Premium Only Content
Measurement - Dimensions
**Measurement and dimensions** are fundamental concepts used to quantify the size, shape, and extent of physical objects or systems. Understanding these concepts is crucial in various fields, including engineering, construction, manufacturing, and science. Here's an overview:
---
### **What is Measurement?**
**Measurement** is the process of determining the size, quantity, or degree of something using a standard unit. Measurements are expressed in terms of dimensions, which describe specific characteristics of an object or system.
#### **Common Measurement Types**:
1. **Length**: Distance between two points (e.g., meters, inches).
2. **Area**: Surface coverage of a two-dimensional shape (e.g., square meters).
3. **Volume**: Space occupied by a three-dimensional object (e.g., cubic meters).
4. **Mass/Weight**: Amount of matter in an object or its weight due to gravity (e.g., kilograms, pounds).
5. **Time**: Duration of an event (e.g., seconds, minutes).
6. **Temperature**: Degree of heat (e.g., Celsius, Fahrenheit).
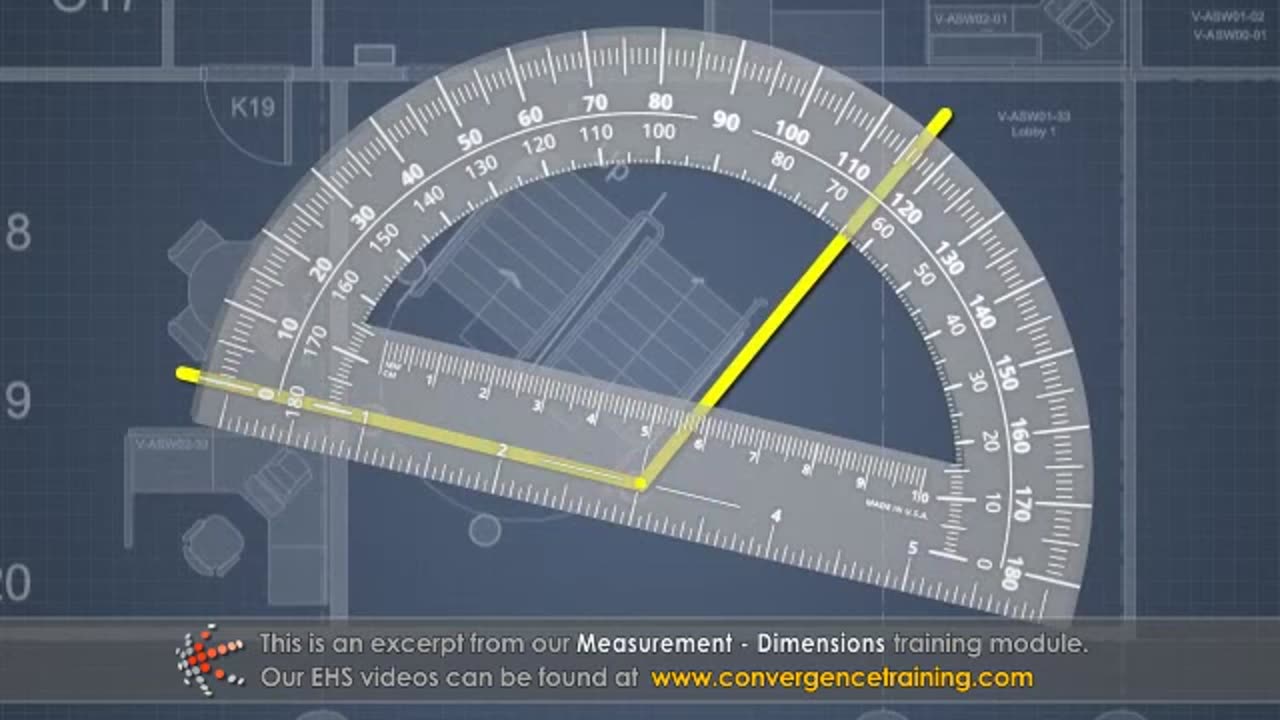
7. **Angle**: Rotation between two intersecting lines (e.g., degrees, radians).
---
### **What are Dimensions?**
**Dimensions** describe the measurable attributes of an object, system, or phenomenon. These attributes can include length, width, height, diameter, depth, and others.
#### **Types of Dimensions**:
1. **Primary Dimensions**:
- Fundamental properties like length (L), mass (M), time (T), temperature (θ).
2. **Derived Dimensions**:
- Formed by combining primary dimensions (e.g., velocity = length/time).
---
### **Measurement Units**
#### **Standard Systems**:
1. **Metric System (SI)**:
- Length: Meter (m)
- Mass: Kilogram (kg)
- Time: Second (s)
- Temperature: Kelvin (K)
2. **Imperial System**:
- Length: Inch, foot
- Mass: Pound (lb)
- Temperature: Fahrenheit (°F)
---
### **Tools for Measurement**
1. **Length and Dimensions**:
- **Ruler**: For small distances.
- **Measuring Tape**: For longer dimensions.
- **Calipers**: For precise internal/external dimensions.
- **Micrometer**: For very small measurements.
2. **Area and Volume**:
- **Planimeter**: For irregular areas.
- **Graduated Cylinder**: For liquid volume.
- **Laser Scanners**: For 3D volumetric measurements.
3. **Mass and Weight**:
- **Balance Scale**: For precision.
- **Spring Scale**: Measures weight using gravity.
4. **Angle and Rotation**:
- **Protractor**: For measuring angles.
- **Goniometer**: For complex angle measurements.
5. **Temperature**:
- **Thermometer**: For general use.
- **Thermocouple**: For industrial applications.
6. **Other Tools**:
- **Theodolite**: For surveying.
- **Digital Multimeter**: For electrical measurements.
---
### **Dimensional Analysis**
Dimensional analysis involves checking the consistency of units in equations and ensuring physical quantities are dimensionally consistent.
#### Example:
- **Force (F)** = mass (M) × acceleration (L/T²)
- Dimensional formula: \( F = M \cdot L \cdot T^{-2} \)
---
### **Applications of Measurements and Dimensions**
1. **Construction**:
- Measuring site dimensions, material sizes, and angles.
2. **Manufacturing**:
- Ensuring precision in component dimensions and tolerances.
3. **Engineering Design**:
- Creating accurate blueprints with dimensions and units.
4. **Science and Research**:
- Recording experimental data with precise measurements.
---
Would you like to explore a specific type of measurement, a tool, or its application? 😊
-
 1:10:22
1:10:22
MTNTOUGH Fitness Lab
1 hour agoBorder Patrol Vs Cartels With Vincent "Rocco" Vargas: The Whole Story Behind the Crisis
129 -
 31:25
31:25
Clownfish TV
13 hours ago2024 Officially ENDED Mainstream Media and DEI, Says Mainstream Media.
9486 -
 28:22
28:22
The Boomer Effect
4 hours agoMillennial's Advise On Success & Overcoming Adversity
237 -

The Charlie Kirk Show
2 hours agoTrump's Return Certified + The Fall of Trudeau + Britain's Grooming Gangs | 1.6.2025
79.6K35 -
 1:04:36
1:04:36
Grant Stinchfield
2 hours ago $0.60 earnedHead Movement, Signal Account Change & More... The Cybertruck Bomber Mystery
6.67K -
 LIVE
LIVE
Dirty Old Plumber games
5 hours agoStar Citizen
87 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Father Russell
3 hours agoDelta Force | Stream Restart | Connection Issues
155 watching -
 1:00:33
1:00:33
The Dan Bongino Show
4 hours agoThe Trump Administration Can't Start Soon Enough (Ep. 2394) - 01/06/2025
722K2.32K -
 50:59
50:59
Rebel News
4 hours ago $15.53 earnedLIVE: Surprise Trudeau press conference, expected to resign after pressure
58.9K152 -
 1:01:07
1:01:07
The Rubin Report
3 hours agoBill Maher Rips Into Hollywood Star for Defending This Ugly Aspect of Islam
61.5K35