Premium Only Content
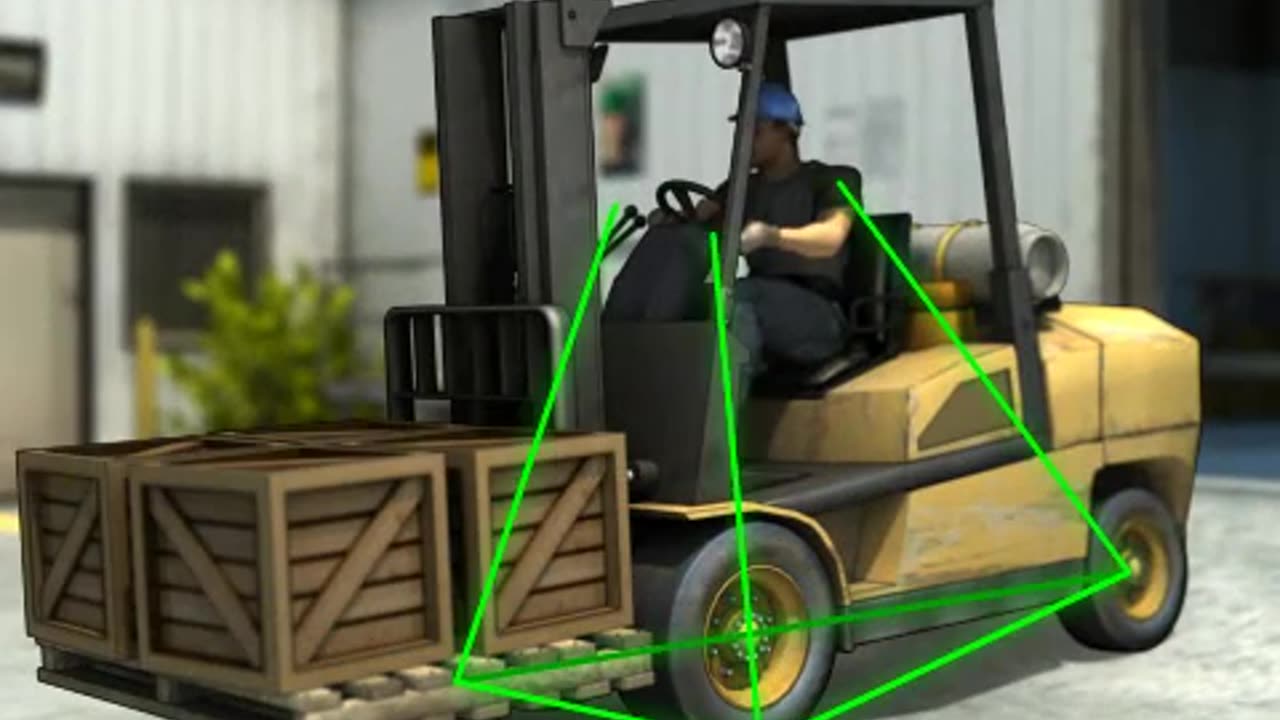
Forklift Safety Training
**Forklift Safety Training** is a vital part of workplace safety, especially in environments where forklifts are used for lifting, moving, and stacking materials. Improper use of forklifts can result in serious injuries, property damage, and accidents. Therefore, forklift safety training is essential for operators to ensure safe and efficient forklift operation while minimizing risks.
### Key Elements of Forklift Safety Training
#### 1. **Introduction to Forklift Safety**
- **Purpose of Forklift Training:** Understanding the importance of proper training to ensure safety, compliance, and efficiency when operating forklifts.
- **Overview of Forklifts:** Different types of forklifts (e.g., counterbalance, reach trucks, order pickers) and their uses.
- **Legal Requirements:** Understanding OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulations regarding forklift operation, specifically OSHA Standard 1910.178.
#### 2. **Forklift Types and Their Uses**
- **Counterbalance Forklifts:** Commonly used for lifting and transporting materials in warehouses and construction sites.
- **Reach Trucks:** Specialized for narrow aisles and high stacking, often used in warehouses.
- **Pallet Jacks and Order Pickers:** Manual or electric forklifts used for smaller loads or specific tasks.
- **Rough Terrain Forklifts:** Designed for outdoor or uneven surfaces.
#### 3. **Forklift Components and Their Functions**
- **Forks and Mast:** The lifting mechanism of a forklift, including the forks that hold materials and the mast that lifts and lowers them.
- **Hydraulics:** The system used to raise, lower, and tilt the forks.
- **Tires:** Differentiating between solid, pneumatic, and cushion tires and their proper use.
- **Controls and Instrumentation:** Understanding the steering wheel, brakes, accelerator, tilt, and other controls specific to the forklift.
#### 4. **Forklift Operation**
- **Pre-Operation Inspections:** Conducting daily checks for safety and maintenance, including fluid levels, tire condition, brakes, and operational controls.
- **Proper Loading and Unloading:** Ensuring that loads are balanced, the forklift is not overloaded, and loads are secure.
- **Forklift Stability:** Understanding the importance of the load center, and keeping the load low to maintain the forklift's stability.
- **Operating in Narrow Aisles:** Techniques for safely navigating tight spaces, using the forklift’s turning radius and adjusting the mast.
- **Speed and Turning:** Adjusting speed and turning to prevent tip-overs or collisions.
#### 5. **Safe Operating Practices**
- **Driving on Inclines and Ramps:** Techniques for driving forklifts on ramps, ensuring the load is tilted back to prevent shifting.
- **Turning and Cornering:** Proper turning radius and awareness of surroundings to avoid hitting other objects or pedestrians.
- **Safe Handling of Loads:** Lifting loads evenly, not exceeding the forklift's rated capacity, and ensuring the load is secure.
- **Stacking and De-stacking:** Safe methods for stacking items, ensuring that loads are stable, and minimizing the risk of falling loads.
- **Forklift Speed Control:** Adhering to facility speed limits and slowing down when turning or approaching pedestrians.
#### 6. **Pedestrian Safety**
- **Visibility and Communication:** Ensuring operators and pedestrians maintain eye contact or use hand signals to communicate.
- **Pedestrian Zones:** Creating designated walking areas that are separate from forklift travel paths.
- **Warning Systems:** Using horns, lights, and other safety indicators to alert pedestrians to the forklift’s presence.
- **Safe Stopping:** Stopping well ahead of pedestrians and giving them the right of way when necessary.
#### 7. **Forklift Maintenance and Inspections**
- **Routine Inspections:** Operators must inspect forklifts before each shift, checking the brakes, tires, lights, forks, and fluid levels.
- **Battery and Fuel Maintenance:** Ensuring proper maintenance of battery-powered or fuel-powered forklifts.
- **Scheduled Maintenance:** Ensuring regular checks and service by qualified mechanics to keep forklifts in optimal working condition.
#### 8. **Load Handling and Stability**
- **Load Capacity and Limitations:** Understanding the forklift's rated load capacity and ensuring the load is within these limits.
- **Center of Gravity:** Ensuring loads are evenly distributed and properly positioned to avoid tipping the forklift.
- **Securing Loads:** Using the appropriate materials or methods (e.g., strapping, stacking) to secure loads during transport.
- **Load Height and Visibility:** Keeping the load low to maintain stability and improve visibility.
#### 9. **Forklift Training and Certification**
- **Training Program Requirements:** Ensuring that operators receive both classroom and hands-on training from qualified instructors.
- **Certification Process:** OSHA requires operators to be certified, which includes a combination of theoretical knowledge and practical driving evaluation.
- **Recertification:** Operators need to be recertified periodically and whenever significant changes in the forklift or workplace occur.
- **Training for Supervisors and Managers:** Ensuring that managers understand forklift safety protocols, including maintenance oversight, inspections, and compliance requirements.
#### 10. **Emergency Procedures**
- **Forklift Malfunctions:** What to do if the forklift breaks down, including shutting down the machine and reporting the issue.
- **Accidents and Injuries:** Procedures for reporting forklift-related accidents and injuries, including first aid and emergency contacts.
- **Fire Hazards:** Awareness of fire risks, particularly for propane or fuel-powered forklifts, and knowing how to use fire extinguishers.
### Key Forklift Safety Rules:
- **Always Wear PPE:** Ensure that operators wear seat belts, hard hats, high-visibility vests, safety shoes, and gloves as necessary.
- **Do Not Overload:** Never exceed the rated load capacity of the forklift, and always check the load balance before lifting.
- **Avoid Stunt Driving:** No sharp turns, quick accelerations, or abrupt stops that could cause the forklift to tip over.
- **Never Carry Passengers:** Only authorized operators should operate the forklift, and passengers should never ride on forklifts unless the vehicle is designed for carrying them.
- **Ensure Clear Vision:** Make sure the operator has clear visibility of the path and load at all times, and drive in reverse when necessary.
- **Forklift Shutdown:** When leaving a forklift, always park it in a safe location, set the brake, and turn off the engine.
### Forklift Safety Training Delivery Methods:
- **Classroom Instruction:** In-person or online lessons on forklift theory, including laws, types of forklifts, and safe operation.
- **Hands-On Training:** Practical training where operators learn to drive and operate forklifts in a controlled environment.
- **Assessments and Certification:** Operators undergo a formal evaluation of their skills, which may include a written test and a driving test.
### Benefits of Forklift Safety Training
- **Reduced Accidents and Injuries:** Proper training minimizes the risk of forklift-related accidents.
- **Compliance with OSHA Regulations:** Ensures compliance with OSHA regulations, avoiding fines and legal issues.
- **Increased Productivity:** Trained operators can work more efficiently, reducing downtime and improving workflow.
- **Equipment Longevity:** Proper operation and care increase the lifespan of forklifts, reducing maintenance costs.
Would you like help with developing a forklift safety training program for your team or facility?
-
 58:14
58:14
theDaily302
20 hours agoThe Daily 302- Tim Ballard
64.1K10 -
 13:22
13:22
Stephen Gardner
13 hours ago🔥You'll NEVER Believe what Trump wants NOW!!
112K300 -
 54:56
54:56
Digital Social Hour
1 day ago $11.17 earnedDOGE, Deep State, Drones & Charlie Kirk | Donald Trump Jr.
61.5K5 -
 DVR
DVR
The Trish Regan Show
15 hours agoTrump‘s FCC Targets Disney CEO Bob Iger Over ABC News Alleged Misconduct
66.1K39 -
 1:48:19
1:48:19
The Quartering
16 hours agoElon Calls White People Dumb, Vivek Calls American's Lazy & Why Modern Christmas Movies Suck!
148K112 -
 2:08:42
2:08:42
The Dilley Show
16 hours ago $37.19 earnedH1B Visa Debate, Culture and More! w/Author Brenden Dilley 12/26/2024
126K42 -
 4:55:59
4:55:59
LumpyPotatoX2
19 hours agoThirsty Thursday on BOX Day - #RumbleGaming
115K8 -
 1:04:52
1:04:52
Geeks + Gamers
18 hours agoDisney RATIO'D on Christmas Day | Mufasa Embarrassed By Sonic 3
84.3K11 -
 8:27:46
8:27:46
Sm0k3m
22 hours agoRumblers Assemble
53.7K3 -
 10:37
10:37
Russell Brand
2 days agoHow is this even allowed?
210K979