Premium Only Content
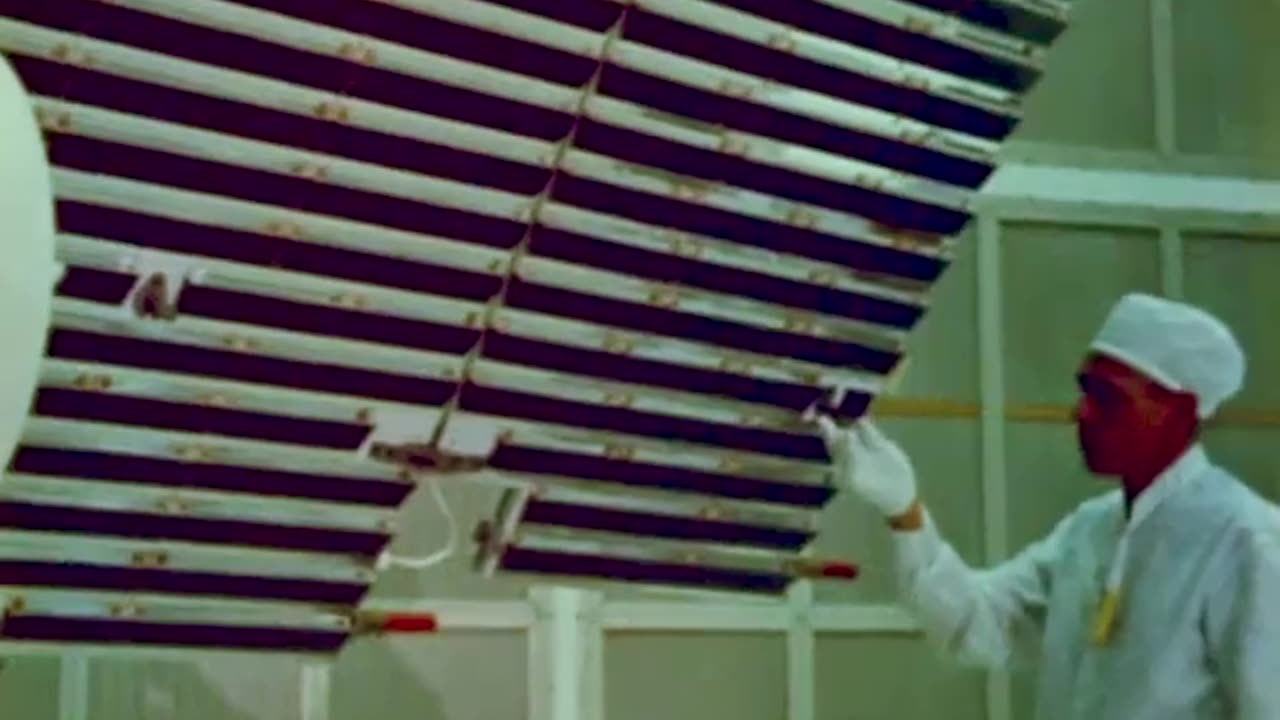
50th Anniversary of NASA's OAO 2 Mission
Hello!
Welcome To Asto Vista Rumble Channel...
On Dec. 7, 1968, an Atlas-Centaur rocket carrying NASA’s heaviest and most ambitious uncrewed satellite to date blasted into the sky from Launch Complex 36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
Formally known as Orbiting Astronomical Observatory (OAO) 2 and nicknamed Stargazer, it would become NASA’s first successful cosmic explorer and the direct ancestor of Hubble, Chandra, Swift, Kepler, FUSE, GALEX and many other astronomy satellites.
OAO 2 provided the first orbital stellar observations in ultraviolet light, shorter than wavelengths in the visible range spanning 3,800 (violet) to 7,500 (red) angstroms. Much of UV light is screened out by the atmosphere and unavailable to ground-based telescopes. Stargazer's experiments made nearly 23,000 measurements, showed that young, hot stars were hotter than theoretical models of the time indicated, confirmed that comets are surrounded by vast clouds of hydrogen and discovered a curious feature of the interstellar medium that would take scientists decades to understand.
One of the key problems scientists had to solve was how to direct a telescope to any point on the celestial sphere and hold it there for a half hour or so in order for instruments to record the data from faint sources. This makes OAO 2 the ancestor of all space telescopes that can point to a given spot on the sky and track it for an extended period.
Prior to OAO 2, ultraviolet observations of stars were acquired by suborbital sounding rockets which collect data for only five minutes each flight as they arc above much of the atmosphere. By 1968, it was estimated that sounding rockets had captured a total of three hours of stellar UV measurements in some 40 flights. OAO 2 could collect more data than this in a single day.
OAO 2 carried two experiments. Project Celescope (from "celestial telescope") was led by Fred Whipple, director of the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Wisconsin Experiment Package was led by Arthur Code, a professor of astronomy at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. The experiments were mounted back-to-back within the 4,436-pound (2,012 kilogram) spacecraft and looked out opposite ends, taking turns viewing the universe.
#OAO2Mission
#NASAAnniversary
#SpaceHistory
#Astronomy
#SpaceScience
#SpaceExploration
#50YearsOAO2
#Astrophysics
#SpaceTechnology
#CelestialObservation
#AstronomicalResearch
#NASAHistory
#SpaceMilestones
#OAO2MissionAnniversary
#SpaceAchievements
#CosmicDiscovery
#SpaceInnovation
#AstroTech
#SpaceLegacy
#50thAnniversaryNASA
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Spartan
1 hour agoFirst time playing Black Myth Wukong
56 watching -

iCkEdMeL
1 hour ago $5.19 earnedFrom Music to Murder? D4VD’s Tesla Horror Story
15.5K6 -
 LIVE
LIVE
TwinGatz
1 hour ago🔴LIVE - Strike Out Saturday | CS2 | Counter-Strike 2 | New Subs = Case Opening
27 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Simulation and Exploration
4 hours agoHow well does this play on a controller? Future console players check this out!
44 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
MrR4ger
6 hours agoTHE THREE SPLOOGES (THE RECKONING) - ACTIVE MATTER w/ AKAGUMO & TONYGAMING
38 watching -
 1:25:04
1:25:04
Michael Franzese
4 hours agoJames Comey, Epstein Files Block, Tylenol | Michael Franzese Live
185K54 -
 1:24:44
1:24:44
Winston Marshall
9 hours agoThe Hamas Hoax That Fooled The West...
19.2K19 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Grant Cardone
4 hours agoReal Estate Live Training
165 watching -
 22:53
22:53
Jasmin Laine
1 day agoParliament ERUPTS After "WORST Decision EVER!"—Carney Left SPEECHLESS by SHOCKING Report
20K31 -
 11:50
11:50
Mrgunsngear
1 day ago $5.89 earnedSteiner MPS Enclosed Red Dot: Better Than The ACRO P2? 🔴
20.7K14