Premium Only Content
NASA, NOAA 2024 Ozone Hole Update
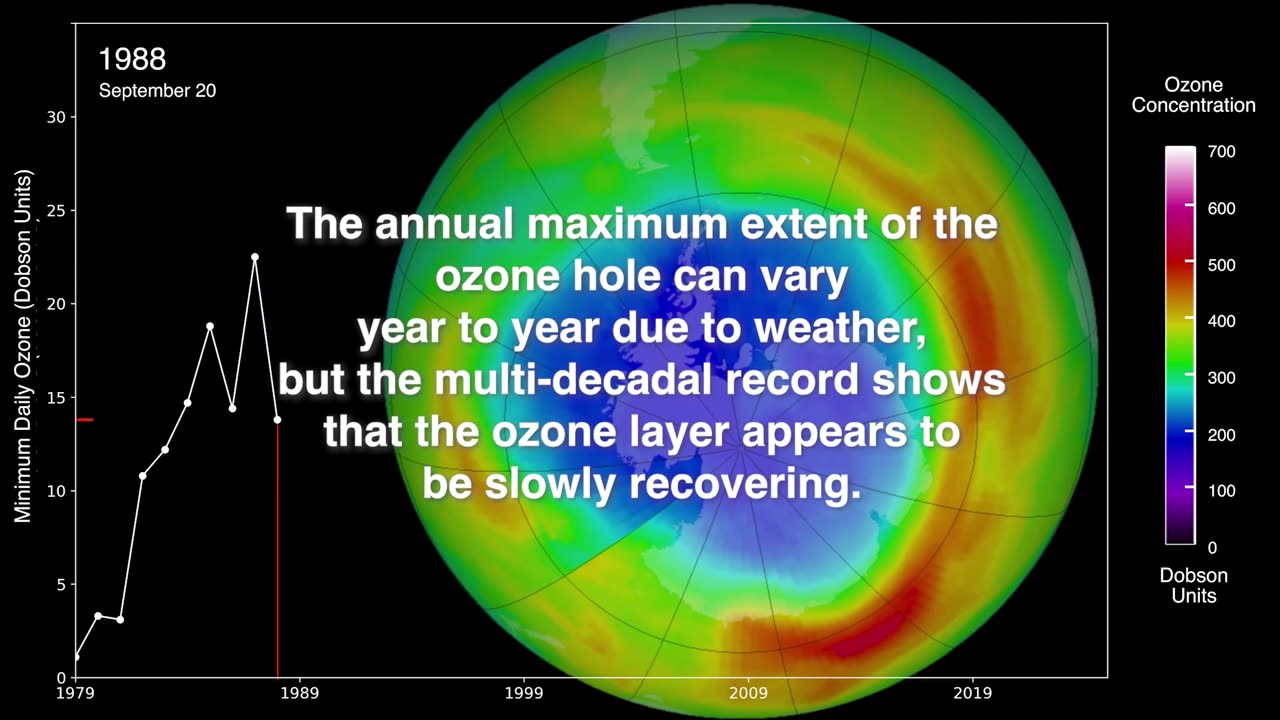
This year, the ozone hole over Antarctica reached its annual maximum extent on September 28th, 2024, with an area of 8.5 million square miles (22.4 square million kilometers.)
The hole, which is actually a region of depleted ozone, was the 20th smallest since scientists began recording the ozone hole in 1979. The average size of the ozone hole between September and October this year was the 7th-smallest since the Montreal Protocol began to take effect.
Universal Music Production: “What Was Reported As Is”
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Kathleen Gaeta (GSFC AMA): Lead Producer
Paul Newman (NASA GSFC): Lead Scientist
Amy Moran (NASA GSFC): Lead Visualizer
James Riordon (NASA GSFC): Writer
This video can be freely shared and downloaded at https://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/14711 . While the video in its entirety can be shared without permission, the music and some individual imagery may have been obtained through permission and may not be excised or remixed in other products. For more information on NASA’s media guidelines, visit https://nasa.gov/multimedia/guidelines.
Transcript:
0:00
This year, the ozone hole over Antarctica reached its annual maximum extent on September 28th, 2024,
0:04
With an area of 8.5 million square miles (22.4 square million kilometers).
0:08
0:12
0:16
The hole, which is actually a region of depleted ozone, was the 20th smallest since scientists began recording the ozone hole in 1979.
0:20
0:24
The average size of the ozone hole between September and October this year was the 7th-smallest since the Montreal Protocol began to take effect.
0:28
0:32
The annual maximum extent of the ozone hole can vary year to year due to weather, but the multi-decadal record shows that the ozone layer appears to be slowly recovering.
0:36
0:40
“The weakening we’ve seen in the last two decades shows that international efforts that curbed ozone-destroying chemicals are working.” -Paul Newman, Chief Scientist for Earth Sciences at NASA Goddard
0:44
0:48
NASA and NOAA researchers continue to observe ozone through instruments aboard NASA’s Aura satellite, NOAA-20 satellites, and a joint NASA and NOAA satellite called Suomi-NPP.
0:52
0:56
NASA
-
 LIVE
LIVE
The StoneZONE with Roger Stone
6 minutes agoTrump Pardons Ross Ulbricht | The StoneZONE w/ Roger Stone
212 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
2 MIKES LIVE
8 hours ago2 MIKES LIVE #170 with special guest Rep. Buddy Carter (R-GA)
490 watching -
 7:09:22
7:09:22
Dr Disrespect
8 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - TRIPLE THREAT CHALLENGE - EXTREME EDITION
195K20 -
 DVR
DVR
LFA TV
8 hours agoThe End of the January 6 Hoax | TRUMPET DAILY 1.22.25 7pm
10K2 -
 1:13:37
1:13:37
Battleground with Sean Parnell
6 hours agoPresident Trump Is On FIRE w/ Savage Rich Baris
154K17 -
 1:59:59
1:59:59
Melonie Mac
2 hours agoGo Boom Live Ep 34!
17.8K2 -
 49:27
49:27
Sarah Westall
1 hour agoTrillion Dollar 5G Lawsuit, Project Archimedes, Mind Control & DEW Weapons w/Attorney Todd Callender
16.7K5 -
 53:11
53:11
Standpoint with Gabe Groisman
1 day agoTrump Is Crucial For Hostage Agreement Says Israeli Colonel
21.5K4 -
 1:01:22
1:01:22
Anthony Pompliano
1 day ago $0.66 earnedTrump Inauguration Sends Bitcoin Flying
16.3K1 -
 15:21
15:21
LFA TV
9 hours agoWHY GOLD WILL CONTINUE TO SKYROCKET
10.8K2