Premium Only Content
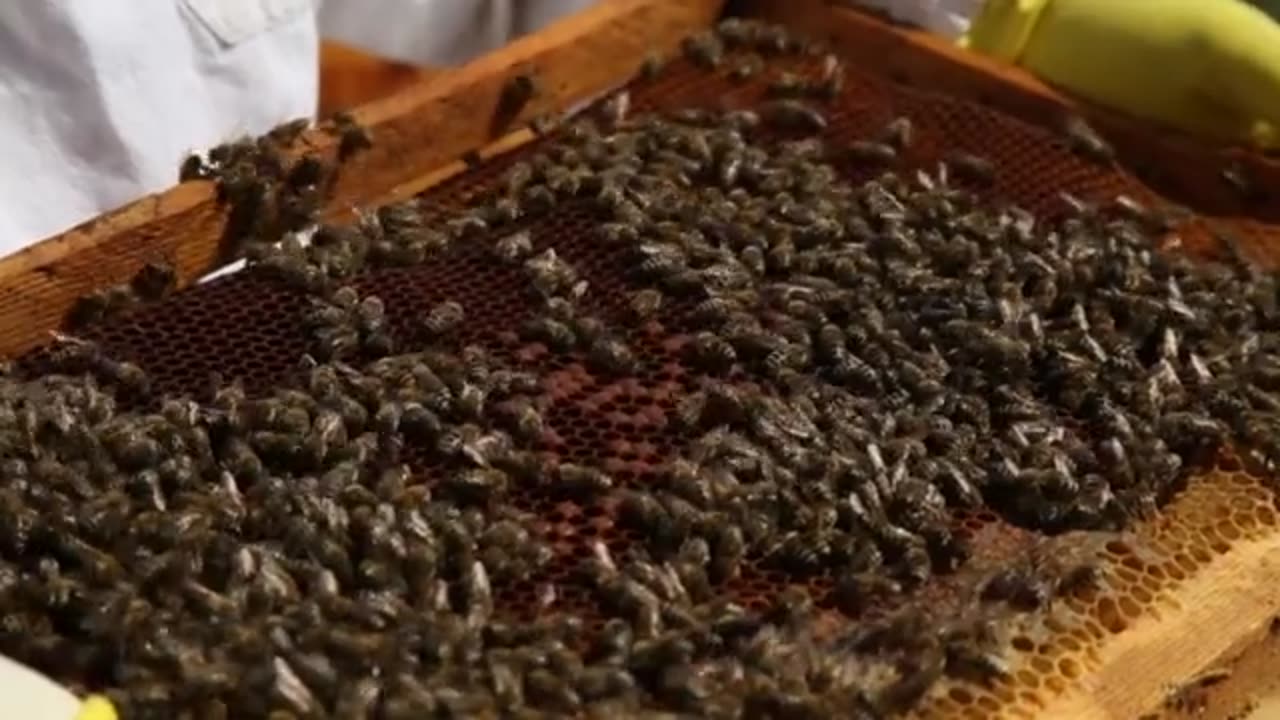

Honey beekeeper bees
Beekeeping (or apiculture) is the maintenance of bee colonies, commonly in man-made beehives. Honey bees in the genus Apis are the most commonly kept species but other honey producing bees such as Melipona stingless bees are also kept. Beekeepers (or apiarists) keep bees to collect honey and other products of the hive: beeswax, propolis, bee pollen, and royal jelly. Other sources of beekeeping income include pollination of crops, raising queens, and production of package bees for sale. Bee hives are kept in an apiary or "bee yard".
The keeping of bees by humans, primarily for honey production, began around 10,000 years ago. A sample of 5,500-year-old honey was unearthed from the grave of a noblewoman during archaeological excavations in 2003 near the town of Borjomi, Georgia. Ceramic jars found in the grave contained several types of honey, including linden and flower honey. Domestication of bees can be seen in Egyptian art from around 4,500 years ago; there is also evidence of beekeeping in ancient China, Greece, and Maya.
In the modern era, beekeeping is often used for crop pollination and the collection of byproducts, such as wax and propolis. The largest beekeeping operations are agricultural businesses but many small beekeeping operations are run as a hobby. As beekeeping technology has advanced, beekeeping has become more accessible, and urban beekeeping was described as a growing trend as of 2016. Some studies have found city-kept bees are healthier than those in rural settings because there are fewer pesticides and greater biodiversity in cities.
Early history
At least 10,000 years ago, humans began to attempt to maintain colonies of wild bees in artificial hives made from hollow logs, wooden boxes, pottery vessels, and woven straw baskets known as skeps. Depictions of humans collecting honey from wild bees date to 10,000 years ago. Beekeeping in pottery vessels began about 9,000 years ago in North Africa. Traces of beeswax have been found in potsherds throughout the Middle East beginning about 7,000 BCE.[6] Domestication of bees is shown in Egyptian art from around 4,500 years ago.[7] Simple hives and smoke were used, and honey was stored in jars, some of which were found in the tombs of pharaohs such as Tutankhamun. In the 18th century, European understanding of the colonies and biology of bees allowed the construction of the movable comb hive so honey could be harvested without destroying the entire colony.
Honeybees were kept in Egypt from antiquity. On the walls of the sun temple of Nyuserre Ini from the Fifth Dynasty before 2,422 BCE, workers are depicted blowing smoke into hives as they remove honeycombs. Inscriptions detailing the production of honey are found on the tomb of Pabasa from the Twenty-sixth Dynasty c. 650 BCE, in which cylindrical hives are depicted along with people pouring honey into jars
-
 LIVE
LIVE
Timcast
47 minutes agoElon Musk Declares WAR Over Trump's BIG BEAUTIFUL BILL, GOP Didnt Even READ IT
22,406 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Steven Crowder
3 hours ago🔴 Donald Trump vs. Elon Musk: The Massive Battle Over the Big Beautiful Bill
27,244 watching -
 48:55
48:55
The Rubin Report
1 hour agoListen to ‘The View’ Crowd Gasp as Host Starts Lying to Her Co-Hosts Faces
7.02K10 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Akademiks
1 hour agoDay 3/30. Diddy Trial Day 16. Jane Doe to take the Stand. Possibly this is 50 Cent Baby moms?
2,129 watching -
 UPCOMING
UPCOMING
Simply Bitcoin
1 hour agoJoe Rogan Admits Bitcoin Is The NEXT GLOBAL Reserve Currency? | EP 1258
-
 LIVE
LIVE
The Mel K Show
1 hour agoMORNINGS WITH MEL K - Who Will Investigate the Investigators? The Audacity of the Globalist Agenda. It’s Time to Draw the Line! 6-4-25
538 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Dana Show with Dana Loesch
22 minutes agoWATCH: The Dana Show LIVE on Rumble! | WEDNESDAY JUNE 4 2025
254 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
NEWSMAX
3 hours agoThe Rob Carson Show LIVE (06/04/2025) | Call 1-800-922-6680 | NEWSMAX Podcasts
338 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
BitLab Academy
2 hours agoBitcoin Pump Signal (Crypto Supercycle Signal!) Altcoin Market Struggles
24 watching -

Discover Crypto
2 hours agoBitcoin Supply CRISIS: The ULTIMATE Confirmation for MASSIVE Breakout!
69