Premium Only Content
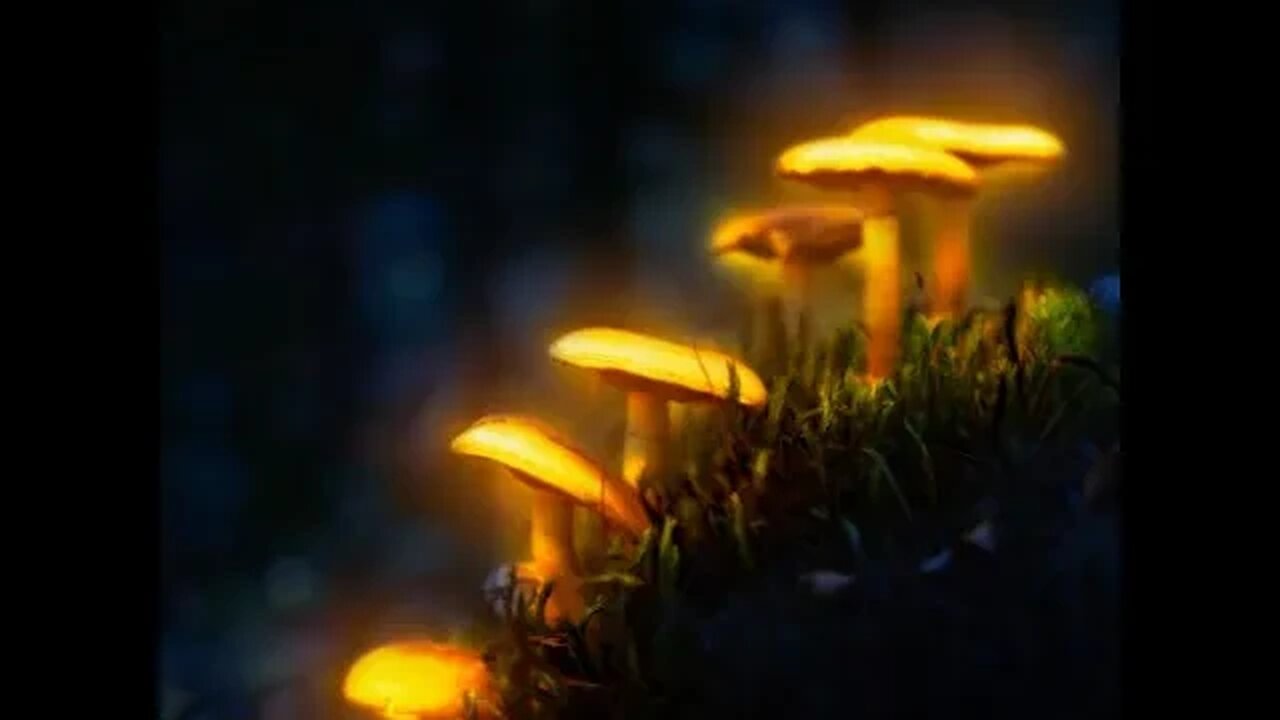

Baeocystin: Psilocybin’s Baby Cousin
https://www.mycophiliac.com/p/baeocystin-psilocybin-s-baby-cousin
Baeocystin: Psilocybin’s Baby Cousin
Introduction
Baeocystin is a zwitterionic alkaloid and an analog of psilocybin. It is a minor compound in most psilocybin mushrooms and psilocybin, norbaeocystin, aeruginascin, and psilocin. Baeocystin is an N-demethylated derivative of psilocybin and a phosphorylated derivative of 4-HO-NMT (4-hydroxy-N-methyltryptamine).
Discovery and Synthesis
Baeocystin was first isolated from the mushroom Psilocybe baeocystis and later from P. semilanceata Panaeolus renenosus, Panaeolus subbalteatus, and Copelandia chlorocystis. It was first synthesized by Troxler et al. in 1959.
Baeocystin: Psilocybin’s Baby Cousin
Baeocystin: Psilocybin’s Baby Cousin
Human Pharmacology
Little information exists about human pharmacology, but in the book Magic Mushrooms Around the World, author Jochen Gartz reports being aware of a study in which "10 mg of baeocystin were found to be about as psychoactive as a similar amount of psilocybin. Gartz also reported in a research paper that a self-administered assay of 4 mg of baeocystin caused "a gentle hallucinogenic experience”.
Psilocybe Baeocystis Magic Mushroom
The species name, Psilocybe Baeocystis, originates from the Greek words for "little" (baeo) and "bladder" (kystis). The reason behind this naming is not explicitly explained in the original article that named the species. However, it may be related to the mushroom's unique features, such as the shape of its inwardly-rolled cap or the appearance of microscopic cells called cheilocystidia, used by mycologists to identify different mushroom species.
Contrasting Studies
While Gartz describes experiencing a "gentle hallucinogenic experience" from baeocystin, this could not be replicated in a mouse model in a 2019 study that found no evidence that baeocystin produces any hallucinogenic effects. Researchers compared psilocybin which is a known hallucinogen to baeocystin by using the mouse head-twitch response.
Upon comparison, baeocystin was indistinguishable from saline solution, indicating "...baeocystin alone would likely not induce hallucinogenic effects in vivo". However, This contrasts with the human experiences mentioned above, although high-quality data is scarce.
Conclusion
Baeocystin, a minor compound in psilocybin mushrooms, has been the subject of limited research. While some reports suggest it has psychoactive properties similar to psilocybin, other studies indicate that it may not induce hallucinogenic effects. Further research is needed to understand the effects and potential uses of baeocystin fully.
-
 9:55
9:55
Mycophiliac
1 year ago $0.02 earnedMushroom Lofi ASMR Study Music
159 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Dr Disrespect
6 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - CRONOS: The New Dawn - FIRST IMPRESSIONS
5,658 watching -
The White House
4 hours agoPresident Trump Makes Announcements, Sep. 5, 2025
15.4K9 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Nerdrotic
2 hours ago $4.53 earnedUK Has Fallen, Hollywood DOOM, DC Dysfunction | Friday Night Tights 370
3,143 watching -

Roseanne Barr
4 hours agoOn the Wrong Side of the Algorithm | The Roseanne Barr Podcast #114
66.2K20 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Red Pill News
2 hours agoBombshell Biden Docs Invalidate Autopen Pardons on Red Pill News Live
2,659 watching -
 13:53
13:53
TundraTactical
2 hours agoFudd Finder : 11 Questions Second Amendment Questions (And Roasts) to Ask Your Friends
4.22K -
 9:36
9:36
Silver Dragons
2 hours agoGold Price NEW ALL TIME HIGH - $5,000 GOLD NEXT?
3.81K -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
11 hours agoLFA TV ALL DAY STREAM - FRIDAY 9/5/25
1,024 watching -
 13:43
13:43
The Kevin Trudeau Show Limitless
2 days agoClassified File 3 | Kevin Trudeau EXPOSES Secret Society Brainwave Training
86.8K16