Premium Only Content
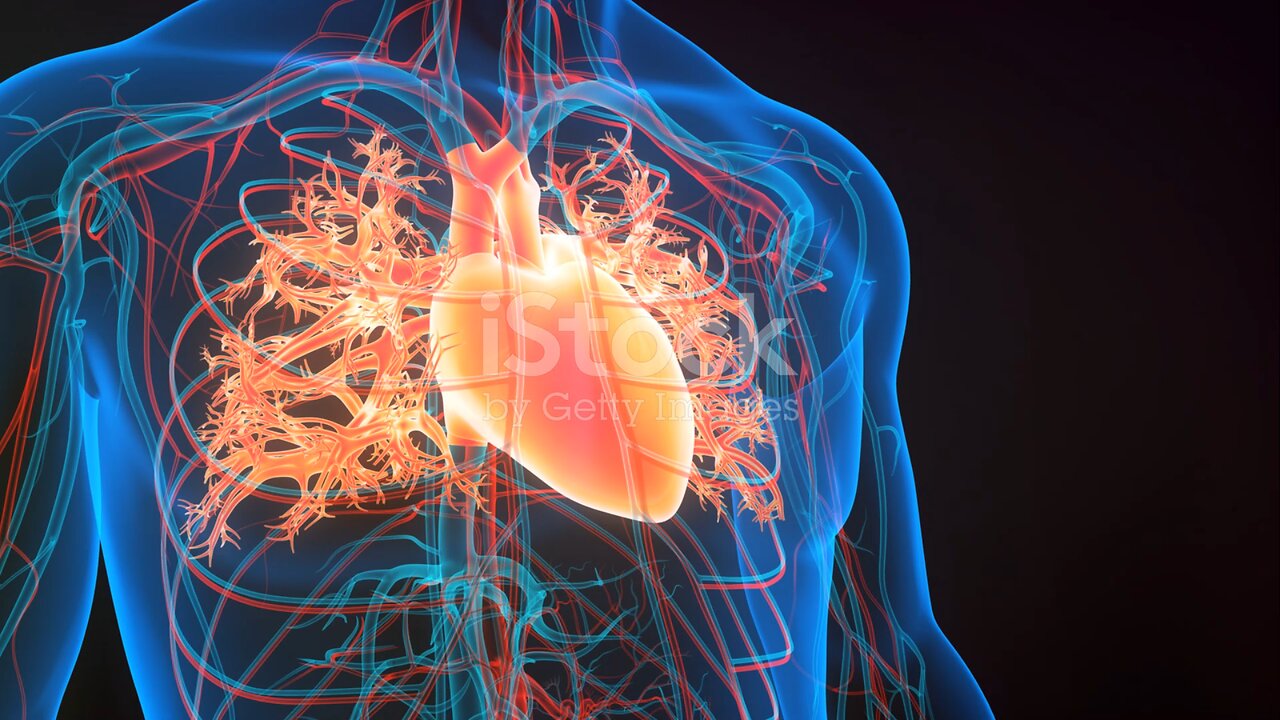
Humen heart anatomy (Basic)
Certainly! Here's a more detailed description of the anatomy of the human heart:
1. **Pericardium:** The heart is surrounded by a double-walled sac called the pericardium. The outer layer is called the fibrous pericardium, which is tough and protective. The inner layer is the serous pericardium, consisting of two layers: the parietal layer (lining the fibrous pericardium) and the visceral layer (also known as the epicardium, which covers the heart muscle).
2. **Heart Wall:** The heart wall is composed of three layers:
- **Epicardium:** The outermost layer, as mentioned, is the visceral layer of the serous pericardium.
- **Myocardium:** The middle layer, consisting of cardiac muscle tissue responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
- **Endocardium:** The innermost layer, a thin layer of endothelial tissue that lines the chambers of the heart and covers the heart valves.
3. **Chambers:** The heart has four chambers:
- **Right Atrium:** Receives deoxygenated blood returning from the body via the superior and inferior vena cava.
- **Right Ventricle:** Receives blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation through the pulmonary artery.
- **Left Atrium:** Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
- **Left Ventricle:** Receives blood from the left atrium and pumps it to the body through the aorta.
4. **Valves:** Valves regulate blood flow between the chambers of the heart and prevent backflow:
- **Tricuspid Valve:** Located between the right atrium and right ventricle.
- **Pulmonary Valve:** Positioned between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery.
- **Mitral Valve (Bicuspid Valve):** Found between the left atrium and left ventricle.
- **Aortic Valve:** Located between the left ventricle and the aorta.
5. **Blood Vessels:**
- **Coronary Arteries:** Supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle.
- **Coronary Veins:** Drain deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle.
- **Pulmonary Arteries and Veins:** Transport blood between the heart and lungs for oxygenation.
6. **Electrical Conduction System:** The heart has its own electrical conduction system, including the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, bundle of His, and Purkinje fibers. This system controls the heart rate and rhythm.
Understanding the detailed anatomy of the heart is crucial for comprehending its function and the pathophysiology of various cardiac conditions.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
13 hours agoLIVE & BREAKING NEWS! | WEDNESDAY 10/8/25
4,222 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Mel K Show
1 hour agoMORNINGS WITH MEL K -Lobbyists and Greed have Replaced the Will of We the People 10-8-25
510 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Shannon Joy Show
36 minutes agoGold Surge Persists Signaling Recession, More Inflation & Potential War - Live W/ Peter Schiff!
162 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Grant Stinchfield
1 hour agoThe People Have Spoken: Trump Rising, Democrats Reeling
65 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Trumpet Daily
49 minutes agoTrumpet Daily LIVE | Oct 8, 2025
154 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Outspoken with Dr. Naomi Wolf
45 minutes ago"October 7: Israel, with all its Flaws, isn't Making me a Zionist. Anti-Semitism Is."
38 watching -
 1:56:24
1:56:24
Benny Johnson
2 hours ago🚨James Comey in Court LIVE Right Now on Criminal Charges | Portland Anarchy Against ICE EXPOSED
22.9K52 -
 1:01:01
1:01:01
VINCE
4 hours agoThe Next CA Governor May Be MUCH Worse Than Newsom | Episode 142 - 10/08/25
156K94 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Side Scrollers Podcast
2 hours agoTwitch CEO Testifies in Congress + Hasan Piker Accused of DOG Abuse + More | Side Scrollers
611 watching -
 1:10:41
1:10:41
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
2 hours agoBuildings That Shouldn’t Be Here
4.88K6
