Premium Only Content
How Michigan explains American politics
The “blue wall” once referred to a group of Northeast, Midwest, and West Coast states that, conventional wisdom said, “always vote for Democrats.” Unfortunately for Democrats, that was wrong, and in 2016 Donald Trump shockingly won three “blue wall” states — including, narrowly, the state of Michigan.
It maybe shouldn’t have been such a shock, though. All three of the “blue” states Trump won actually had a history of electing Republicans at the state level. Michigan in particular had been fully taken over since 2010 by Republicans, who then spent years gutting unions, restricting abortion, loosening environmental protections, and generally just turning a Republican policy wish list into law. So Trump winning Michigan was, in a way, just the culmination of a years-long drift to the right there.
But by 2022, something had changed dramatically. In a midterm election where Republicans were favored, Democrats won every branch of elected government in Michigan — governor, state House, and state Senate. The state Senate in particular had not been under Democratic control since 1984. And Democrats got busy using their new power immediately: repealing much of the right-wing legislation of the previous years, passing strong LGBTQ protections, quadrupling a tax credit for the poor, and allocating a billion dollars for the auto industry to transition to electric cars. Suddenly Michigan was cranking out more progressive legislation than almost any other state in the US.
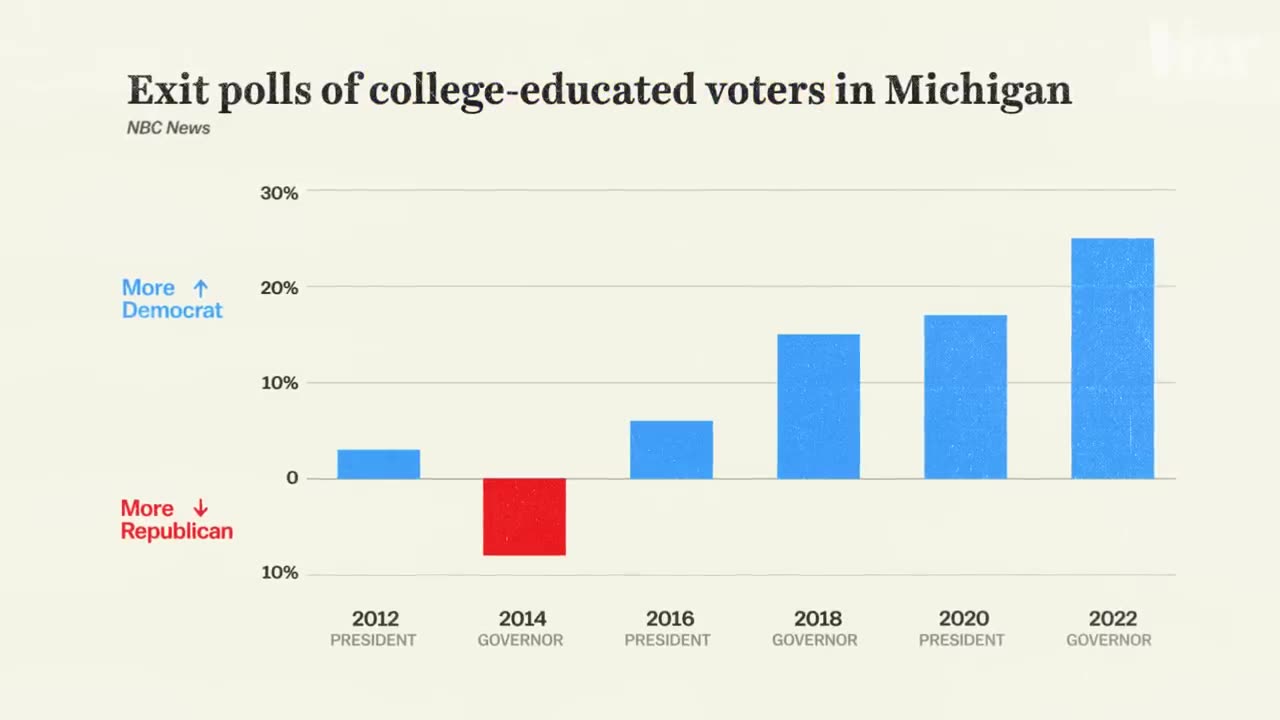
So to recap: Michigan was once a blue state, except it wasn’t actually, and in fact over time it got pretty red, but then it became an actual blue state. (Again?) Or something like that. Obviously, the truth is that Michigan is a swing state. But the story of each of those swings is actually key to understanding how US politics work in the 2010s and 2020s. And it can tell us a lot about our next election, too.
-
 1:05:23
1:05:23
Man in America
14 hours agoSoaring Gold Exposes the Imminent Crash of the Old System w/ John Perez
39.5K7 -
 2:42:40
2:42:40
TruthStream with Joe and Scott
14 hours agoTHOMAS AND GROK: AI, Bible decodes, The JESUS Cube live 9/6 #487
25K2 -
 2:34:46
2:34:46
BlackDiamondGunsandGear
9 hours agoGet Prepped / After Hours Armory / LIVE SHOW /
17K1 -
 2:01:39
2:01:39
Tundra Tactical
7 hours ago $6.38 earned🛑LIVE NOW!! This spits in the face of the Second Amendment.🛑
27.1K8 -
 2:34:46
2:34:46
DLDAfterDark
6 hours ago $1.64 earnedIt's SHTF! Do You Have What You Need?? Let's Review Items & Priorities
19.1K4 -
 28:58
28:58
Stephen Gardner
7 hours ago🚨Explosive allegations: Rosie O’Donnell connects Trump to Epstein scandal!?
33.9K64 -
 LIVE
LIVE
SavageJayGatsby
2 days agoSpicy Saturday | Let's Play: Grounded
524 watching -
 2:06:27
2:06:27
MattMorseTV
8 hours ago $50.92 earned🔴Vance just went SCORCHED EARTH.🔴
128K182 -
 46:41
46:41
The Mel K Show
13 hours agoMel K & Corey DeAngelis | The Hopelessly Captured Teacher’s Unions: Biggest Threat to Our Children & Future | 9-6-25
36.5K5 -
 2:52:42
2:52:42
Mally_Mouse
1 day ago🔥🍺Spicy HYDRATE Saturday!🍺🔥-- Let's Play: Grounded
32.7K3