Premium Only Content
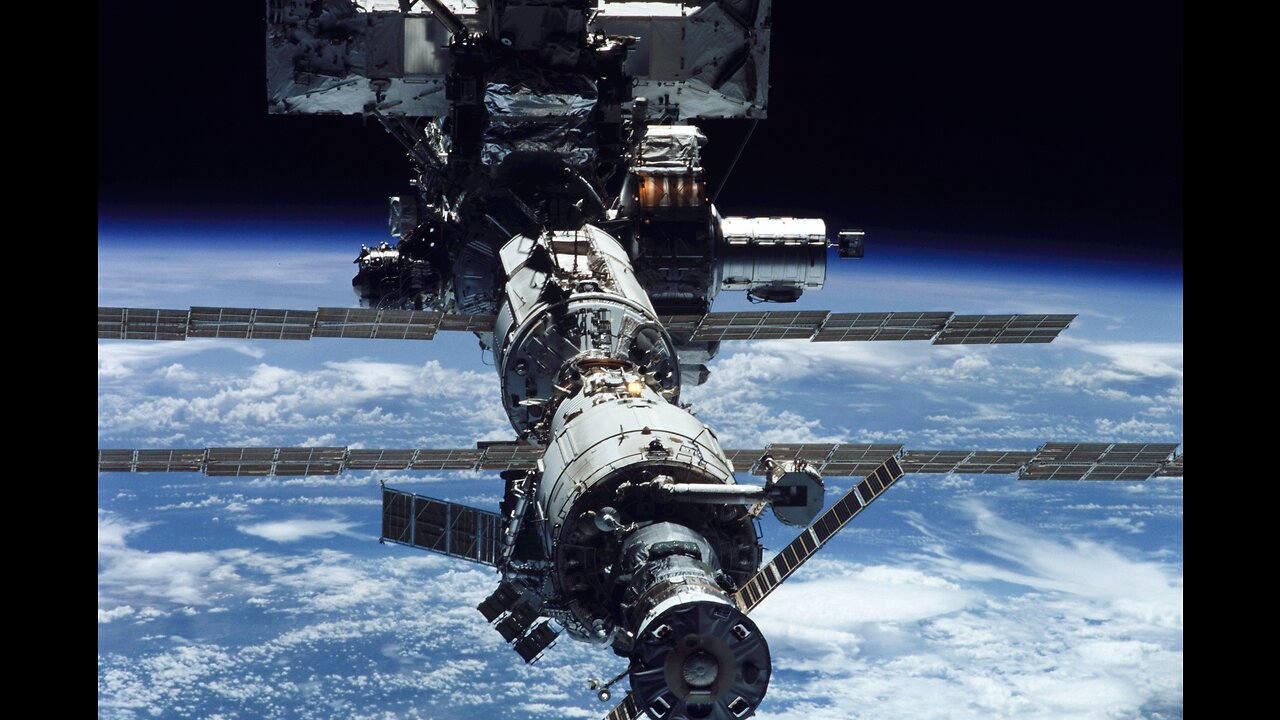

How at work international space station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a complex and collaborative project involving multiple space agencies from around the world. Here's a general overview of how it operates:
1. **Construction and Assembly**: The ISS was built and assembled in space over several years. Modules and components were launched into orbit and then assembled in space by astronauts using robotic arms and spacewalks. This construction phase began in the late 1990s and continued until the station reached its current configuration.
2. **Crewed Missions**: The ISS is continuously crewed by astronauts and cosmonauts from various space agencies, including NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (European Space Agency), JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and CSA (Canadian Space Agency). These astronauts live and work on the station for several months at a time.
3. **Research and Experiments**: The primary purpose of the ISS is scientific research. Astronauts conduct experiments in various fields, including biology, physics, astronomy, and Earth sciences. This research helps us better understand how the human body responds to long-duration spaceflight and provides insights into fundamental scientific questions.
4. **Maintenance and Upkeep**: Astronauts on the ISS are responsible for maintaining the station's systems and equipment. This includes performing routine maintenance tasks, fixing any issues that arise, and occasionally upgrading hardware.
5. **Resupply Missions**: The ISS requires a regular supply of food, water, equipment, and scientific instruments. Cargo spacecraft from different space agencies, such as SpaceX's Dragon, Northrop Grumman's Cygnus, and Russian Progress spacecraft, are launched to resupply the station.
6. **Communication**: The ISS maintains constant communication with mission control centers on Earth. Astronauts and ground control teams communicate through a network of tracking and data relay satellites.
7. **International Collaboration**: The ISS is a symbol of international cooperation in space exploration. Participating space agencies share responsibilities, costs, and resources. They work together to ensure the station's safe and efficient operation.
8. **Orbit and Reboost**: The ISS orbits Earth at an altitude of approximately 420 kilometers (260 miles). To counteract the effects of atmospheric drag, periodic reboost maneuvers are performed to raise its orbit.
9. **Return to Earth**: Astronauts typically spend several months on the ISS before returning to Earth via Soyuz spacecraft or, in recent years, commercial crew vehicles like SpaceX's Crew Dragon.
The ISS serves as a unique platform for scientific research, international cooperation, and testing technologies for future deep-space missions. It has been continuously inhabited since November 2000 and is expected to remain in operation until at least 2030, with discussions ongoing about its future beyond that date.
-
 11:23
11:23
Nikko Ortiz
1 day agoArmy Tik Tok Fails Go Hard
52.5K7 -
 2:27:44
2:27:44
Side Scrollers Podcast
18 hours agoSilksong is “TRANS CODED” + YouTube GASLIGHTS Creators + Asmongold Stops Streaming | Side Scrollers
8.31K17 -
 16:08
16:08
GritsGG
9 hours agoRank 1 Warzone Player VS Stream Snipers & a Cheater!
7.54K1 -
 1:39:16
1:39:16
The HotSeat
13 hours ago👉 STOP Blaming Each Other — Look at the Media!
24.7K25 -
 22:34
22:34
The Pascal Show
9 hours ago $0.98 earnedFEDERAL CHARGES?! Iryna Zarutska's Attacker Gets Hit With Federal Charges After Fatal Train Attack
7.57K9 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Lofi Girl
2 years agoSynthwave Radio 🌌 - beats to chill/game to
198 watching -
 13:05
13:05
Mike Rowe
4 days agoIs College DEAD? Inside America’s #1 Trade School | Sheree Utash From #448 | The Way I Heard It
78.6K27 -
 3:01:13
3:01:13
FreshandFit
6 hours agoAyesha Curry Never Wanted Steph Curry
65.8K11 -
 23:28
23:28
DeVory Darkins
10 hours ago $11.49 earnedTrump official ANNIHILATES Democrats in heated debate as CNN gets caught sympathizing with criminals
26K72 -
 1:02:26
1:02:26
The Nick DiPaolo Show Channel
13 hours agoPOC Murders Another White Woman | The Nick Di Paolo Show #1790
61K76