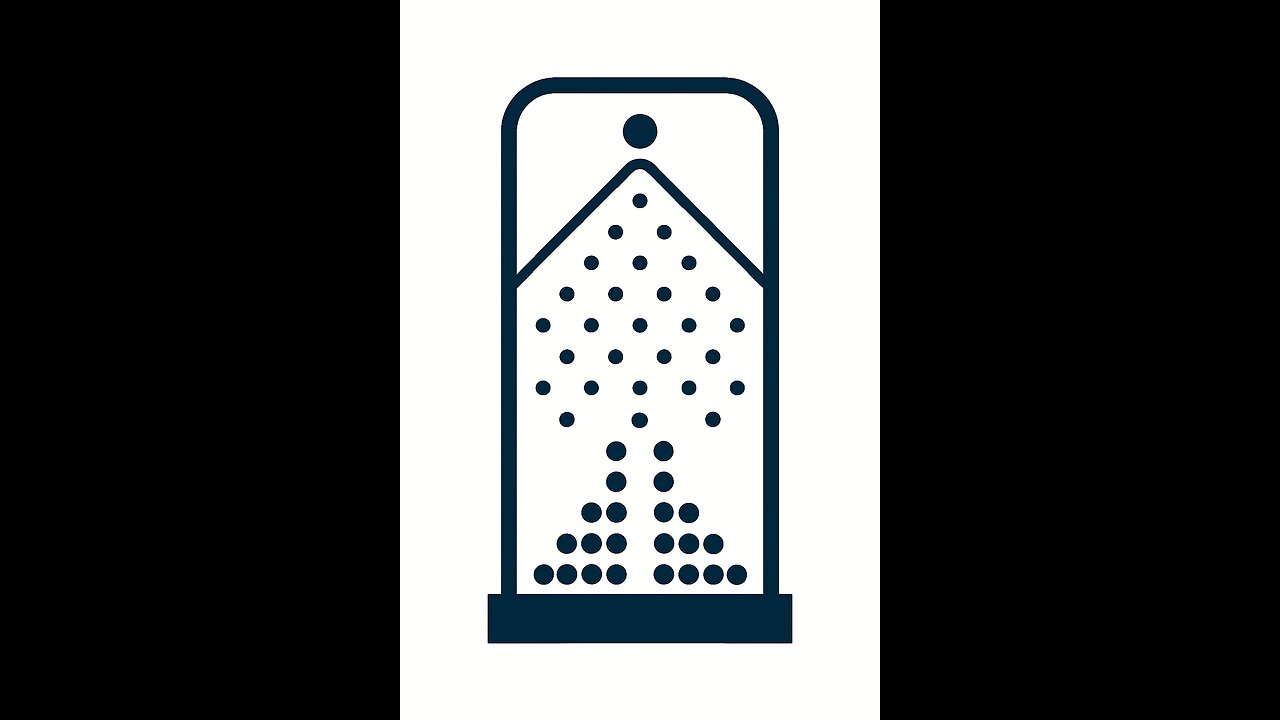
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) states that when independent, random variables are summed, their normalized sum tends toward a normal distribution as the number of variables increases, regardless of the original distributions’ shapes.
This emergence of the bell curve is due to the additive accumulation of small, random fluctuations balancing each other out—large deviations become increasingly unlikely.
The CLT explains why normal distributions appear in nature and statistics: even if individual phenomena are random and varied, their collective behavior converges to predictable patterns, with the mean and variance of the sum stabilizing around central, Gaussian-like tendencies.
Loading 1 comment...
-
 1:31:18
1:31:18
Graham Allen
5 hours agoErika Fights Back: Vows To EXPOSE TRUTH & DEMANDS Trial Goes Public!! Left Says Her Grief Is FAKE!
130K80 -
 2:08:47
2:08:47
Badlands Media
9 hours agoBadlands Daily: November 3, 2025 – Tariff Wars, SNAP Panic & Brennan Gets Confronted
53.9K14 -
 2:59:32
2:59:32
Wendy Bell Radio
8 hours agoThings Will Get Worse Before They Get Better
78K106 -
 1:18:28
1:18:28
The Big Mig™
5 hours agoICE Will Use Private Bounty Hunters, LFG
20.1K13 -
 1:08:17
1:08:17
Chad Prather
11 hours agoHow to Get Along With People You Don’t Even Like (Most of the Time)
113K33 -
 1:45:29
1:45:29
MTNTOUGH Podcast w/ Dustin Diefenderfer
11 hours agoTaya + Colton Kyle: Can American Marriages Survive 2025? | MTNPOD #140
26.2K -
 1:12:23
1:12:23
MikeMac - Say Something
19 hours agoSay Something Beyond W/MikeMac: JOKER - Ep.12
25.6K1 -
 1:30:13
1:30:13
Game On!
16 hours ago $10.53 earnedChiefs Dynasty OVER, New Longest FG RECORD, and Patriots Are Winning The Super Bowl!
45.2K4 -
 4:02:17
4:02:17
The Bubba Army
3 days agoIS AMERICA OVER TRUMP? - Bubba the Love Sponge® Show | 11/03/25
101K37 -
 48:57
48:57
Man in America
21 hours agoThe Sinister Reason They Put Fluoride in Everything w/ Larry Oberheu
383K118