Premium Only Content
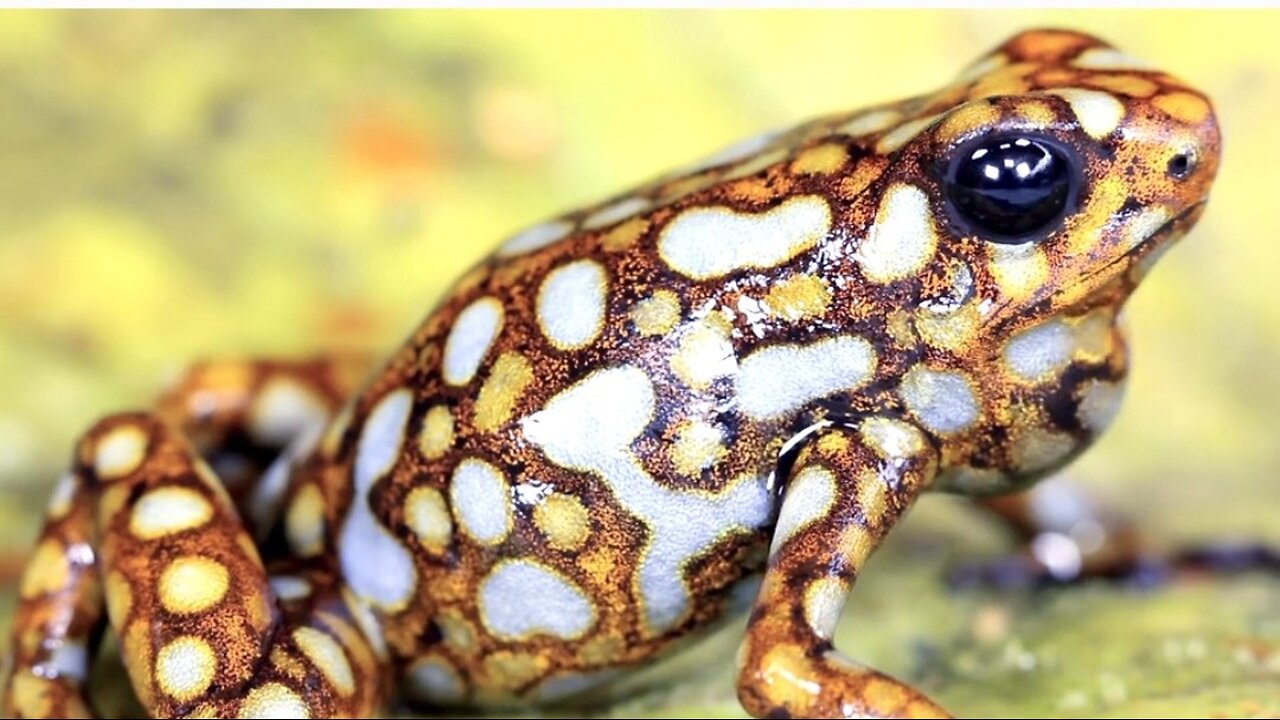

"Frog Facts: A Deep Dive into Amphibian Life"
Frogs are fascinating amphibians that belong to the order Anura. They are widely distributed across the world and are known for their distinctive jumping abilities, croaking sounds, and metamorphic life cycle. Here's a detailed overview of frogs:
1. Physical Characteristics
Body Structure: Frogs have a short, squat body with strong hind legs that are specialized for jumping and swimming. Their feet are often webbed to assist in movement through water.
Skin: Frog skin is thin and permeable, allowing them to absorb water and breathe through it, making them vulnerable to environmental changes and pollution.
Colors: Frogs display a wide variety of colors, ranging from brown, green, and gray for camouflage, to bright colors such as red, blue, or yellow in some species to ward off predators by signaling toxicity.
2. Life Cycle
Frogs undergo complete metamorphosis, transitioning through several stages in their life:
Eggs: Frogs typically lay their eggs in water. The eggs are usually in clusters or strings, depending on the species.
Tadpoles: The eggs hatch into tadpoles, which are fully aquatic and resemble small fish. They breathe through gills and primarily feed on algae.
Metamorphosis: Tadpoles undergo significant changes during metamorphosis, including the development of legs, the loss of their tail, and the emergence of lungs to replace gills.
Adult Frogs: Once metamorphosis is complete, the frog becomes terrestrial or semi-aquatic, depending on the species.
3. Habitat
Frogs are found in a wide variety of environments:
Aquatic: Many frogs live near bodies of freshwater, such as ponds, lakes, and marshes, where they lay eggs and find abundant food.
Terrestrial: Some species live in forests or grasslands but still need moist environments to keep their skin hydrated and return to water to reproduce.
Arboreal: Tree frogs have specialized toe pads that help them grip onto vegetation, allowing them to live in trees.
4. Diet
Frogs are carnivorous and primarily eat insects, worms, spiders, and other small invertebrates. Larger species may eat small mammals, birds, or even other frogs.
They have a sticky tongue that shoots out rapidly to catch prey.
5. Behavior
Croaking: Male frogs croak or make calls to attract mates, and the sound can vary greatly between species.
Nocturnal: Most frogs are active at night (nocturnal), making them harder to spot during the day.
Hibernation: In colder climates, frogs hibernate during the winter by burrowing into mud or hiding in logs or leaf litter.
6. Adaptations
Jumping: Frogs have muscular hind legs that allow them to leap several times their body length.
Camouflage: Many frogs have coloration that helps them blend into their surroundings, hiding them from predators.
Toxicity: Some species, like poison dart frogs, have toxins in their skin that make them dangerous to predators.
7. Species Diversity
There are over 7,000 species of frogs worldwide, including:
Common Frog (Rana temporaria): Found across Europe, it is known for its brownish color and preference for temperate environments.
Poison Dart Frog (Dendrobatidae): These brightly colored frogs from Central and South America are highly toxic.
Tree Frogs (Hylidae): These are known for their ability to live in trees and have adaptations for climbing.
8. Conservation Status
Frogs are sensitive to environmental changes due to their permeable skin and reliance on both land and water ecosystems. Many species are threatened or endangered due to habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and disease (e.g., chytrid fungus).
9. Interesting Facts
Frogs can absorb oxygen through their skin in water, allowing them to stay submerged for extended periods.
Some species, such as the Wood Frog (Rana sylvatica), can survive being frozen during the winter and thaw out in the spring to continue their life cycle.
Frogs play a vital role in ecosystems, both as predators of insects and as prey for larger animals, making their conservation crucial to maintaining biodiversity.
-
 2:00:02
2:00:02
Inverted World Live
4 hours agoMake Crop Circles Great Again | Ep. 64
113K9 -
 2:45:21
2:45:21
TimcastIRL
4 hours agoIRAN STRIKE FAILED Claims LEAKED Intel Report, Trump Admin DENIES Report | Timcast IRL
206K108 -
 LIVE
LIVE
PandaSub2000
2 days agoLIVE 10:30pm ET | GOLLUM (The Worst Game Ever)
138 watching -
 45:05
45:05
Man in America
8 hours agoThe Banking Cartel NEEDS WW3—Can a Ceasefire Derail the Reset? w/ Collin Plume
40.1K12 -
 LIVE
LIVE
SpartakusLIVE
6 hours agoDuos w/ Rallied || The Spartan and The Dragon DOMINATE the Tower of Power
458 watching -
 1:36:08
1:36:08
Adam Does Movies
7 hours ago $2.11 earnedTalking Movies + Ask Me Anything - LIVE
33.4K1 -
 DVR
DVR
MissesMaam
3 hours agoBack At It Again | Stardew Co-Op 💚✨
11.6K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
BSparksGaming
2 hours agoSplitgate 2 - sday! Tagging Tactics Event! Graffiti Galor!
557 watching -
 2:20:41
2:20:41
Barry Cunningham
5 hours agoPRESIDENT TRUMP FACES THE WRATH OF THE DEEP STATE AND MORE NEWS!
67.6K68 -
 29:54
29:54
Producer Michael
11 hours agoThe Art Of Layering Luxury Fragrances
33.7K1