Premium Only Content
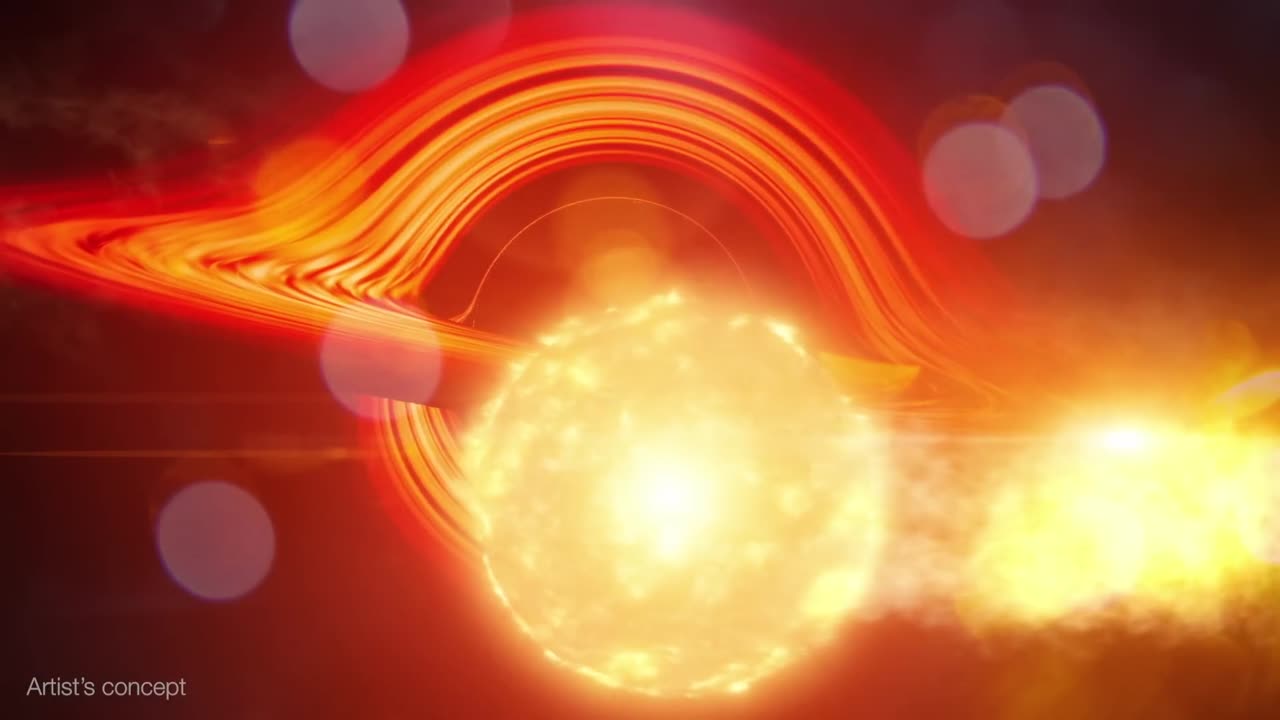

Black Hole Snack Attack
Using NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, which launched in 2004, scientists have discovered a black hole in a distant galaxy repeatedly nibbling on a Sun-like star. The object heralds a new era of Swift science made possible by a novel method for analyzing data from the satellite’s X-ray Telescope (XRT).
When a star strays too close to a monster black hole, gravitational forces create intense tides that break the star apart into a stream of gas. The leading edge swings around the black hole, and the trailing edge escapes the system. These destructive episodes are called tidal disruption events. Astronomers see them as flares of multiwavelength light created when the debris collides with a disk of material already orbiting the black hole.
Recently, astronomers have been investigating variations on this phenomena, which they call partial or repeating tidal disruptions.
During these events, every time an orbiting star passes close to a black hole, the star bulges outward and sheds material, but survives. The process repeats until the star looses too much gas and finally breaks apart. The characteristics of the individual star and black hole system determine what kind of emission scientists observe, creating a wide array of behaviors to categorize.
On June 22, 2022, XRT captured Swift J0230 for the first time. It lit up in a galaxy around 500 million light-years away in the northern constellation Triangulum. Swift’s XRT has observed nine additional outbursts from the same location roughly every few weeks.
Scientists propose that Swift J0230 is a repeating tidal disruption of a Sun-like star orbiting a black hole with over 200,000 times the Sun’s mass. They estimate the star loses around three Earth masses of material on each pass. This system provides a bridge between other types of suspected repeating disruptions and allowed scientists to model how interactions between different star types and black hole sizes affect what we observe.
Swift J0230’s discovery was possible thanks to a new, automated search of XRT observations called the Swift X-ray Transient Detector.
After the instrument observes a portion of the sky, the data is transmitted to the ground, and the program compares it to previous XRT snapshots of the same spot. If that portion of the X-ray sky has changed, scientists get an alert. In the case of Swift J0230, astronomers were able to rapidly coordinate additional observations of the region.
Music credit: "Teapot Waltz" by Benjamin Parsons from Universal Production Music
Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
-
 1:32:24
1:32:24
Tucker Carlson
54 minutes agoTucker and MTG on the 5 Pillars of MAGA and the Snakes in Washington Trying to Tear Them Down
20 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Side Scrollers Podcast
3 days ago🔴FIRST EVER RUMBLE SUB-A-THON🔴DAY 3🔴PLAYING MIKE TYSON'S PUNCH OUT TILL I WIN!
1,314 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Barry Cunningham
2 hours agoMUST SEE: PRESIDENT TRUMP NATO PRESSER! AND NEW YORK CITY MAYORAL DEBATE!
977 watching -
 13:15
13:15
Cash Jordan
5 hours ago"INVASION" Mob STRIKES Chicago Jail… FRONTLINE Marines IGNORE Judge, SMASH Illegals
2.34K3 -
 LIVE
LIVE
SpartakusLIVE
1 hour ago#1 Solo Challenge CHAMPION entertains HERDS of NERDS
125 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Alex Zedra
40 minutes agoLIVE! New Game | DeathWatchers
54 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Nikko Ortiz
1 hour agoShotguns With A Magazine... |Rumble Live
66 watching -
 23:18
23:18
Lady Decade
6 hours agoThe Diversity Lie Gaming Refuses To Talk About
1.1K4 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Geeks + Gamers
1 hour agoGeeks+Gamers Play- MARIO KART WORLD
143 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Midnight In The Mountains™
4 hours agoGaming w/ Midnight | Studio is BACK and SO ARE WE | 3 AWAY FROM 1,500 WILL YOU GET ME THERE?!
39 watching