Premium Only Content
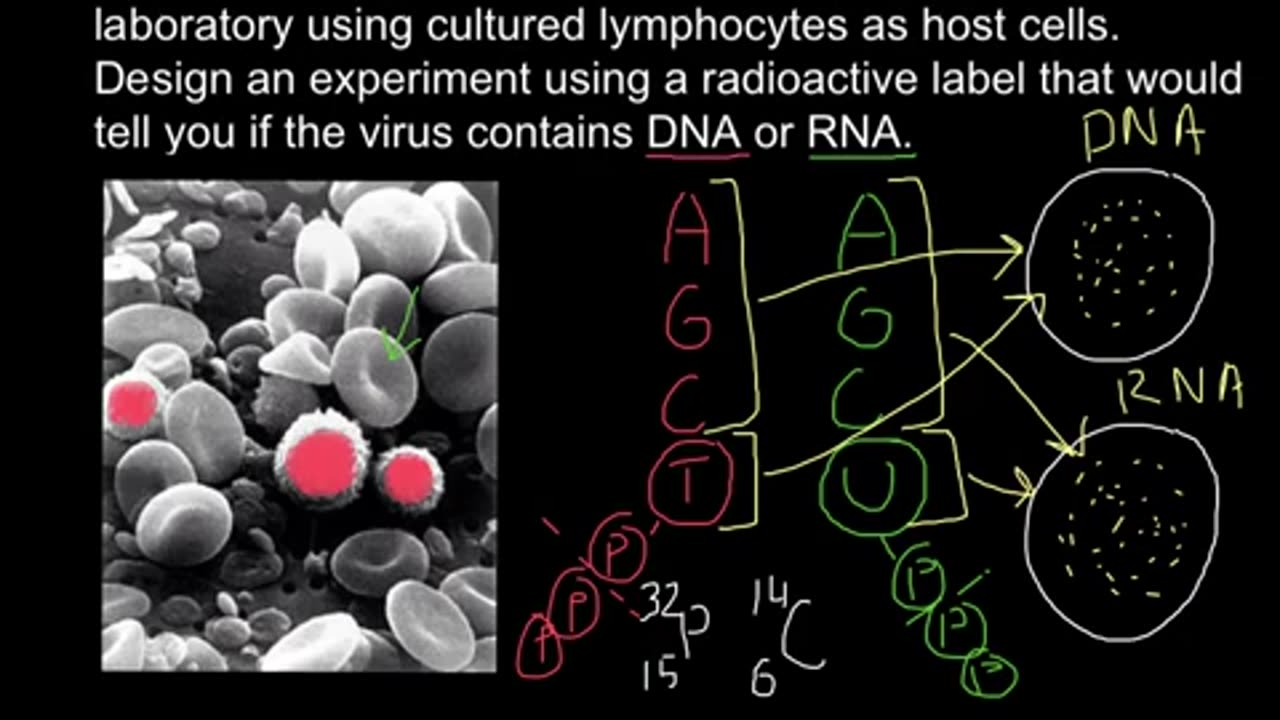
How to determine if virus DNA or RNA based using radioactive labeling?
Nucleic acids may be modified with tags that enable detection or purification. The resulting nucleic acid probes can be used to identify or recover other interacting molecules. Common labels used to generate nucleic acid probes include radioactive phosphates, biotin, fluorophores and enzymes. In addition, the bioconjugation methods used for nucleic acid probe generation may be adapted for attaching nucleic acids to other molecules or surfaces to facilitate targeted delivery or immobilization, respectively.
Overview
Enzymatic methods for nucleic acid probe labeling
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)
T4 RNA ligase
T4 polynucleotide kinase (PNK)
DNA polymerase
RNA polymerase
Chemical methods for nucleic acid probe labeling
Periodate oxidation of RNA
EDC activation of 5′ phosphate
Chemical random-labeling
Protein Methods Library Home
Overview of Protein-Nucleic Acid Interactions
Overview
Nucleic acid probes can be labeled with tags or other modifications during synthesis. However, purchasing custom oligonucleotide probes (especially RNA) can be quite expensive depending on the modification and if costly purification services are required. Additionally, the minimum order quantity for modified oligonucleotides is typically much higher than unmodified versions and may be excessive compared to the amount required for the intended application. Because of this, many researchers may choose in-house methods or labeling kits for probe generation.
Numerous reagents are available for quick and efficient bench top oligonucleotide labeling, and are most useful for making small amounts of probe or when many different probes with the same label are required (i.e., for mutational analysis). For small-scale probe generation needs, enzymatic methods are an economical method for labeling probes. In contrast, chemical methods are amenable to larger scale reactions. There are enzymatic and chemical methods for creating probes labeled at either the 5′ or 3′ ends of the oligonucleotide as well as randomly incorporated throughout the sequence. The choice of which method needed is determined in part by the degree of labeling required and if the modification will cause steric hindrance that prevents the desired interactions. Typically, nucleic acids hybridization reactions (i.e., Northern blotting) benefit from the high specific activity gained through random incorporation of label into a probe. However, assays requiring protein interactions (i.e., gel shift and pull-down assays) require end-labeling to allow protein binding.
-
 21:57
21:57
GritsGG
16 hours agoBO7 Warzone Patch Notes! My Thoughts! (Most Wins in 13,000+)
1.69K -
 2:28:08
2:28:08
PandaSub2000
9 hours agoMyst (Part 1) | MIDNIGHT ADVENTURE CLUB (Edited Replay)
1.47K -
 1:12:43
1:12:43
TruthStream with Joe and Scott
5 days agoJason Van Blerk from Human Garage: Reset your life with Fascial Maneuvers,28 day reset, Healing, Spiritual Journey, Censorship, AI: Live 12/3 #520
6.32K4 -
 24:21
24:21
The Pascal Show
1 day ago $8.25 earned'CHALLENGE ACCEPTED!' TPUSA Breaks Silence On Candace Owens Charlie Kirk Allegations! She Responds!
28.6K19 -
 17:41
17:41
MetatronGaming
2 days agoI should NOT Have taken the elevator...
1.62K1 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Lofi Girl
3 years agolofi hip hop radio 📚 - beats to relax/study to
659 watching -
 1:20:23
1:20:23
Man in America
13 hours agoHow Epstein Blackmail & FBI Cover-Ups Are Fracturing MAGA w/ Ivan Raiklin
192K32 -
 2:13:49
2:13:49
Inverted World Live
8 hours agoSolar Storms Ground 1000 Planes | Ep. 151
110K10 -
 2:54:08
2:54:08
TimcastIRL
8 hours agoJ6 Pipe Bomb Suspect ARRESTED, Worked With BLM, Aided Illegal Immigrants | Timcast IRL
256K127 -
 3:59:02
3:59:02
Alex Zedra
7 hours agoLIVE! Bo7 Warzone
39.1K1