Premium Only Content
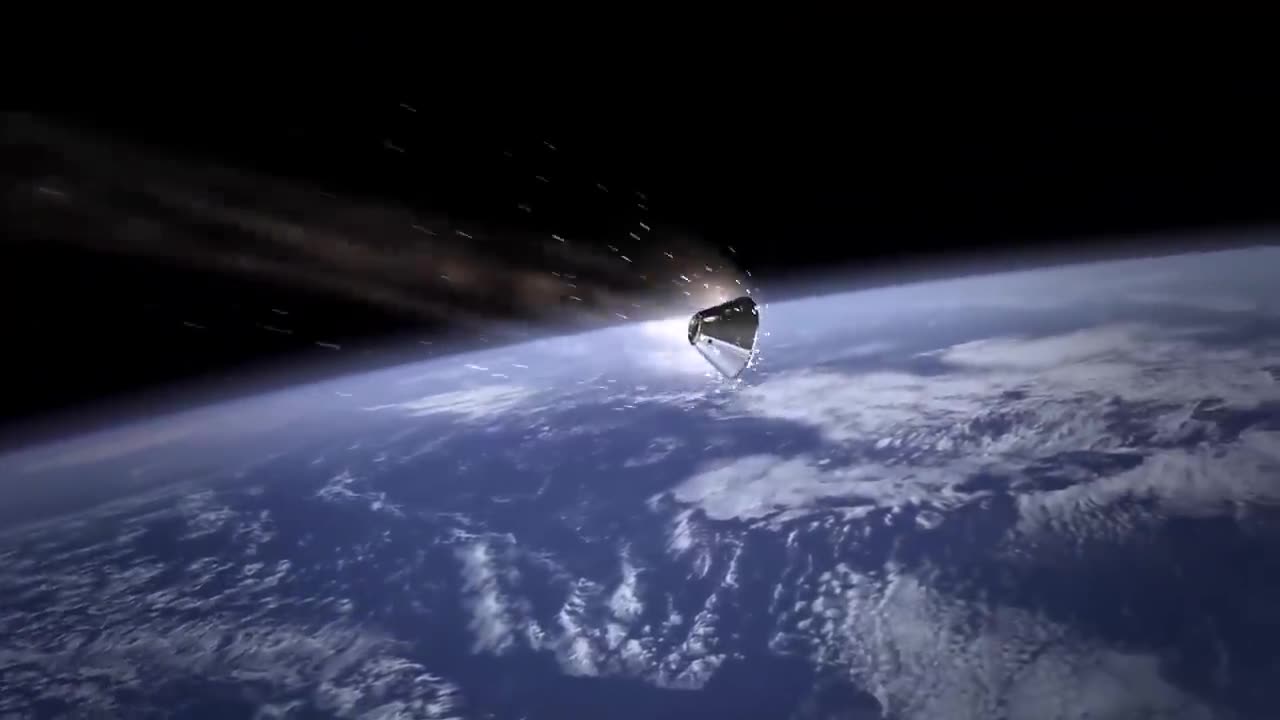

How Do Spacecraft Slow Down? We Asked a NASA Technologist//dxbduba1
Spacecraft slow down in space by using various methods and propulsion systems, depending on their mission objectives and the specific phase of their journey. I'll outline some of the common methods:
Rocket Engine Firing: This is the most straightforward way to slow down a spacecraft. By firing its rocket engines in the opposite direction of its velocity, a spacecraft can decrease its speed. The principle is based on Newton's third law of motion: for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. The expelled exhaust gas from the rocket engines provides the thrust needed to slow down the spacecraft.
Aerobraking: For missions that involve entering a planet's or moon's atmosphere, aerobraking is used. The spacecraft dips into the atmosphere at a specific angle, using the planet's atmosphere to slow it down. The friction between the spacecraft and the atmosphere generates drag, reducing the spacecraft's speed.
Gravity Assists: In some cases, spacecraft can use the gravity of a celestial body to change their trajectory and speed. By performing a gravity assist maneuver, a spacecraft can gain or lose velocity, depending on the direction of the gravity assist. This technique is often used to save fuel or increase a spacecraft's speed.
Ion Propulsion: Ion propulsion systems are more efficient than traditional chemical rocket engines and are often used for deep-space missions. These engines continuously expel ions at high speeds, creating thrust and gradually slowing down the spacecraft.
Tethers: Electrodynamic tethers can be deployed in space to interact with a planet's magnetic field. By generating an electrical current through the tether, the spacecraft can create magnetic forces that act as a brake, slowing it down.
Orbital Mechanics: Spacecraft can use precise orbital mechanics to alter their speed and trajectory. For example, by changing their orbit's shape or inclination, they can adjust their speed relative to a target body.
Ballooning: In the case of missions involving atmospheres with extremely low densities, such as Venus, some spacecraft have used inflatable balloons or aerodynamic devices to slow down and navigate.
The specific method chosen depends on the spacecraft's design, its mission profile, and the celestial body it is targeting. NASA and other space agencies carefully plan and execute these maneuvers to achieve their mission objectives while conserving fuel and energy whenever possible.
-
 8:07:01
8:07:01
Dr Disrespect
12 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - ARC RAIDERS - SOLO RAIDING THE GALAXY
119K12 -
 1:32:00
1:32:00
Kim Iversen
7 hours agoThe World’s Most “Moral” Army — Kills 40 Kids During "Ceasefire" | Socialism's Coming: The Zohran Mamdani Agenda
96.8K172 -
 1:04:50
1:04:50
TheCrucible
6 hours agoThe Extravaganza! EP: 63 with Guest Co-Host: Rob Noerr (10/30/25)
82.8K8 -
 LIVE
LIVE
GritsGG
6 hours agoQuads! #1 Most Wins 3880+!
103 watching -
 2:51:31
2:51:31
Spartan
6 hours agoFirst playthrough of First Berserker Khazan
24.5K1 -
 5:48:29
5:48:29
The Rabble Wrangler
20 hours agoBattlefield 6 - RedSec with The Best in the West
26.4K1 -
 37:53
37:53
Donald Trump Jr.
7 hours agoAmerican Dominance vs Dems' Delusion | TRIGGERED Ep.287
44.6K65 -
 1:14:57
1:14:57
The White House
9 hours agoPresident Trump and the First Lady Participate in Halloween at The White House
39.7K28 -
 1:05:02
1:05:02
Candace Show Podcast
6 hours agoBREAKING NEWS! The Egyptian Military Was In Provo On 9/10. | Candace Ep 255
76.8K228 -
 2:12:54
2:12:54
Redacted News
7 hours agoBREAKING! KASH PATEL'S FBI SHUTS DOWN CHARLIE KIRK ASSASSINATION FOREIGN INTEL PROBE BY JOE KENT
135K120