Premium Only Content
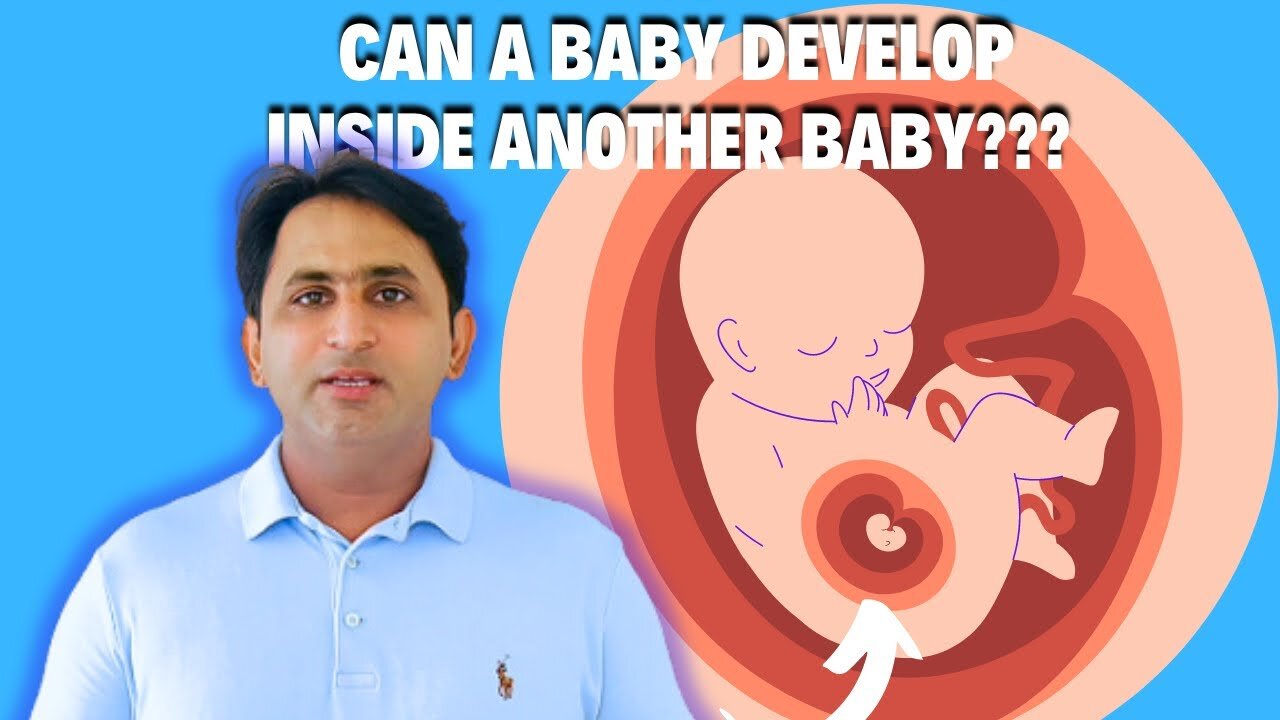
Can a Baby Develop Inside Another Baby? Possible? کیا ایک بچہ دوسرے بچے کے اندر نشوونما پا سکتا ہے؟
Can a Baby Develop Inside Another Baby? Possible? کیا ایک بچہ دوسرے بچے کے اندر نشوونما پا سکتا ہے؟
#fetusinfetu #parasitictwins #babyinsideababy
Fetus in Fetu: Can a Baby Develop Inside Another Baby? Parasitic Twins
Fetus in fetu (FIF) is a rare congenital anomaly in which a malformed fetus is enclosed within the body of its twin. It is a parasitic twin, meaning that it survives by drawing nutrients from the host twin. The parasitic twin is usually much smaller than the host twin and lacks some organs. It is thought to be caused by an early defect in the development of the twins, such as unequal division of the fertilized egg.
FIF is a very rare condition, with an estimated incidence of 1 in 500,000 births. It is most often diagnosed in infants or young children, but it can also be found in adults. The symptoms of FIF vary depending on the size and location of the parasitic twin. Some common symptoms include:
Abdominal mass
Pain
Nausea and vomiting
Constipation
Urinary problems
Fever
The diagnosis of FIF is usually made with ultrasound or MRI. Treatment is surgical removal of the parasitic twin. This is usually a safe and successful procedure.
Here are some additional facts about fetus in fetu:
The parasitic twin is usually anencephalic, meaning that it does not have a brain.
The parasitic twin may have some other organs, such as a heart, lungs, or limbs.
The parasitic twin may be attached to the host twin by a stalk of tissue.
FIF is not a hereditary condition.
There is no way to prevent FIF.
The most common location of FIF is the retroperitoneum, which is the space behind the abdominal organs. Other possible locations include the chest, pelvis, neck, and head. The parasitic twin can be any size, but it is usually much smaller than the host twin.
The symptoms of FIF can be vague and nonspecific, so it can be difficult to diagnose. The most common symptoms are abdominal mass, pain, nausea and vomiting, constipation, urinary problems, and fever. If a child or adult presents with these symptoms, the doctor may order an ultrasound or MRI to look for a parasitic twin.
Treatment for FIF is surgical removal of the parasitic twin. This is usually a safe and successful procedure. The prognosis for the host twin is usually good, but it can depend on the size and location of the parasitic twin.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about fetus in fetu:
The condition is more common in males than females.
The average age of diagnosis is 10 years old, but it can be diagnosed at any age.
There have been reports of FIF surviving for many years, but it is usually not compatible with life.
-
 LIVE
LIVE
TimcastIRL
1 hour agoU.S. Enters Israel Iran War In Defense Of Israel, Deaths CONFIRMED After Iran Strikes | Timcast IRL
23,115 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Barry Cunningham
3 hours agoHERE'S THE NEWS AND SCHEDULE FOR AN AMERICA FIRST WEEKEND!
6,518 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Nerdrotic
6 hours ago $9.42 earnedThe World is Burning, Let's TACO BOUT Hollywood! | Friday Night Tights 358
5,473 watching -

Turning Point USA
3 hours agoWELCOME HOME! YWLS 2025 is LIVE! Hear from Alex Clark, Erika & Charlie Kirk, and more!!
29.4K2 -
 LIVE
LIVE
SpartakusLIVE
2 hours ago#1 Specialist EASTER EGG Champion brings YOU Friday Night HYPE
306 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
TheItalianCEO
41 minutes agoALL the tools you need to pitch a brand( for free) + Channel review!
77 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
SynthTrax & DJ Cheezus Livestreams
1 day agoFriday Night Synthwave 80s 90s Electronica and more DJ MIX Livestream Last Action User Edition
64 watching -
 50:57
50:57
RiftTV/Slightly Offensive
3 hours agoGen Z Conservative UNVEILS Israel Truth, GOP Shift & Masculinity Woes! | Guest: Braeden Sorbo
11.2K6 -
 54:56
54:56
BonginoReport
9 hours agoResident Speaks Out Years After East Palestine Train Derailment - (Ep.69)
82K29 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Amish Zaku
6 hours agoRumble Spartan's June Event
112 watching