Premium Only Content
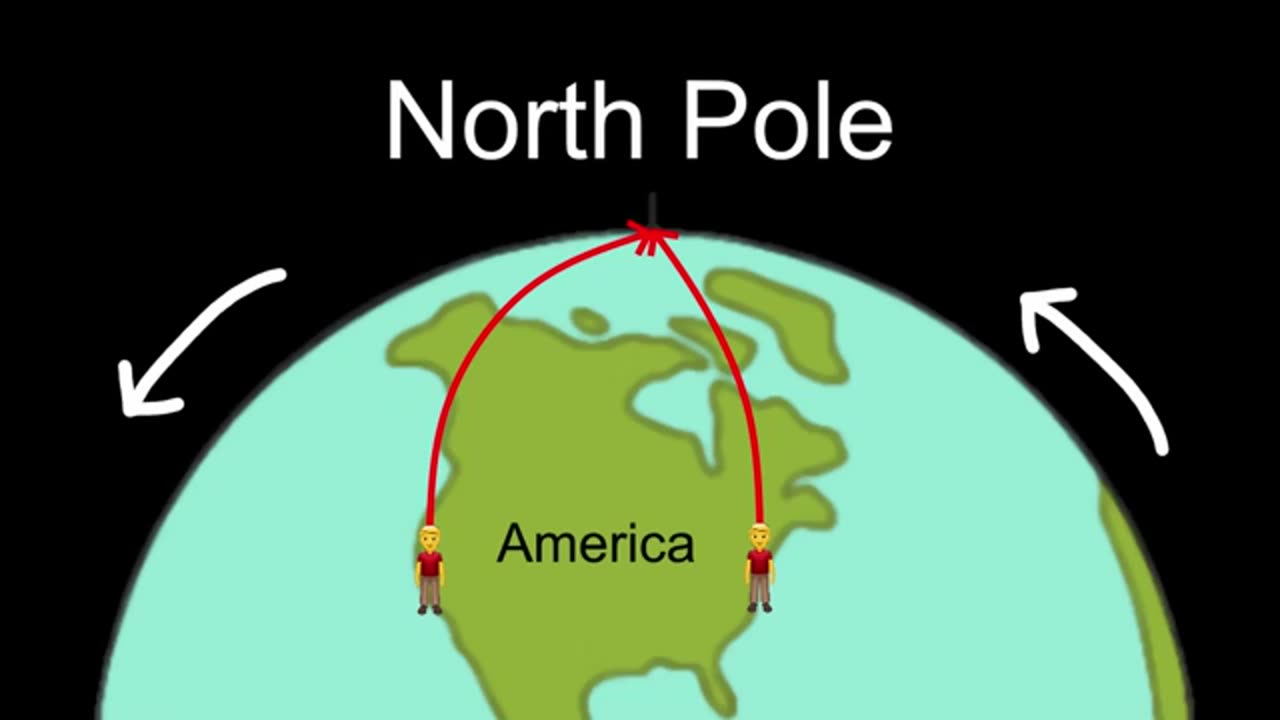
ALL OF PHYSICS
Explaining *all of physics* in 14 minutes is a bold challenge, but it’s possible to give an overview of the field by summarizing its major concepts, branches, and theories. Here’s a concise guide:
---
### **1. The Foundations of Physics**
Physics is the study of matter, energy, space, and time, as well as the fundamental forces that govern the universe. It seeks to explain how the universe behaves, from the tiniest particles to the largest cosmic structures.
#### **Key Pillars of Physics:**
1. **Laws of Motion** (Newtonian Mechanics):
- Describe the motion of objects under the influence of forces.
- Newton’s laws (inertia, F = ma, action-reaction) form the basis of classical mechanics.
2. **Conservation Laws**:
- **Energy**: Total energy remains constant in a closed system.
- **Momentum**: The momentum of a system is conserved unless acted upon by an external force.
- **Charge**: Electric charge is conserved.
---
### **2. Classical Physics**
#### **Mechanics**:
- Explores motion (kinematics) and forces (dynamics).
- Includes **fluid dynamics**, studying the behavior of liquids and gases.
#### **Thermodynamics**:
- Examines heat, work, and energy transfer.
- **Key Laws**:
1. Energy cannot be created or destroyed (First Law).
2. Entropy of the universe increases (Second Law).
3. Absolute zero is unattainable (Third Law).
#### **Electromagnetism**:
- Unites electricity and magnetism.
- Maxwell’s equations describe how electric and magnetic fields propagate and interact.
---
### **3. Modern Physics**
#### **Relativity** (Einstein):
- **Special Relativity**: Time and space are relative, unified as spacetime.
- E = mc² relates energy and mass.
- **General Relativity**: Gravity is the warping of spacetime by mass and energy.
#### **Quantum Mechanics**:
- Governs the behavior of particles at atomic and subatomic scales.
- **Key Principles**:
1. Wave-particle duality: Particles can behave like waves and vice versa.
2. Uncertainty Principle: You can’t precisely measure both position and momentum simultaneously.
---
### **4. The Four Fundamental Forces**
1. **Gravitational Force**: Attraction between masses.
2. **Electromagnetic Force**: Interaction of charged particles.
3. **Weak Nuclear Force**: Responsible for radioactive decay.
4. **Strong Nuclear Force**: Binds protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
---
### **5. The Standard Model**
The Standard Model describes fundamental particles (quarks, leptons, bosons) and their interactions. It unifies the electromagnetic, weak, and strong forces but does not include gravity.
#### **Key Particles**:
- **Quarks**: Building blocks of protons and neutrons.
- **Leptons**: Includes electrons and neutrinos.
- **Bosons**: Force carriers (e.g., photons, gluons, W/Z bosons, and the Higgs boson).
---
### **6. Cosmology and Astrophysics**
Physics extends to the largest scales, explaining the origins and evolution of the universe:
- **Big Bang Theory**: Universe began as a singularity ~13.8 billion years ago.
- **Dark Matter and Dark Energy**: Unseen components that shape the cosmos.
- **Black Holes**: Regions of spacetime with gravity so intense that nothing can escape.
---
### **7. Cutting-Edge Physics**
1. **Quantum Field Theory (QFT)**: Combines quantum mechanics and relativity to describe particle interactions.
2. **String Theory**: Proposes that particles are vibrating strings in higher-dimensional space.
3. **Theory of Everything (TOE)**: Seeks to unify all physical forces.
---
### **Summary**
Physics is a journey from the laws of motion and classical mechanics to quantum mysteries and cosmic wonders. Its core principles—forces, particles, energy, and spacetime—intertwine to reveal the universe's intricate dance. While we’ve come far, much remains to be explored, keeping physics vibrant and full of possibilities.
-
 1:51:08
1:51:08
Redacted News
2 hours agoEMERGENCY! BILL GATES CULT MEMBERS FOUND PLANTED INSIDE MULTIPLE FEDERAL AGENCIES, RFK FURIOUS
91K52 -
 31:02
31:02
Kimberly Guilfoyle
3 hours agoFull Breaking News Coverage: Live with John Nantz & Steve Moore | Ep250
11.4K5 -
 1:15:19
1:15:19
vivafrei
4 hours agoShameless Politicization of Tragedy! Susan Monarez is OUT! Pritzker is an IDIOT! & MORE!
98.6K41 -

Tundra Tactical
1 hour agoCracker Meme Review On Tundra Meme Review!!
28 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Wayne Allyn Root | WAR Zone
5 hours agoWAR Zone LIVE | 28 AUGUST 2025
87 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
11 hours agoLFA TV ALL DAY STREAM - THURSDAY 8/28/25
1,180 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
freecastle
3 hours agoTAKE UP YOUR CROSS- CREATED IN HIS IMAGE
124 watching -
 1:49:30
1:49:30
The Quartering
5 hours agoCount Dankula Live On Migrant Crisis In Europe, Whiteness & More
121K162 -
 3:46:59
3:46:59
Barry Cunningham
8 hours agoBREAKING NEWS: KAROLINE LEAVITT HOLDS WHITE HOUSE PRESS CONFERENCE (AND MORE NEWS)
72K54 -
 47:21
47:21
Stephen Gardner
22 hours ago🔥Elon Just Exposed the Most Corrupt Man on Earth - Trump Makes BOLD MOVE!
36.1K106