Premium Only Content
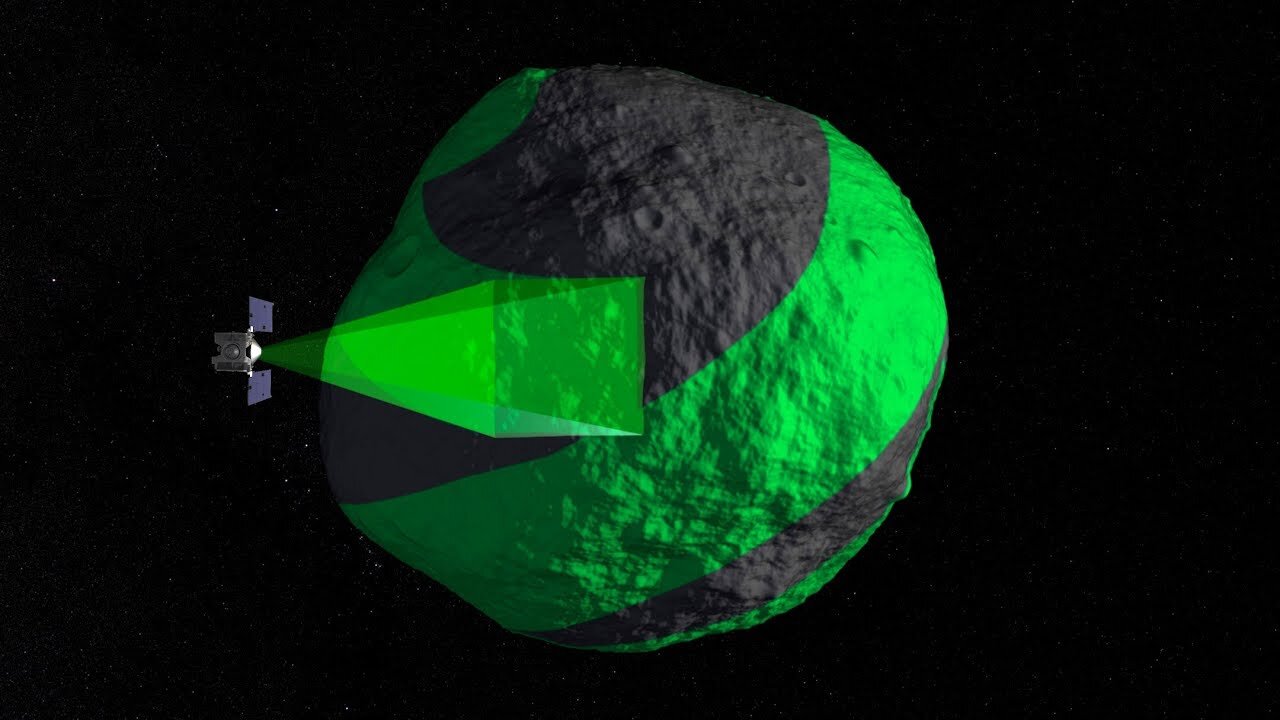
The OSIRIS-REx mission reached Bennu //dxbduba1
NASA's OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security, Regolith Explorer) mission was a spacecraft mission launched in 2016 with the goal of studying and collecting samples from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu. The mission had several key objectives:
Sample Collection: OSIRIS-REx was designed to approach Bennu, study it in detail, and collect a sample of regolith (loose surface material) from the asteroid. This material would provide valuable insights into the composition and history of Bennu and its potential as a resource for future space exploration.
Return to Earth: After collecting the sample, OSIRIS-REx was intended to return to Earth with the precious cargo. The sample capsule was designed to re-enter Earth's atmosphere and land in a remote area in Utah, where scientists could retrieve and study the samples.
Asteroid Characterization: The spacecraft was equipped with a suite of instruments to study Bennu's size, shape, rotation, composition, and spectral properties. This information was expected to help scientists understand the formation and evolution of asteroids and their role in the early solar system.
Impact Hazard Assessment: Bennu is classified as a potentially hazardous asteroid, which means it had a small chance of impacting Earth in the late 22nd century. OSIRIS-REx's data collection aimed to improve our understanding of the Yarkovsky effect (a non-gravitational force that affects asteroid orbits) and refine Bennu's orbit predictions to assess its long-term impact risk.
Spacecraft Operations and Technology: The mission provided valuable experience in spacecraft operations, autonomous navigation, and sample collection, which could inform future asteroid missions and deep space exploration efforts.
The OSIRIS-REx mission reached Bennu in December 2018, spent several years surveying the asteroid, and successfully collected a sample from its surface in October 2020. The sample return capsule containing the asteroid material safely landed on Earth in September 2023, completing the primary mission objectives.
The samples collected from Bennu are expected to provide valuable insights into the early solar system's composition, the origins of water and life-building compounds on Earth, and the behavior of near-Earth asteroids. Scientists will analyze these samples in laboratories around the world to answer fundamental questions about our solar system's history and the potential for asteroid resources.
-
 1:56:31
1:56:31
The Pascal Show
16 hours ago $1.17 earnedGHISLAINE FLIPS?! DOJ Receives SECRET LIST of 100 Epstein Associates!”
5.39K1 -
 10:17
10:17
Dr Disrespect
11 days agoIt's Time To Get Serious
178K27 -
 2:15:09
2:15:09
Badlands Media
23 hours agoDevolution Power Hour Ep. 375: Obama’s Orders, Ukraine’s Collapse & the Inversion of Justice
292K101 -
 2:32:03
2:32:03
BlackDiamondGunsandGear
12 hours agoAFTER HOURS ARMORY w/ DLD & John from GOA & FLR
26.6K3 -
 1:05:28
1:05:28
Man in America
13 hours agoTREASON? Obama, Hillary, and Soros in the New World Order Agenda EXPOSED w/ Mel K
86.8K77 -
 2:22:46
2:22:46
The Connect: With Johnny Mitchell
14 hours ago $6.07 earnedOne Man's Mission To Stop Human Trafficking: How A Billionaire Mercenary Saved Hundreds Of Children
23.8K18 -
 2:35:13
2:35:13
Tundra Tactical
9 hours ago $12.41 earned🔫 California Ammo Win, Sig Sauer P320 Controversy, Meme Review & Would You Rather! 🎉🔥
40.3K6 -
 16:24
16:24
Forrest Galante
7 hours ago6 Deadliest Man Eaters to Ever Exist
28.1K5 -
 10:14
10:14
MattMorseTV
11 hours ago $15.76 earnedThe EU is in HOT WATER.
96K59 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Rabble Wrangler
1 day agoPUBG with The Best in the West!
634 watching