Premium Only Content
This video is only available to Rumble Premium subscribers. Subscribe to
enjoy exclusive content and ad-free viewing.

Thundereggs!
HumbleConservative
- 42 / 60
1
Whole & Broken Geodes!
HumbleConservative
A geode is a hollow, usually spherical rock, that when broken open reveals a cavity lined with crystals or other mineral formations. Here are some key points about geodes:
Formation: Geodes form when gas bubbles or cavities in volcanic or sedimentary rock are filled with mineral-rich water. As the water evaporates, it leaves behind minerals which crystallize over time, lining the inside of the cavity.
Structure: The outer layer of a geode is typically rough and nondescript, often making it look like an ordinary rock until it's cracked open. Inside, you might find crystals like quartz, amethyst, calcite, or even rarer minerals.
Location: They are commonly found in regions with volcanic activity or limestone deposits. Famous locations include parts of the United States, Brazil, Uruguay, and Mexico.
Uses: Geodes are popular among rock collectors and are often cut and polished for use in jewelry or as decorative pieces. Some are also used in metaphysical practices for their supposed healing properties.
Identification: To identify a geode, one would typically look for a rock that is unusually light for its size or has a hollow sound when tapped. However, the only definitive way to confirm is by breaking it open or using specialized equipment like X-rays.
If you're interested in finding or identifying geodes, or if you have any other questions about them, feel free to ask!Rabbit Springs Geode Field, is a well-known rockhounding site located in southern Idaho near the Nevada border. It’s a popular spot for collectors seeking thundereggs—spherical rocks that often contain beautiful agate or crystal-filled centers, some of which fluoresce under UV light due to mineral content like chalcedony or quartz.
2
Geode Field!
HumbleConservative
Rabbit Springs Geode Field, also known as Rabbit Springs Thundereggs, is a well-known rockhounding site located in southern Idaho near the Nevada border. It’s a popular spot for collectors seeking thundereggs—spherical rocks that often contain beautiful agate or crystal-filled centers, some of which fluoresce under UV light due to mineral content like chalcedony or quartz. This site sits along U.S. Highway 93, roughly 38 miles from Twin Falls, Idaho, and about 130 miles from Mountain Home, making it accessible yet remote enough to feel like a true adventure.
The coordinates for Rabbit Springs are approximately 42.06572°N, -114.67387°W. You can get there by driving south from Twin Falls toward Jackpot, Nevada, and looking for the old Rabbit Springs rest area, a historical marker for the site. The terrain is rugged, typical of the high desert landscape in this region, with volcanic and sedimentary rocks from ancient geological activity providing the perfect conditions for thunderegg formation. These rocks are remnants of gas pockets in lava flows that filled with silica-rich fluids over millions of years.
No heavy digging is necessary here—surface collecting with a bucket is the way to go, as many thundereggs are weathered out and scattered across the ground. A rock hammer might come in handy to crack them open, but locals and seasoned rockhounds suggest the best finds are often already exposed, and breaking into the bedrock isn’t worth the effort. The thundereggs vary in size, from plums to grapefruits, and some glow a striking green or orange under a 365nm UV light, thanks to trace minerals. Rumors of radioactivity have floated around, but tests with Geiger counters have debunked that myth.
The site is on public land managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM), so casual collecting is allowed as long as you’re not using heavy machinery or digging extensive tunnels—stick to hand tools and surface finds. Any vehicle can make the trip, though the final approach might involve a short walk from the highway. September’s cooler weather makes it an ideal time to visit, avoiding the summer heat of this arid region.
3
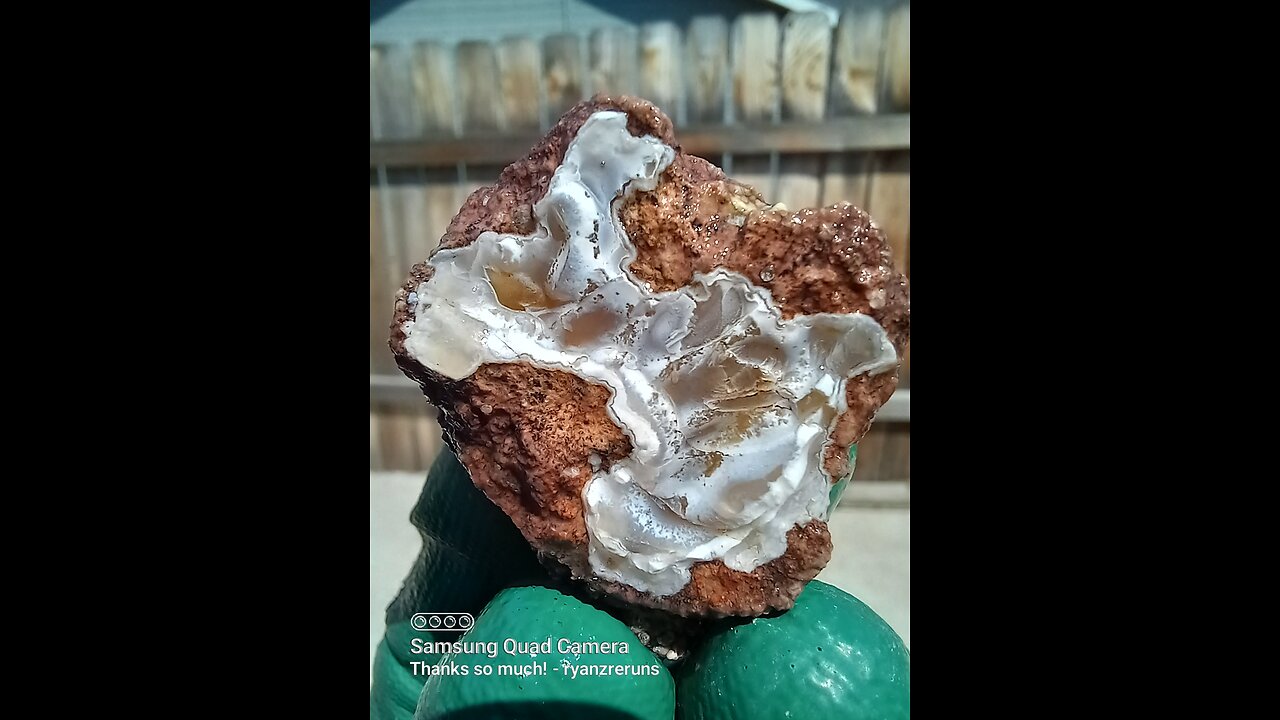
Botryoidal cut!
HumbleConservative
Botryoidal is a term used in mineralogy to describe a mineral or rock formation that has a rounded, grape-like, or botryoidal (from the Greek word "botryoeidēs" meaning "like a bunch of grapes") shape. Here are some key points about botryoidal formations:
Formation: Botryoidal structures form when minerals precipitate from solution in a way that creates rounded, nodular surfaces. This often happens in cavities or vugs within rocks where mineral-rich solutions slowly deposit layers of minerals, building up in a manner that mimics the shape of grapes.
Common Minerals: Some minerals commonly found in botryoidal forms include:
Hematite: Often forms botryoidal shapes with a metallic luster.
Malachite: Known for its vibrant green botryoidal formations.
Goethite: Can exhibit botryoidal textures, usually in brown or yellow hues.
Chalcedony: Including varieties like agate, which can form botryoidal layers within geodes.
Psilomelane: A manganese oxide mineral often found in botryoidal shapes.
Texture: The texture of botryoidal minerals is smooth and rounded, with a surface that looks like clusters of small spheres or nodules. This texture is due to the slow, even deposition of mineral material from solution.
Uses:
Jewelry and Decoration: Botryoidal minerals are prized for their unique shapes and are often polished or cut into cabochons for use in jewelry. They can also be used as decorative stones.
Collectors: Due to their distinctive appearance, botryoidal specimens are popular among mineral collectors.
Art: Their natural beauty makes them suitable for artistic endeavors, including sculptures or inlays.
Geological Significance: Botryoidal formations can provide insights into the conditions under which the minerals precipitated, often indicating slow, stable conditions conducive to this type of growth. They are also indicators of the fluid dynamics and chemistry in the environment where they formed.
4
Shaping!
HumbleConservative
A Thunderegg is a geological structure similar to a geode but with unique characteristics. Here's an overview:
Formation: Thundereggs form within rhyolitic volcanic ash layers. They start as gas bubbles or steam pockets in the lava, which act as molds. Over time, these are filled with silica-rich fluids, mainly chalcedony, agate, jasper, or opal, creating intricate patterns and colors inside.
Appearance: On the outside, thundereggs look like ordinary, rough-textured rocks, often with a white-gray to reddish-brown surface. However, when cut and polished, they reveal a variety of internal structures, from solid agate or chalcedony cores to sometimes hollow centers with crystals.
Size: They can range from small, about the size of a baseball, to larger specimens over a meter across, though most commonly they are between two to six inches in diameter.
Locations: While Oregon, USA, is particularly famous for thundereggs, especially in counties like Crook, Jefferson, Malheur, Wasco, and Wheeler, they are found globally wherever the geological conditions are right. Other notable locations include Germany, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Poland, Romania, and Turkey.
Cultural Significance: In Oregon, the thunderegg was designated as the state rock in 1965, reflecting its importance in local geology and culture. Native American legends attribute their formation to thunder spirits or gods throwing these rocks during thunderstorms.
Collection and Use: Thundereggs are popular among rock collectors for their unique beauty once cut open. They're often used in jewelry making or as display pieces due to their aesthetic appeal after being sliced and polished.
Variations: Each thunderegg is unique due to the minerals present in the area where it forms, leading to a wide variety in color, pattern, and structure even from the same bed.
5
Broken Thunderegg Cluster!
HumbleConservative
A Thunderegg is a geological structure similar to a geode but with unique characteristics. Here's an overview:
Formation: Thundereggs form within rhyolitic volcanic ash layers. They start as gas bubbles or steam pockets in the lava, which act as molds. Over time, these are filled with silica-rich fluids, mainly chalcedony, agate, jasper, or opal, creating intricate patterns and colors inside.
Appearance: On the outside, thundereggs look like ordinary, rough-textured rocks, often with a white-gray to reddish-brown surface. However, when cut and polished, they reveal a variety of internal structures, from solid agate or chalcedony cores to sometimes hollow centers with crystals.
Size: They can range from small, about the size of a baseball, to larger specimens over a meter across, though most commonly they are between two to six inches in diameter.
Locations: While Oregon, USA, is particularly famous for thundereggs, especially in counties like Crook, Jefferson, Malheur, Wasco, and Wheeler, they are found globally wherever the geological conditions are right. Other notable locations include Germany, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Poland, Romania, and Turkey.
Cultural Significance: In Oregon, the thunderegg was designated as the state rock in 1965, reflecting its importance in local geology and culture. Native American legends attribute their formation to thunder spirits or gods throwing these rocks during thunderstorms.
Collection and Use: Thundereggs are popular among rock collectors for their unique beauty once cut open. They're often used in jewelry making or as display pieces due to their aesthetic appeal after being sliced and polished.
Variations: Each thunderegg is unique due to the minerals present in the area where it forms, leading to a wide variety in color, pattern, and structure even from the same bed.
6
Half a thunderegg!
HumbleConservative
A Thunderegg is a geological structure similar to a geode but with unique characteristics. Here's an overview:
Formation: Thundereggs form within rhyolitic volcanic ash layers. They start as gas bubbles or steam pockets in the lava, which act as molds. Over time, these are filled with silica-rich fluids, mainly chalcedony, agate, jasper, or opal, creating intricate patterns and colors inside.
Appearance: On the outside, thundereggs look like ordinary, rough-textured rocks, often with a white-gray to reddish-brown surface. However, when cut and polished, they reveal a variety of internal structures, from solid agate or chalcedony cores to sometimes hollow centers with crystals.
Size: They can range from small, about the size of a baseball, to larger specimens over a meter across, though most commonly they are between two to six inches in diameter.
Locations: While Oregon, USA, is particularly famous for thundereggs, especially in counties like Crook, Jefferson, Malheur, Wasco, and Wheeler, they are found globally wherever the geological conditions are right. Other notable locations include Germany, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Poland, Romania, and Turkey.
Cultural Significance: In Oregon, the thunderegg was designated as the state rock in 1965, reflecting its importance in local geology and culture. Native American legends attribute their formation to thunder spirits or gods throwing these rocks during thunderstorms.
Collection and Use: Thundereggs are popular among rock collectors for their unique beauty once cut open. They're often used in jewelry making or as display pieces due to their aesthetic appeal after being sliced and polished.
Variations: Each thunderegg is unique due to the minerals present in the area where it forms, leading to a wide variety in color, pattern, and structure even from the same bed.
7
Thunderegg Cluster w Common Opal!
HumbleConservative
A Thunderegg is a geological structure similar to a geode but with unique characteristics. Here's an overview:
Formation: Thundereggs form within rhyolitic volcanic ash layers. They start as gas bubbles or steam pockets in the lava, which act as molds. Over time, these are filled with silica-rich fluids, mainly chalcedony, agate, jasper, or opal, creating intricate patterns and colors inside.
Appearance: On the outside, thundereggs look like ordinary, rough-textured rocks, often with a white-gray to reddish-brown surface. However, when cut and polished, they reveal a variety of internal structures, from solid agate or chalcedony cores to sometimes hollow centers with crystals.
Size: They can range from small, about the size of a baseball, to larger specimens over a meter across, though most commonly they are between two to six inches in diameter.
Locations: While Oregon, USA, is particularly famous for thundereggs, especially in counties like Crook, Jefferson, Malheur, Wasco, and Wheeler, they are found globally wherever the geological conditions are right. Other notable locations include Germany, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Poland, Romania, and Turkey.
Cultural Significance: In Oregon, the thunderegg was designated as the state rock in 1965, reflecting its importance in local geology and culture. Native American legends attribute their formation to thunder spirits or gods throwing these rocks during thunderstorms.
Collection and Use: Thundereggs are popular among rock collectors for their unique beauty once cut open. They're often used in jewelry making or as display pieces due to their aesthetic appeal after being sliced and polished.
Variations: Each thunderegg is unique due to the minerals present in the area where it forms, leading to a wide variety in color, pattern, and structure even from the same bed.
8
Red Thunderegg Shard!
HumbleConservative
A Thunderegg is a geological structure similar to a geode but with unique characteristics. Here's an overview:
Formation: Thundereggs form within rhyolitic volcanic ash layers. They start as gas bubbles or steam pockets in the lava, which act as molds. Over time, these are filled with silica-rich fluids, mainly chalcedony, agate, jasper, or opal, creating intricate patterns and colors inside.
Appearance: On the outside, thundereggs look like ordinary, rough-textured rocks, often with a white-gray to reddish-brown surface. However, when cut and polished, they reveal a variety of internal structures, from solid agate or chalcedony cores to sometimes hollow centers with crystals.
Size: They can range from small, about the size of a baseball, to larger specimens over a meter across, though most commonly they are between two to six inches in diameter.
Locations: While Oregon, USA, is particularly famous for thundereggs, especially in counties like Crook, Jefferson, Malheur, Wasco, and Wheeler, they are found globally wherever the geological conditions are right. Other notable locations include Germany, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Poland, Romania, and Turkey.
Cultural Significance: In Oregon, the thunderegg was designated as the state rock in 1965, reflecting its importance in local geology and culture. Native American legends attribute their formation to thunder spirits or gods throwing these rocks during thunderstorms.
Collection and Use: Thundereggs are popular among rock collectors for their unique beauty once cut open. They're often used in jewelry making or as display pieces due to their aesthetic appeal after being sliced and polished.
Variations: Each thunderegg is unique due to the minerals present in the area where it forms, leading to a wide variety in color, pattern, and structure even from the same bed.
9
Thunderegg Cut!
HumbleConservative
A Thunderegg is a geological structure similar to a geode but with unique characteristics. Here's an overview:
Formation: Thundereggs form within rhyolitic volcanic ash layers. They start as gas bubbles or steam pockets in the lava, which act as molds. Over time, these are filled with silica-rich fluids, mainly chalcedony, agate, jasper, or opal, creating intricate patterns and colors inside.
Appearance: On the outside, thundereggs look like ordinary, rough-textured rocks, often with a white-gray to reddish-brown surface. However, when cut and polished, they reveal a variety of internal structures, from solid agate or chalcedony cores to sometimes hollow centers with crystals.
Size: They can range from small, about the size of a baseball, to larger specimens over a meter across, though most commonly they are between two to six inches in diameter.
Locations: While Oregon, USA, is particularly famous for thundereggs, especially in counties like Crook, Jefferson, Malheur, Wasco, and Wheeler, they are found globally wherever the geological conditions are right. Other notable locations include Germany, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Poland, Romania, and Turkey.
Cultural Significance: In Oregon, the thunderegg was designated as the state rock in 1965, reflecting its importance in local geology and culture. Native American legends attribute their formation to thunder spirits or gods throwing these rocks during thunderstorms.
Collection and Use: Thundereggs are popular among rock collectors for their unique beauty once cut open. They're often used in jewelry making or as display pieces due to their aesthetic appeal after being sliced and polished.
Variations: Each thunderegg is unique due to the minerals present in the area where it forms, leading to a wide variety in color, pattern, and structure even from the same bed.
1
comment
10
Thunderegg Inspection!
HumbleConservative
A Thunderegg is a geological structure similar to a geode but with unique characteristics. Here's an overview:
Formation: Thundereggs form within rhyolitic volcanic ash layers. They start as gas bubbles or steam pockets in the lava, which act as molds. Over time, these are filled with silica-rich fluids, mainly chalcedony, agate, jasper, or opal, creating intricate patterns and colors inside.
Appearance: On the outside, thundereggs look like ordinary, rough-textured rocks, often with a white-gray to reddish-brown surface. However, when cut and polished, they reveal a variety of internal structures, from solid agate or chalcedony cores to sometimes hollow centers with crystals.
Size: They can range from small, about the size of a baseball, to larger specimens over a meter across, though most commonly they are between two to six inches in diameter.
Locations: While Oregon, USA, is particularly famous for thundereggs, especially in counties like Crook, Jefferson, Malheur, Wasco, and Wheeler, they are found globally wherever the geological conditions are right. Other notable locations include Germany, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Poland, Romania, and Turkey.
Cultural Significance: In Oregon, the thunderegg was designated as the state rock in 1965, reflecting its importance in local geology and culture. Native American legends attribute their formation to thunder spirits or gods throwing these rocks during thunderstorms.
Collection and Use: Thundereggs are popular among rock collectors for their unique beauty once cut open. They're often used in jewelry making or as display pieces due to their aesthetic appeal after being sliced and polished.
Variations: Each thunderegg is unique due to the minerals present in the area where it forms, leading to a wide variety in color, pattern, and structure even from the same bed.
This gives you a comprehensive view of what a thunderegg is, its formation, and its significance.
11
Globular cut!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
12
Bulbas glob cut!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
13
Robbed! Grabbed the wrong half!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
14
Thunderegg Cut!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
15
Thunderegg Cut w/Opal!
HumbleConservative
These rocks appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
16
Thundereggs?
HumbleConservative
These rocks appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
17
Thought it would be three thundereggs!?!?
HumbleConservative
Based on the visual characteristics of the rock in the image, it appears to be an iron-rich sedimentary rock, possibly an ironstone or banded iron formation (BIF). Here are some key observations:
Color: The rock has a reddish-brown hue, which is typical of iron oxides like hematite (Fe₂O₃) or goethite (FeO(OH)).
Texture: The rock shows a layered or banded structure with a mix of different shades of red, brown, and some lighter minerals, which suggests it might be a sedimentary rock formed in layers over time.
Luster: The wet appearance gives it a glossy look, which can sometimes help in identifying minerals by enhancing their color and luster.
Composition: The presence of small white or light-colored inclusions could be quartz, calcite, or other minerals commonly found in iron-rich sedimentary environments.
Ironstones are often formed in ancient marine or lake environments where iron was precipitated out of the water and deposited in layers. Banded iron formations are particularly notable for their distinct layers of iron oxides and silica, formed under specific chemical conditions in the Earth's early history.
18
Thundercup glow!
HumbleConservative
These rocks appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
19
Thunderegg glow!
HumbleConservative
These rocks appears to be a type of **thunder egg**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
1
comment
20
Rabbit Springs Lava Flow!
HumbleConservative
Thundereggs can indeed be found near Jackpot, Nevada, particularly in an area known as Rabbit Springs, which is located just off Highway 93 about three miles north of Jackpot. Here's what you need to know based on the available information:
Location and Accessibility: The Rabbit Springs site between Twin Falls and Jackpot is noted for containing clusters of fluorescent thundereggs. These are accessible from Highway 93, making them relatively easy to find for rockhounding enthusiasts. The area is on Bureau of Land Management (BLM) land, which generally allows for rock collecting under certain conditions.
Nature of Thundereggs: Thundereggs found here are described as being made up of a combination of volcanic and agate materials. Their true beauty is fully realized when they are viewed under a fluorescent light source, which makes them glow. This property makes them particularly interesting to collectors.
Historical Context: While the specific site in Jackpot isn't detailed in historical context, the broader area of Nevada has a rich history of thunderegg mining, with notable sites like the Black Rock Desert being closed off, highlighting the rarity and value of these geological formations.
For anyone interested in rockhounding near Jackpot, Nevada:
Preparation: Bring tools like a rake, shovel, and perhaps a GPS unit as suggested for other rockhounding trips in the region. Be prepared for potentially digging into the soil to find these gems.
Legal Considerations: Always verify the current regulations for rock collecting on BLM land, as rules can change. Respect the environment by not over-digging or leaving the area in disarray.
Experience: Rockhounding here can be a fun family activity or a serious pursuit for collectors, given the unique properties of these thundereggs.
Remember, while the information provided here is based on the search results, conditions like access, rules, or even the availability of thundereggs can change. It's always good to check with local resources or BLM offices for the latest information before heading out.
21
Broken Geodes & Thundereggs!
HumbleConservative
These rocks appears to be a type of **thunder eggs** and **geodes**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
22
Whole Thundereggs from Rabbit Springs Lava Flow!
HumbleConservative
Rabbit Springs, which is located just off Highway 93 about three miles north of Jackpot, Nevada. Here's a little bit on the lava field based on the available information:
Location and Accessibility: The Rabbit Springs site between Twin Falls and Jackpot is noted for containing clusters of fluorescent thundereggs. These are accessible from Highway 93, making them relatively easy to find for rockhounding enthusiasts. The area is on Bureau of Land Management (BLM) land, which generally allows for rock collecting under certain conditions.
Nature of Thundereggs: Thundereggs found here are described as being made up of a combination of volcanic and agate materials. Their true beauty is fully realized when they are viewed under a fluorescent light source, which makes them glow. This property makes them particularly interesting to collectors.
Historical Context: While the specific site in Jackpot isn't detailed in historical context, the broader area of Nevada has a rich history of thunderegg mining, with notable sites like the Black Rock Desert being closed off, highlighting the rarity and value of these geological formations.
For anyone interested in rockhounding near Jackpot, Nevada:
Preparation: Bring tools like a rake, shovel, and perhaps a GPS unit as suggested for other rockhounding trips in the region. Be prepared for potentially digging into the soil to find these gems.
Legal Considerations: Always verify the current regulations for rock collecting on BLM land, as rules can change. Respect the environment by not over-digging or leaving the area in disarray.
Experience: Rockhounding here can be a fun family activity or a serious pursuit for collectors, given the unique properties of these thundereggs.
Remember, while the information provided here is based on the search results, conditions like access, rules, or even the availability of thundereggs can change. It's always good to check with local resources or BLM offices for the latest information before heading out.
23
Thunderegg Nest!
HumbleConservative
Rabbit Springs, which is located just off Highway 93 about three miles north of Jackpot, Nevada. Here's a little bit on the lava field based on the available information:
Location and Accessibility: The Rabbit Springs site between Twin Falls and Jackpot is noted for containing clusters of fluorescent thundereggs. These are accessible from Highway 93, making them relatively easy to find for rockhounding enthusiasts. The area is on Bureau of Land Management (BLM) land, which generally allows for rock collecting under certain conditions.
Nature of Thundereggs: Thundereggs found here are described as being made up of a combination of volcanic and agate materials. Their true beauty is fully realized when they are viewed under a fluorescent light source, which makes them glow. This property makes them particularly interesting to collectors.
Historical Context: While the specific site in Jackpot isn't detailed in historical context, the broader area of Nevada has a rich history of thunderegg mining, with notable sites like the Black Rock Desert being closed off, highlighting the rarity and value of these geological formations.
For anyone interested in rockhounding near Jackpot, Nevada:
Preparation: Bring tools like a rake, shovel, and perhaps a GPS unit as suggested for other rockhounding trips in the region. Be prepared for potentially digging into the soil to find these gems.
Legal Considerations: Always verify the current regulations for rock collecting on BLM land, as rules can change. Respect the environment by not over-digging or leaving the area in disarray.
Experience: Rockhounding here can be a fun family activity or a serious pursuit for collectors, given the unique properties of these thundereggs.
Remember, while the information provided here is based on the search results, conditions like access, rules, or even the availability of thundereggs can change. It's always good to check with local resources or BLM offices for the latest information before heading out.
24
Crushed Thunderegg!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
25
Tri-cluster of Thundereggs!
HumbleConservative
This rock appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, green, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
26
Tiny Thundereggs!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
27
What's inside this Thunderegg?!?
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
28
Is it a Thunderegg?
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
29
Thunderegg twins!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
30
Love the green inside!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
31
Part of a Thunderegg!?
HumbleConservative
@RyanzRocks #noob #rockhound #rockformation #tumbling #agates #rocks #rockhounders #rockstructure #metamorphicrocks #metamorphic #igneousrocks #igneous #quartz #quartzite #geology #nodules #minerals #crystals #glowrocks #idahorockhunting #idahogems #rockcutting #thundereggs #chalcedony #opal #lavarock #rigidtools #ryobitools #riverrocks #translucentrocks #translucent #rockgarden #flow #vevortools #jasper #granite #caves #marble #carnelian #gneiss #limestone #calcite #gold #silver #botryoidal
32
Thunderegg!
HumbleConservative
@RyanzRocks #noob #rockhound #rockformation #sandstone #tumbling #agates #rocks #rockhounders #rockstructure #metamorphicrocks #metamorphic #igneousrocks #igneous #quartz #quartzite #geology #nodules #minerals #crystals #glowrocks #idahorockhunting #idahogems #rockcutting #thundereggs #chalcedony #opal #lavarock #rigidtools #ryobitools #riverrocks #translucentrocks #translucent #rockgarden #flow #vevortools #jasper #granite #caves #marble #carnelian #gneiss #limestone #calcite #gold #silver #botryoidal #geodes
33
Half a Thunderegg w/Opal!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silica, with a water content typically between 3 and 21% by weight, most commonly around 6-10%. It's deposited at relatively low temperatures and can be found in the fissures of various rock types, including limonite, sandstone, rhyolite, marl, and basalt. Here's a deeper look into opal:
Types of Opal:
Precious Opal: Known for its "play-of-color," which is an optical phenomenon where colors flash or change as the angle of light or observation changes. This effect is due to the diffraction of light through the microscopic silica spheres within the opal.
Common Opal: Lacks the play-of-color and can come in a variety of colors like white, black, grey, yellow, orange, red, or brown. It's often referred to as "potch" when not gem-quality.
Fire Opal: Typically ranges in color from yellow to orange to red and can be transparent to translucent. Fire opals can exhibit play-of-color, but their name comes from the fiery body color.
Boulder Opal: A type of opal naturally attached to its host rock. It's often cut with the host rock to provide stability and to enhance the visual appeal.
Matrix Opal: The opal fills the cracks and cavities within the host rock, creating a network of opal that's visible on the surface.
Formation:
Primary Opal: Forms through the slow deposition of silica from groundwater in cavities or fractures of rocks.
Secondary Opal: Can form by weathering or alteration of other minerals, often in more superficial environments or through the action of silica-rich waters.
Locations:
Australia: The world's leading source, especially for precious opal, with significant deposits in places like Coober Pedy, Lightning Ridge, and White Cliffs.
Ethiopia: Known for its black opals and more recently discovered opal fields.
Mexico: Famous for fire opals.
Brazil: Produces a variety of opals, including crystal opal.
Properties:
Hardness: Typically ranges between 5.5 to 6.5 on the Mohs scale, though it can be softer if less hydrated or harder if more silica-rich.
Luster: Can range from waxy to resinous to vitreous.
Transparency: Varies from opaque to semi-translucent to transparent.
34
Thunderegg Cluster!
HumbleConservative
@RyanzRocks #noob #rockhound #rockformation #sandstone #tumbling #agates #rocks #rockhounders #rockstructure #metamorphicrocks #metamorphic #igneousrocks #igneous #quartz #quartzite #geology #nodules #minerals #crystals #glowrocks #idahorockhunting #idahogems #rockcutting #thundereggs #chalcedony #opal #lavarock #rigidtools #ryobitools #riverrocks #translucentrocks #translucent #rockgarden #flow #vevortools #jasper #granite #caves #marble #carnelian #gneiss #limestone #calcite #gold #silver #botryoidal #geodes
1
comment
35
Circular Formation!
HumbleConservative
The rock in the image appears to be a type of **thunder egg** or **agate**. Here's why:
1. **Coloration and Banding**: The rock shows a combination of colors, including brown, white, and possibly some hints of other colors, which is typical for agates and thunder eggs. The banding pattern is also characteristic of agates, which form in cavities of volcanic rocks.
2. **Translucency**: Some parts of the rock are translucent, which is common in agates due to their chalcedony composition.
3. **Texture**: The rock's texture looks somewhat waxy or glassy, which is typical for agates that have been polished or naturally worn smooth.
4. **Inclusions**: The yellowish or brownish areas could be due to iron oxide or other mineral inclusions, which are often found in agates. Thunder eggs are nodules of agate found in volcanic rocks, and they often have a hollow or partially hollow interior filled with crystals or banded agate.
However, without specific tests like a hardness test, streak test, or chemical analysis, this identification remains speculative. For a more precise identification: - **Hardness Test**: Agate has a hardness of around 7 on the Mohs scale, meaning it should scratch glass but not be scratched by a knife. - **Streak Test**: The streak of agate would typically be white or colorless. - **Consulting a Geologist or Using Spectroscopy**: For a definitive identification, especially if this rock might be of value or scientific interest. Remember, rock identification can be complex due to the natural variability and the presence of multiple minerals in one specimen. Visual characteristics alone can sometimes lead to misidentification.
36
Thought this Thunderegg would be hollow!
HumbleConservative
@RyanzRocks #noob #rockhound #rockformation #tumbling #agates #rocks #rockhounders #rockstructure #metamorphicrocks #metamorphic #igneousrocks #igneous #quartz #quartzite #geology #nodules #minerals #crystals #glowrocks #idahorockhunting #idahogems #rockcutting #thundereggs #chalcedony #opal #lavarock #rigidtools #ryobitools #riverrocks #translucentrocks #translucent #rockgarden #flow #vevortools #jasper #granite #caves #marble #carnelian #gneiss #limestone #calcite #gold #silver #botryoidal
41
44
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
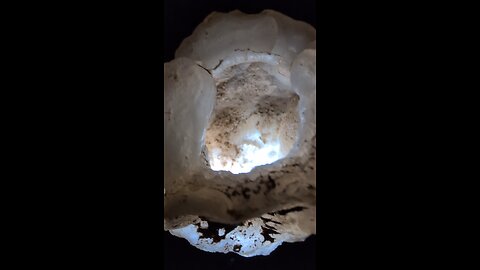
Opal Inside!
1 year ago
26
Loading comments...
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Steven Crowder
2 hours ago🔴The Murder of A Ukrainian Refugee is A Tipping Point in American History
54,907 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Right Side Broadcasting Network
3 hours agoLIVE: President Donald J. Trump Delivers Remarks to the WH Religious Liberty Commission - 9/8/25
3,422 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Rubin Report
56 minutes agoMedia Caught Trying to Ignore Ugly New Details of Charlotte Train Stabbing Caught on Tape
1,498 watching -
 1:01:19
1:01:19
VINCE
2 hours agoNightmare In North Carolina | Episode 120 - 09/08/25
128K66 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Nikko Ortiz
1 hour agoLive - Reaction Time, News, Politics, and More!
165 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
13 hours agoLFA TV ALL DAY STREAM - MONDAY 9/8/25
4,700 watching -
 1:49:43
1:49:43
Dear America
3 hours agoRepeat Offender Kills a Woman on a train!! WHY IS MSM SILENT!? + Are We Attacking Cartels??
69.2K67 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Viss
59 minutes ago🔴LIVE - How To Win! - PUBG 101
95 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Caleb Hammer
12 hours agoMost Batsh*t Insane Woman I’ve Ever Met | Financial Audit
126 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Badlands Media
9 hours agoBadlands Daily: Sept. 8, 2025
4,218 watching