Premium Only Content
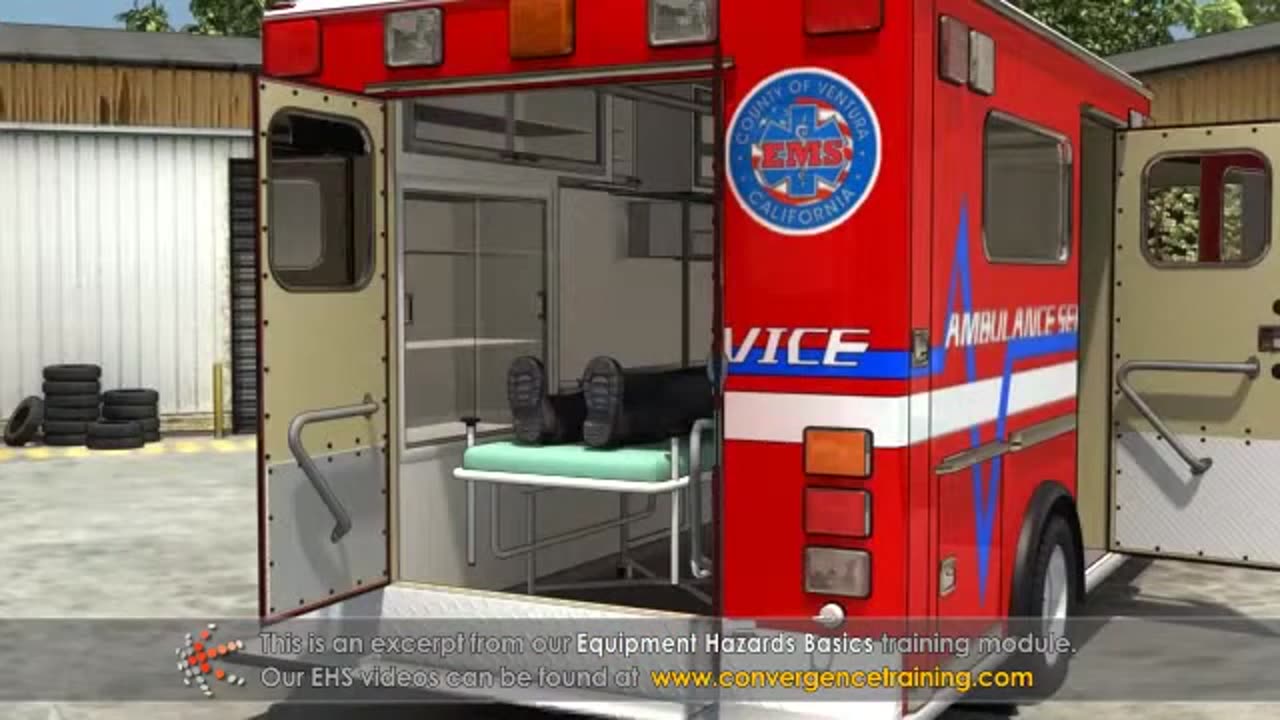

Equipment Hazards Basics Training
**Equipment Hazards Basics Training** focuses on educating workers about the potential risks associated with the operation, maintenance, and repair of various types of machinery and equipment in the workplace. It is essential to ensure that employees understand how to safely work with equipment and the safety measures they must take to prevent accidents and injuries.
Here’s an overview of the key elements typically covered in **Equipment Hazards Basics Training**:
### 1. **Introduction to Equipment Hazards**
- **Definition of Equipment Hazards:** Understanding the dangers posed by moving parts, electrical systems, sharp edges, and heavy loads.
- **Common Equipment Types:** Includes forklifts, cranes, power tools, manufacturing machinery, conveyors, and construction equipment.
- **Common Injuries:** Types of injuries that occur, such as crush injuries, cuts, electric shocks, burns, and repetitive strain injuries.
### 2. **Types of Equipment Hazards**
- **Mechanical Hazards:** Pinch points, rotating parts, belts, gears, blades, and other moving parts that can cause entanglement, crushing, or impact injuries.
- **Electrical Hazards:** Risks of electrocution or electrical burns from faulty wiring, exposed parts, or improper grounding.
- **Thermal Hazards:** Burns from hot surfaces, electrical components, and processes that involve extreme heat.
- **Noise Hazards:** Loud equipment that can cause hearing damage if proper hearing protection isn’t used.
- **Ergonomic Hazards:** Risks from poor ergonomics, such as awkward postures, repetitive motions, and heavy lifting associated with handling equipment.
- **Impact Hazards:** Injuries from objects falling off equipment, being struck by moving parts, or tools.
- **Chemical Hazards:** Exposure to hazardous substances from equipment such as welding machines, certain manufacturing processes, and chemical mixers.
### 3. **Safe Equipment Operation**
- **Pre-Operation Checks:** Ensuring that equipment is properly maintained and safe to use (e.g., checking for wear, malfunctions, and safety device functionality).
- **Proper Use of Equipment:** Understanding the correct way to operate specific types of machinery and equipment to minimize risk.
- **Start-up and Shut-down Procedures:** Step-by-step guidance on safely starting and stopping equipment, and securing it during non-use.
- **Operating Instructions:** Reading and following manufacturer’s instructions and warning labels on equipment.
- **Using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):** Ensuring appropriate PPE, such as gloves, safety glasses, hearing protection, and respiratory protection, is used.
### 4. **Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Procedures**
- **Definition of Lockout/Tagout:** Lockout/tagout (LOTO) is a safety procedure used to ensure that equipment is properly shut down and cannot be accidentally started during maintenance.
- **Steps for LOTO:** Isolating energy sources, applying lockout devices, and confirming that equipment is de-energized before performing maintenance or repairs.
- **Importance of LOTO:** Prevents workers from accidental exposure to hazardous energy and machinery.
### 5. **Handling and Storing Equipment Safely**
- **Storage of Equipment:** Proper storage techniques for tools and equipment to avoid tripping hazards or damage.
- **Lifting Techniques:** Safe lifting methods for heavy or awkward equipment to prevent strain or injury.
- **Transporting Equipment:** Safety practices for moving equipment from one location to another within a facility.
### 6. **Equipment Maintenance and Inspections**
- **Regular Inspections:** How to inspect equipment regularly for damage, wear, or malfunction, and the importance of doing so.
- **Scheduled Maintenance:** The importance of preventive maintenance and adhering to equipment service schedules to ensure safe operation.
- **Reporting Malfunctions:** Procedures for reporting equipment issues or unsafe conditions and how to address them.
### 7. **Emergency Response Procedures**
- **In Case of an Equipment Failure:** Steps to follow in case of equipment breakdowns or malfunctions that might endanger the worker or others.
- **Handling Equipment Accidents:** What to do if a worker is injured by equipment (e.g., stopping the equipment, providing first aid, or calling emergency services).
- **Fire Response:** In case of electrical or fuel-powered equipment fires, how to use fire extinguishers or other suppression systems.
### 8. **Common Safety Devices on Equipment**
- **Guards and Shields:** Importance of safety guards, shields, and covers that protect workers from moving parts.
- **Emergency Stop Buttons:** How and when to use emergency stop buttons or shut-off switches to prevent injury or damage.
- **Safety Alarms and Lights:** Understanding equipment warning systems like lights, buzzers, and alarms that signal unsafe conditions.
- **Safety Interlocks:** Mechanisms that prevent equipment from operating when guards are not in place or safety conditions are not met.
### 9. **Employee Roles and Responsibilities**
- **Operators:** Ensuring proper operation of equipment and reporting malfunctions or unsafe conditions.
- **Maintenance Personnel:** Following strict protocols during maintenance, ensuring safe shutdowns and lockout/tagout practices.
- **Supervisors:** Enforcing safety rules, ensuring proper training, and investigating incidents.
- **Safety Officers:** Conducting audits, inspecting equipment, and overseeing compliance with safety standards.
### 10. **Training and Certification**
- **Initial and Ongoing Training:** New workers should receive thorough equipment safety training, and regular refresher courses are essential to maintain awareness.
- **Certification:** Workers may need certification for specific equipment, such as forklifts or cranes, to demonstrate proficiency and compliance.
### 11. **Incident Reporting and Safety Culture**
- **Reporting Hazards:** Training employees on how to report hazards, unsafe equipment, or near misses.
- **Creating a Safety Culture:** Encouraging open communication about equipment hazards, safety improvements, and sharing best practices.
### Benefits of Equipment Hazards Basics Training
- **Prevention of Injuries and Accidents:** Employees who understand the risks and safety protocols are less likely to suffer injuries.
- **Enhanced Equipment Longevity:** Proper use and maintenance can extend the life of equipment and reduce downtime.
- **Compliance with OSHA and Regulations:** Ensures the facility complies with safety regulations and avoids penalties.
### Training Delivery Methods
- **In-Person Workshops:** Hands-on demonstrations with actual equipment and real-life scenarios.
- **Online Courses:** Ideal for theoretical knowledge, often combined with in-person practical demonstrations.
- **On-the-Job Training:** Learning while operating equipment under the guidance of experienced mentors.
Would you like more specific training materials or guidance on creating a custom equipment hazards safety program for your workplace?
-
 1:35
1:35
HSESafetyInformation
8 months agoMutton Chops two ways- baked & grilled Recipe by Food Fusion (Eid Recipe)
78 -
 59:40
59:40
American Thought Leaders
14 hours agoHe Said No to Billions from China. Now They’re After Him | Declan Ganley
3.37K6 -
 4:58
4:58
GreenMan Studio
13 hours agoTHE RUMBLE COLLAB SHOW EP.4 W/Greenman Reports
1.63K2 -
 8:05
8:05
Freedom Frontline
16 hours agoAOC DISRESPECTS Byron Donalds And Gets DESTROYED Immediately
2K2 -
 11:53
11:53
GBGunsRumble
14 hours agoGBGuns Range Report 15NOV25
5.93K2 -
 21:37
21:37
Forrest Galante
9 hours ago6 Deadly Sea Monsters That Actually Exist
83.5K3 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Lofi Girl
3 years agolofi hip hop radio 📚 - beats to relax/study to
646 watching -
 43:24
43:24
ThisIsDeLaCruz
1 day ago $9.06 earnedWhat Fans Never Knew About Falling In Reverse’s Guitarist
26.8K -
 14:57
14:57
The Pascal Show
1 day ago $4.83 earnedTHIS IS INSANE! Megyn Kelly SLAMMED For Questioning Whether Epstein Was a P*dophile?!
13.7K13 -
 55:46
55:46
PandaSub2000
1 day agoBeyond Good & Evil | ULTRA BEST AT GAMES (HD Edited Replay)
40.4K3