Premium Only Content
Mpox (Monkeypox) | Transmission, Pathophysiology, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Mpox (Monkeypox) | Transmission, Pathophysiology, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
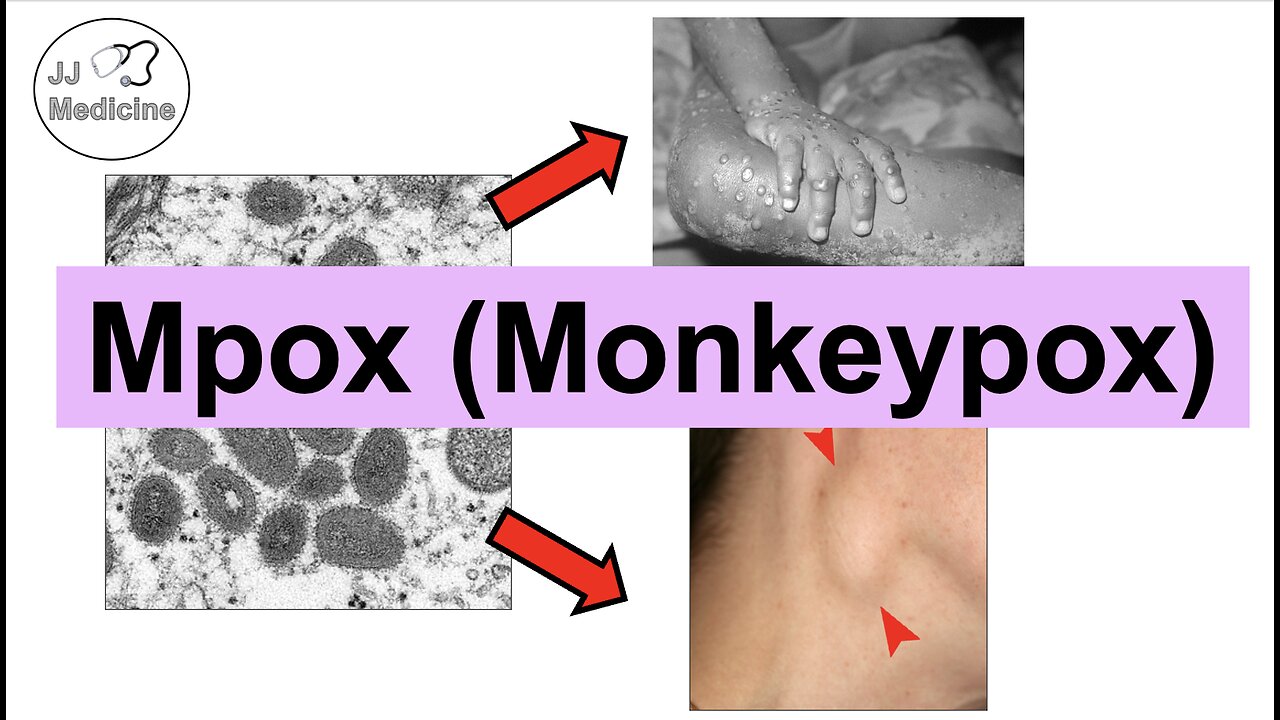
Mpox (previously known as Monkeypox) is a viral infection caused by the Mpox virus, which is an orthopox virus in the same genus as Smallpox. Mpox was a relatively unknown infection until early 2022, at which time human-to-human transmission began to occur more frequently, leading to an exponential increase in number of cases. Transmission began to take place between humans, either via direct, indirect or vertical transmission. Once the Mpox virus is exposed to an individual, it uses particular membrane proteins on it’s surface to bind to and infiltrate into host cells. One of the first places it enters is the lymph nodes, and then will enter into the blood leading to the initial viremia stage of infection. The virus will eventually lead to symptoms after an approximately 4-21 day incubation period. Symptoms involve a flu-like prodromal stage of infection, with subsequent pox-like rash that occurs with vesicles and pustules. Eventually, skin lesions will resolve over the course of weeks in most patients; however, in patients with immunocompromise they can have issues with complications of Mpox, including eye issues, septicemia and encephalitis.
I hope you find this lesson helpful. If you do, please like and subscribe for more lessons like this one!
JJ
REFERENCES:
StatPearls - "MPox (Monkeypox)" 2023
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK574519/
**MEDICAL LEGAL DISCLAIMER**: JJ Medicine does not provide medical advice, and the information available on this channel does not offer a diagnosis or advice regarding treatment. Information presented in these lessons is for educational purposes ONLY, and information presented here is not to be used as an alternative to a healthcare professional’s diagnosis and treatment of any person/animal. Only a physician or other licensed healthcare professional are able to determine the requirement for medical assistance to be given to a patient. Please seek the advice of your physician or other licensed healthcare provider if you have any questions regarding a medical condition.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
The Charlie Kirk Show
38 minutes agoLet's Talk Legal Immigration + Tulsi on ObamaGate + Hillary's Bribes | Gabbard, Rep. Steube, Basham
4,491 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Donut Operator
1 hour agoI'M BACK/ CRIME/ GAMEBOY CAMERA CHAD
401 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Flyover Conservatives
11 hours agoTracing the Nephilim from Noah to the US Dollar - Dr. Laura Sanger | FOC Show
2,052 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Mel K Show
1 hour agoMORNINGS WITH MEL K - Hunters Become the Hunted: The Truth Will Set Us Free 7-24-25
888 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Grant Stinchfield
57 minutes agoThe Dark Side of Organ Donation & Hillary’s Hidden Seditious Sedation
172 watching -
 1:03:59
1:03:59
The Rubin Report
1 hour agoPress Stunned by Tulsi Gabbard’s Scathing Remarks During Her Shock Announcement
21.6K19 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Shannon Joy Show
2 hours ago🔥🔥While Headlines Scream About Epstein, Obama, Hillary Scandals - Trump’s Digital Leviathan Is Unleashed With The BBB, AI.GOV & Three New Executive Orders🔥🔥
201 watching -
 1:00:02
1:00:02
VINCE
3 hours agoAre The Walls Closing In On Obama? (w/ Victor Davis Hanson) | Episode 92 - 07/24/25
154K124 -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
15 hours agoLFA TV ALL DAY STREAM - THURSDAY 7/24/25
4,827 watching -
 DVR
DVR
Bannons War Room
5 months agoWarRoom Live
29.6M7.32K