Premium Only Content
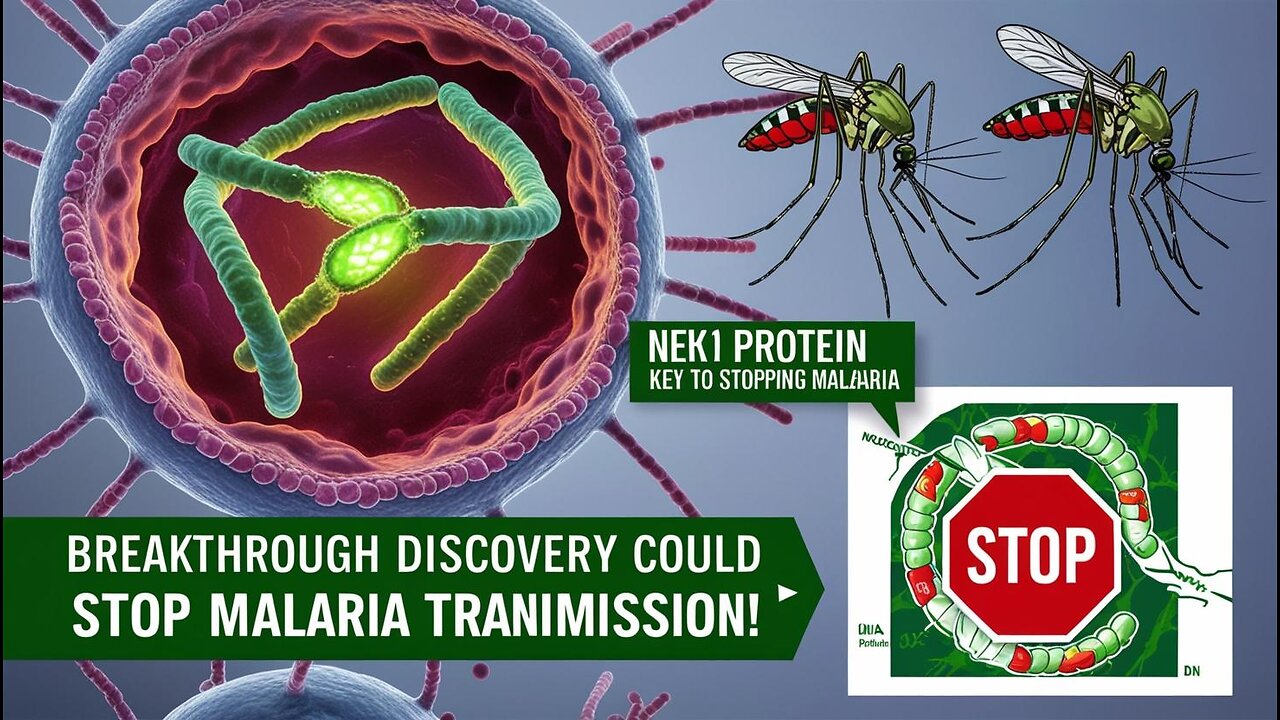
Scientists Uncover Key Protein That Could Stop Malaria Transmission Globally
Groundbreaking Discovery in Malaria Research
A major breakthrough has revealed the role of NEK1, a critical protein in the malaria parasite's cell division, offering exciting new possibilities for stopping malaria transmission globally! This discovery could revolutionize how we fight the disease, which kills over 600,000 people annually.
🔬 What is NEK1 and Why Is It Important?
NEK1 is a protein essential for organizing the malaria parasite's cell division process—specifically, during male gamete formation within the mosquito host.
Disrupting NEK1 could halt the parasite's ability to reproduce and spread, both within humans and mosquitoes, making it a promising target for new malaria drugs.
💡 How Does It Work?
The malaria parasite uses a unique cell division process, including a special structure called the bipartite microtubule-organizing center (MTOC).
NEK1 helps organize this structure, ensuring the parasite's chromosomes are properly divided during reproduction, especially during rapid gametogenesis in mosquitoes.
⚠️ What Does This Mean for Malaria Control?
Targeting NEK1 could stop not only the spread of malaria in humans but also prevent transmission through mosquitoes, breaking the cycle of infection.
The research paves the way for innovative malaria therapies that focus on disrupting the parasite's cell cycle, similar to how kinase inhibitors are used in cancer treatments.
💬 Comment Below: Do you think targeting proteins like NEK1 could be the key to eradicating malaria? What other diseases do you think could benefit from this kind of research?
👍 Like if you're excited about new breakthroughs in malaria treatment and global health!
🔔 Subscribe for the latest updates on cutting-edge scientific discoveries and how they can help us combat deadly diseases worldwide
-
 15:24
15:24
Degenerate Jay
19 hours ago5 Best Moments In Batman: Arkham Asylum
117 -
 12:24
12:24
The Shannon Joy Show
13 hours ago🔥From Flock Cameras to Palantir: America’s Expanding Digital Cage🔥
6222 -
 LIVE
LIVE
BEK TV
22 hours agoTrent Loos in the Morning - 8/27/2025
366 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Bubba Army
21 hours agoTaylor Swift & Travis Kelce ENGAGED! - Bubba the Love Sponge® Show | 8/27/25
3,255 watching -
 40:14
40:14
Uncommon Sense In Current Times
16 hours ago $1.23 earnedThe Dating Crisis in America | J.P. De Gance on the Church’s Role in Restoring Family & Faith
25.4K3 -
 12:35
12:35
Red Pill MMA
18 hours agoNow We Know The Truth.. Hero Who Stopped Raja Jackson Speaks Out
2.84K4 -
 41:04
41:04
Coin Stories with Natalie Brunell
1 day agoCooking, Culture & Crypto: Norma Chu’s Food Empire Turns Bitcoin Treasury
5.75K -
 8:03
8:03
MattMorseTV
17 hours ago $7.28 earnedThings in the UK just got INSANE...
84.2K125 -
 3:02:10
3:02:10
daniellesmithab
11 hours agoAlberta Next: Fort McMurray Town Hall
15K1 -
 2:11:17
2:11:17
Side Scrollers Podcast
20 hours agoINSANE Illegal Migrant Propaganda Xbox Game + Paypal REFUSES To Pay Dev + More | Side Scrollers
62.7K3