Premium Only Content
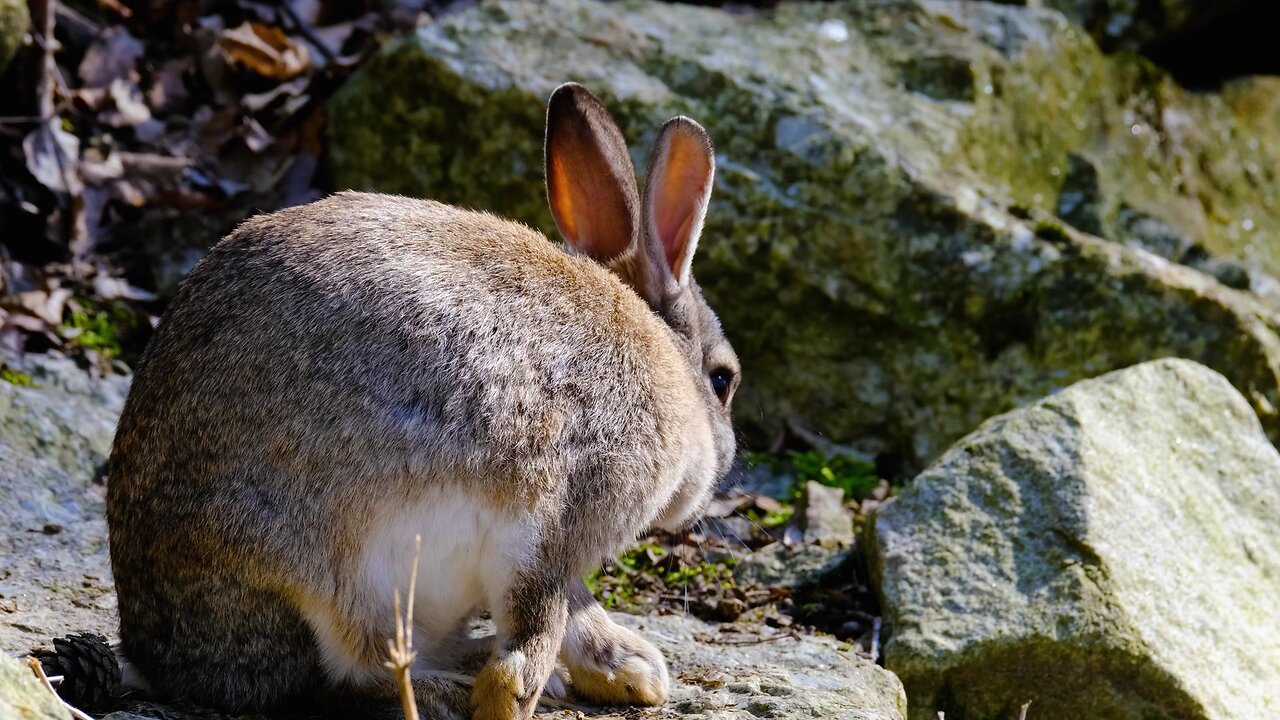

"European Rabbit: Nature's Burrow Builder"
The European rabbit (*Oryctolagus cuniculus*) is a small mammal native to the Iberian Peninsula, which includes Spain and Portugal, and has been widely introduced elsewhere, including Europe, Australia, and the Americas. This species has had a significant impact on ecosystems, agriculture, and human culture.
### **Physical Characteristics:**
- **Size:** Adult European rabbits typically weigh between 1.2 to 2 kilograms (2.6 to 4.4 pounds) and measure about 34 to 45 cm (13 to 18 inches) in length.
- **Appearance:** They have soft, dense fur, which is usually grey-brown but can vary from sandy to black, depending on the individual and the environment. Their underparts are lighter, often white or light gray. They have large ears, which can be up to 7 cm (2.8 inches) long, and a distinctive white tail.
- **Eyes:** The eyes are positioned on the sides of the head, giving them a wide field of vision, which is vital for spotting predators.
### **Behavior:**
- **Social Structure:** European rabbits are social animals that live in groups, typically in complex burrow systems known as warrens. These burrows provide shelter from predators and extreme weather.
- **Reproduction:** They are known for their prolific breeding capabilities. A female rabbit (doe) can give birth to multiple litters per year, with each litter consisting of 3-12 young, called kits. The gestation period is around 30 days.
- **Diet:** European rabbits are herbivores, feeding primarily on grasses, herbs, and leafy weeds. They are also known to consume crops, making them a significant pest in agricultural areas.
### **Habitat:**
- **Range:** Originally from the Iberian Peninsula, European rabbits have been introduced to various parts of the world. They thrive in a wide range of environments, from grasslands and forests to deserts and coastal areas.
- **Warrens:** They dig complex burrow systems, which can have multiple entrances and extend for several meters underground. These warrens provide safety from predators and harsh environmental conditions.
### **Ecological Impact:**
- **Ecosystem Role:** In their native range, European rabbits play a crucial role in maintaining the landscape. Their grazing habits help shape the vegetation, and their burrows provide homes for other species.
- **Invasive Species:** In regions where they have been introduced, such as Australia, European rabbits have become invasive, causing extensive ecological damage. They compete with native species for food and habitat, and their burrowing can lead to soil erosion.
### **Conservation Status:**
- **Threats:** While they are considered a pest in many regions, European rabbits are facing threats in their native range due to habitat loss, disease (such as myxomatosis and rabbit hemorrhagic disease), and hunting.
- **IUCN Status:** The European rabbit is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List due to the significant decline in their populations in their native range.
### **Cultural Significance:**
- European rabbits have been domesticated for thousands of years and are the ancestors of the various breeds of domestic rabbits kept as pets and farm animals. They also hold cultural importance in many societies, symbolizing fertility and rebirth.
This overview should give you a comprehensive understanding of the European rabbit and its significance in various contexts.
-
 UPCOMING
UPCOMING
Man in America
5 hours agoThe DISTURBING Truth: How Seed Oils, the Vatican, and Procter & Gamble Are Connected w/ Dan Lyons
5.79K2 -
 6:46:07
6:46:07
Rance's Gaming Corner
7 hours agoTime for some RUMBLE FPS!! Get in here.. w/Fragniac
107K1 -
 DVR
DVR
Josh Pate's College Football Show
6 hours ago $2.83 earnedCFP Reaction Special | Early Quarterfinal Thoughts | Transfer Portal Intel | Fixing The Playoff
16.1K -
 23:55
23:55
CartierFamily
3 days agoElon & Vivek TRIGGER Congress as DOGE SHUTS DOWN Government
61.3K76 -
 5:43:44
5:43:44
Scammer Payback
2 days agoCalling Scammers Live
146K21 -
 18:38
18:38
VSiNLive
2 days agoProfessional Gambler Steve Fezzik LOVES this UNDERVALUED Point Spread!
109K17 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Right Side Broadcasting Network
10 days agoLIVE REPLAY: President Donald J. Trump Keynotes TPUSA’s AmFest 2024 Conference - 12/22/24
5,143 watching -
 4:31
4:31
CoachTY
1 day ago $26.84 earnedCOINBASE AND DESCI !!!!
158K11 -
 10:02
10:02
MichaelBisping
23 hours agoBISPING: "Was FURY ROBBED?!" | Oleksandr Usyk vs Tyson Fury 2 INSTANT REACTION
84.1K13 -
 8:08
8:08
Guns & Gadgets 2nd Amendment News
2 days ago16 States Join Forces To Sue Firearm Manufacturers Out of Business - 1st Target = GLOCK
110K87