Premium Only Content

HMB and Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Muscular Function
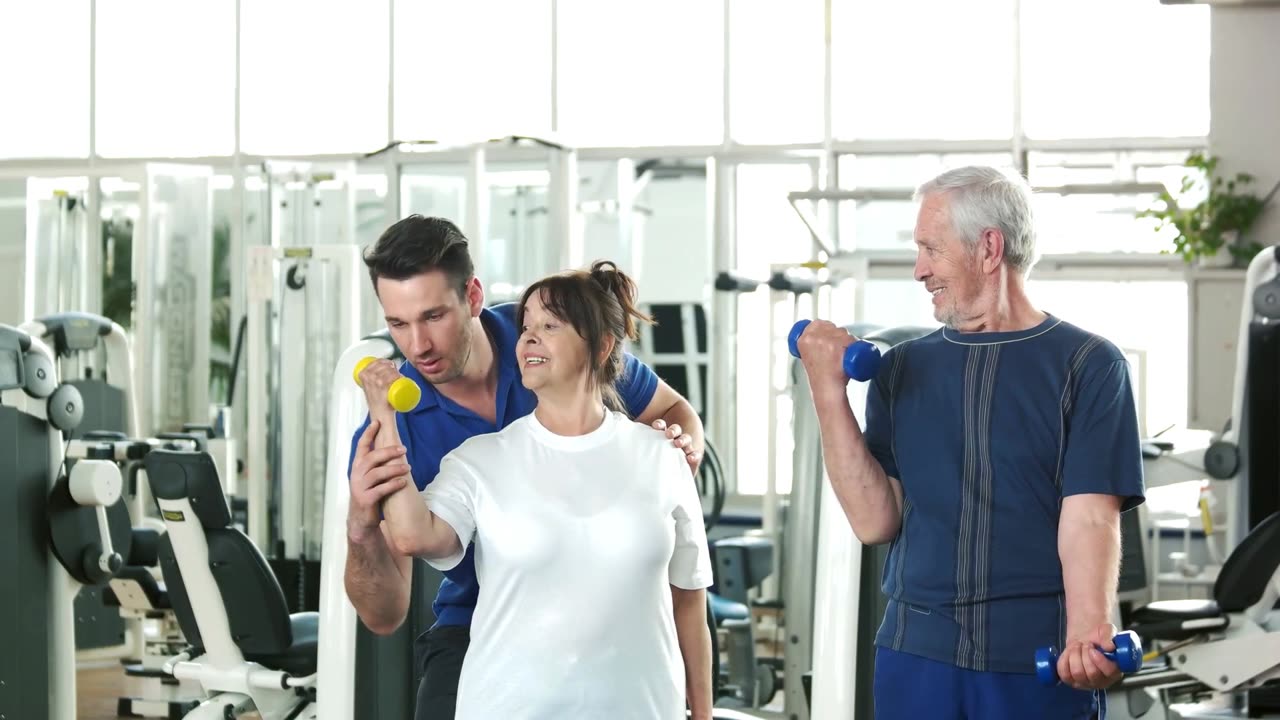
I had started to use this supplement algorithm along with Maca for two years before my Cancer diagnosis. I am part of a Marine Rescue team where swim tests were quantitatively measured on a 6mo cycle. Along with physical agility tests. Since I started the regimen I was able to significantly see improved stamina, endurance and strength is my agility tests. For example being able to perform 300 pushups and 700 leg lifts per-day, over the time of training and supplements in one year. No doubt that these supplements had a direct correlation with the significant improvements I was experiencing. Even though I lost 45 pounds during my 9 months of Chemotherapy, I feel my ability to recover and get back to normal weight and muscle fitness were helped by the residual effects of this supplementation. Most importantly, is to research for yourself the available data on HMB, if you are considering the regimen. But please feel free to reach out on the Comments for any questions.
...
NatureBell HMB Supplements - Triple Strength HMB (Beta-Hydroxy Beta-Methylbutyrate) Capsules – Lean Muscle Mass & Recovery Support
...
Swanson Vitamin D3 - Vitamin Supplement Promoting Bone Health & Immune System Support - Natural Support for Calcium Distribution & Absorption
...
Article:
Long-term Effects of HMB (β-Hydroxy β-methylbutyric acid) and Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Muscular Function in Older Adults, A Prospective
Study.
Lean body mass (LBM) decreases at a rate of about 8% per decade after the age of 40 and accelerates to about 15% per decade after the age of 70. Decreasing LBM typically reflects a loss of muscle mass and is accompanied by reduced muscular strength and physical function. These losses have serious, wide-ranging implications for older adults. LBM and strength are inversely associated with loss of independence, fall risk, morbidity, and mortality. Thus, attenuating the age-related losses of muscle mass and function has great potential to improve health and quality of life. Several strategies have been proposed to slow age-related muscle loss, but to date, only resistance training, alone or in combination with nutritional interventions, has been consistently shown to be effective. However, nutritional interventions alone are generally only effective in cases of restricted food intake or overt malnutrition Insufficient protein intake, less than the recommended daily allowance R.D.A of 0.8 g per kg per day, is associated with reduced LBM and physical performance. Although protein insufficiency affects relatively few older adults, about 10%, increasing protein intake above the RDA increases muscle mass but does not improve muscle strength or global physical functioning. Similarly, pharmacological interventions, primarily using anabolic agents, have been less convincing with some studies showing beneficial and others showing adverse outcomes. Additionally, the use of anabolic hormones has been associated with significant morbidities, limiting the utility of these agents in the general population.
This study is the first long-term prospective investigation directly comparing calcium HMB and vitamin D3supplementation in exercising and non-exercising healthy older adults. Combined supplementation with HMB and vitamin D3 for 12 months was safe and increased circulating levels of 25OH-D to within the sufficient range, 30–100 nano grams per milliliter, previously shown to support a beneficial effect of HMB on lower body strength. The main finding of this study was that co-supplementation with calcium HMB and vitamin D3to healthy older adults improved the composite functional strength index and that this benefit was independent of a moderate resistance exercise program similar to that commonly practiced by older populations on their own.
In summary, this study demonstrated the potential of long-term co-supplementation with calcium HMB and vitamin D3 to enhance physical functionality and muscle strength in older adults, even in individuals not engaged in a resistance exercise training program. While adequate nutrition and participation in resistance exercise training remain valuable for the maintenance of muscle strength, quality, and function, the combined supplementation with calcium HMB and vitamin D3 may provide a unique protective effect for the substantial population of older adults who are unable or unwilling to exercise. Although the results of the present study are difficult to generalize to a sarcopenic/presarcopenic or frail population, we hypothesize that the benefits of HMB+D could be even more valuable in these individuals given their lower baseline functional status. Furthermore, HMB has been previously shown to have substantial benefits on muscle health in various populations with established sarcopenia, chronic disease patients, and individuals with temporary or ongoing limitations to physical activity.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Rebel News
1 hour agoCanada to recognize Palestine, US trade deadline looms, Charter-protected bike lanes | Rebel Roundup
374 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
TheAlecLaceShow
1 hour agoGuest: Roger Stone | Kash Patel Finds Hoax Docs in Secret FBI Room | The Alec Lace Show
168 watching -
 1:43:37
1:43:37
The Rubin Report
3 hours agoWhy I’m Taking a Break
38.2K27 -
 1:36:22
1:36:22
The Mel K Show
2 hours agoMORNINGS WITH MEL K -Truth Tsunami Alert: Panic in DC! 7-31-25
17.7K3 -
 2:08:44
2:08:44
Benny Johnson
4 hours ago🚨CIA Whistleblower SPEAKS! Tulsi Gabbard Joins LIVE to Expose New Obama-Gate BOMBSHELL: 'Burn Bags'
80.1K90 -
 DVR
DVR
The Shannon Joy Show
3 hours ago🔥🔥Trump To Pardon Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs? Live Exclusive with Child Sex Trafficking Expert & Advocate Dani Pinter! 🔥🔥
26.4K3 -
 1:01:05
1:01:05
Trumpet Daily
2 hours ago $1.45 earnedTrumpet Daily LIVE - July 31, 2025
22.3K -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
15 hours agoLFA TV ALL DAY STREAM - THURSDAY 7/31/25
2,775 watching -
 43:09
43:09
VINCE
4 hours agoSPECIAL: "Obamagate" DEEP-DIVE with Gen. Mike Flynn, Mike Benz and Paul Sperry
124K96 -
 1:23:19
1:23:19
The Big Mig™
5 hours agoFBI Burn Bags, Hidden SCIF’s & Truth About Mar-A-Lago Raid
20.9K15