Premium Only Content
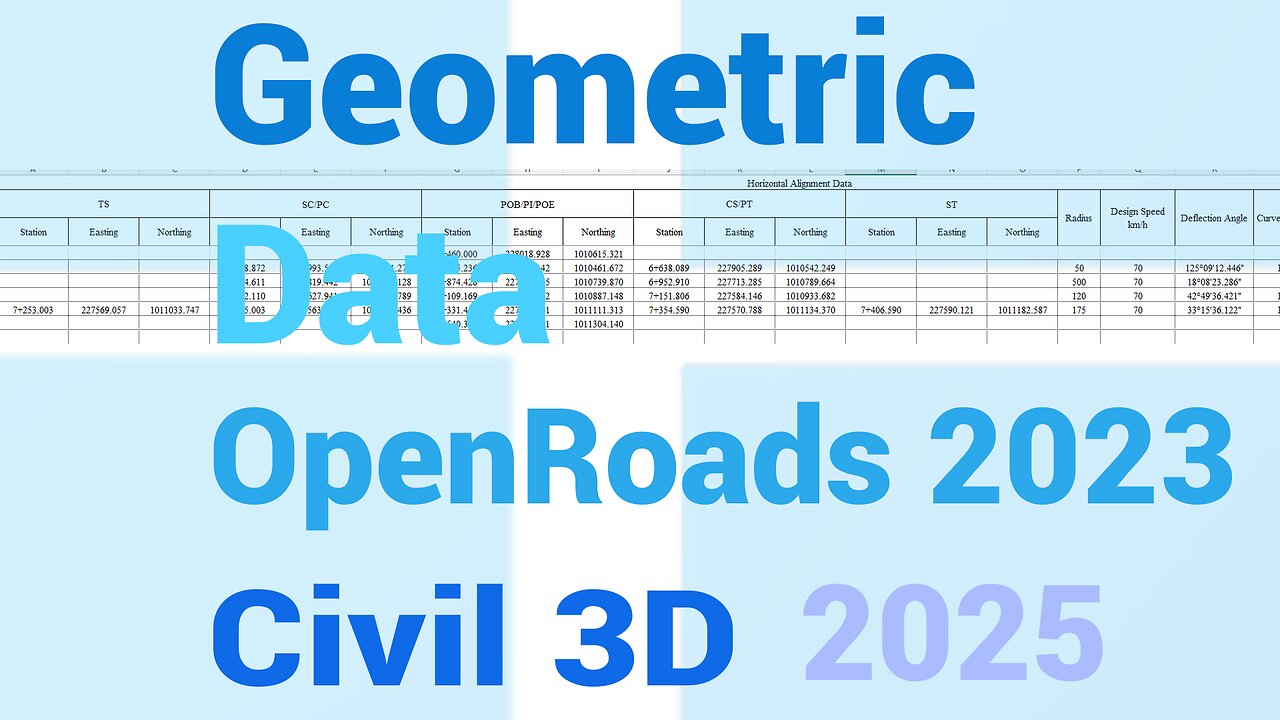
Master Geometric Data Extraction in OpenRoads - Horizontal, Vertical, & Centerline Alignment Guide
Welcome to this in-depth 43-minute tutorial that covers everything you need to know about Geometric Data Generation and Extraction in OpenRoads.
This video is perfect for engineers and designers who want to efficiently generate and extract critical geometric data for road design projects. Whether you're new to OpenRoads or looking to enhance your design workflow, this video will guide you step-by-step through the process of generating precise data for your highway projects. 🚧
What You’ll Learn:
Horizontal Alignment Data:
BOP: Beginning of Pavement
EOP: End of Pavement
PI: Point of Intersection
TS: Tangent to Spiral
Sc: Spiral Curve
PC: Point of Curvature
PT: Point of Tangency
CS: Curve to Spiral
ST: Spiral to Tangent
Deflection Angle: The angle between two tangents at the PI.
Curve Length: The length of the curve between the PC and PT.
Design Speed: The speed at which a road is designed to be safely navigated.
Curve Radius: The radius of the curve, determining its sharpness.
Superelevation: The banking of the roadway to help vehicles maintain speed through a curve.
Curve Direction: The orientation of the curve, whether it turns to the left or right.
Curve Widening: An increase in the width of the road on curves for safety.
Spiral Length: The length of the transition spiral between a tangent and a curve.
Vertical Alignment Data:
PVI: Point of Vertical Intersection
PVC: Point of Vertical Curvature
PVT: Point of Vertical Tangency
K-Value: A measure of the sharpness of a vertical curve.
Tangent Length: The length of the straight sections in the vertical alignment.
Curve Length: The length of the vertical curve.
Middle Ordinate: The maximum distance between the curve and the chord.
Centerline Data:
Centerline by 20 m intervals: Centerline data extracted at every 20 meters along the alignment.
Critical Points of Horizontal Alignment: Includes TS, Sc, PC, PT, CS, ST, which are key points in defining the geometry of the road’s path.
Critical Points of Vertical Alignment: Includes PVC, PVI, PVT, which are important points for defining the elevation profile of the road.
📌 Don't forget to subscribe to the Musa Fide YouTube channel for more tutorials and design tips: / @musfide
📌 Join the Musa Fide Telegram Channel for updates and discussions: https://t.me/musafide
📌 Visit the Musa Fide website for more resources: www.musfide.com
🔔 Make sure to like, share, and comment! Let me know what you think and if you have any questions.
Highway Design, OpenRoads, Civil Engineering, Geometric Data, Horizontal Alignment, Vertical Alignment, Centerline Data, Road Design, Mus Fide, Geometric Data Extraction, Civil 3D, Roadway Design, Infrastructure Design, K-Value, Superelevation, Spiral Length, Curve Widening, Alignment Design, Roadway Geometrics, Transportation Engineering, Engineering Tutorials, Musfide YouTube Channel,BOP, EOP, PI, TS, Sc, PC, PT, CS, ST, Deflection Angle, Curve Length, Design Speed, Curve Radius, Superelevation, Curve Direction, Curve Widening, Spiral Length,PVI, PVC, PVT, K-Value, Tangent Length (Vertical), Curve Length (Vertical), Middle Ordinate,Centerline by Interval (e.g., 20m), Horizontal Alignment Critical Points (TS, Sc, PC, PT, CS, ST), Vertical Alignment Critical Points (PVC, PVI, PVT),OpenRoads Designer, Geometric Data, Road Design, Highway Design, Alignment, Profile, Cross-section,Data Extraction, Data Generation, Civil Engineering, Infrastructure Design, Design Workflow
-
 1:09:24
1:09:24
Timcast
4 hours agoZohran Mamdani BLAMES Trump Over Bomb Threats At Polling Locations
149K87 -
 3:09:52
3:09:52
Right Side Broadcasting Network
5 hours agoLIVE REPLAY: White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt Holds a Press Briefing - 11/4/25
69.8K14 -
 1:58:04
1:58:04
The Charlie Kirk Show
3 hours agoGo Vote! + Healthcare and the Shutdown | Dr. Oz, Baris | 11.4.2025
79.1K9 -
 58:49
58:49
The White House
4 hours agoPress Secretary Karoline Leavitt Briefs Members of the Media, Nov. 4, 2025
32.4K16 -
 1:00:22
1:00:22
Sean Unpaved
3 hours agoCarousel Chaos: CFB Week 10 Shocks & Drops, Cardinals Stun MNF, & CBB's Opening Tip-Off Frenzy
28.9K1 -
 1:57:43
1:57:43
Steven Crowder
6 hours agoFailed Hit Job: Another Trump Media Hoax Exposed
377K328 -
 56:36
56:36
The Rubin Report
5 hours agoFox Hosts Stunned by Piers Morgan’s Dark Prediction for NYC Under Zohran Mamdan
49.2K48 -
![GRAY ZONE DEVLOG FOR .3.5 UPDATE!!! [RGMT CONTENT Mgr. | RGMT GL | GZW CL]](https://1a-1791.com/video/fww1/c0/s8/1/y/7/B/w/y7Bwz.0kob-small-GRAY-ZONE-DEVLOG-FOR-.3.5-U.jpg) 2:11:58
2:11:58
XDDX_HiTower
3 hours ago $1.75 earnedGRAY ZONE DEVLOG FOR .3.5 UPDATE!!! [RGMT CONTENT Mgr. | RGMT GL | GZW CL]
27K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
18 hours agoLIVE & BREAKING NEWS! | TUESDAY 11/4/25
1,809 watching -
 1:39:26
1:39:26
The Shannon Joy Show
5 hours agoICE Brutality In Evanston, Illinois Sparks New Outrage * GOP Seeks New FISA Re-Authorization * Are Tucker Carlson & Nick Fuentes Feds?
26.2K9