Premium Only Content
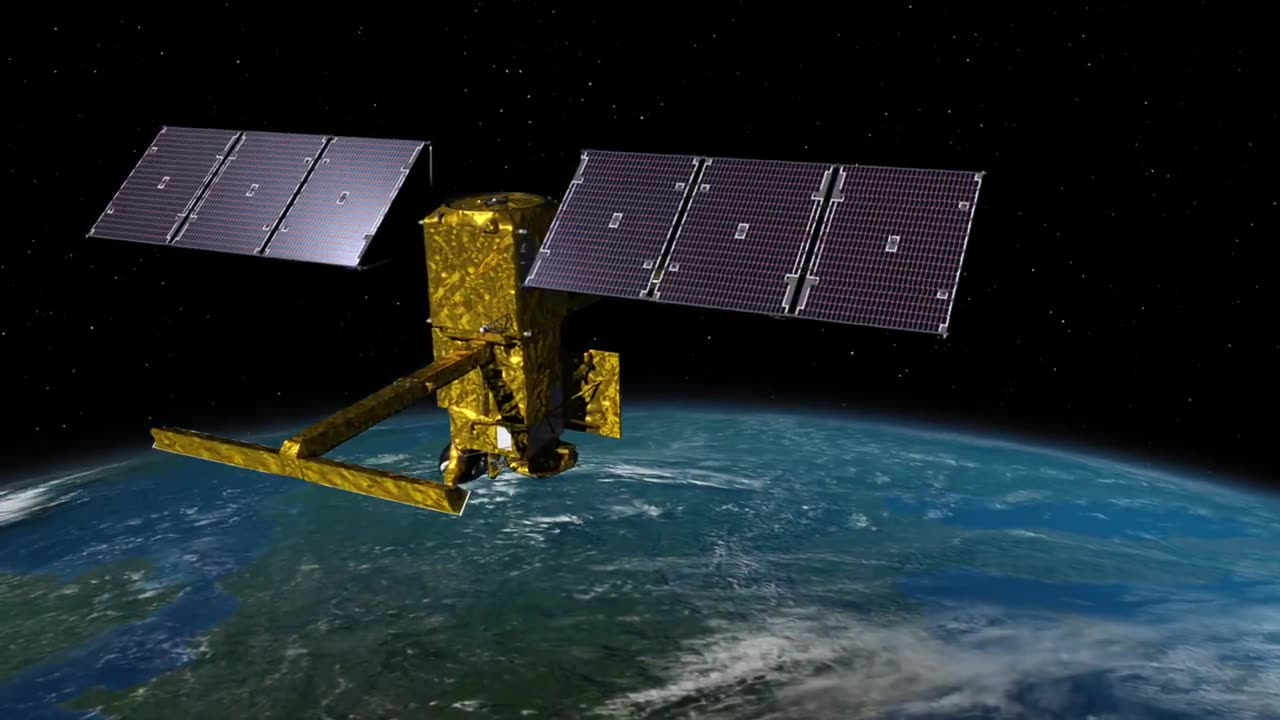

SWOT: Earth Science Satellite Will Help Communities Plan for a Better Future
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats associated with a specific project, idea, or situation. In this case, let's conduct a SWOT analysis for the scenario of using an Earth science satellite to help communities plan for a better future.
Strengths:
Data Accuracy: Earth science satellites provide high-resolution data, allowing for accurate and detailed observations of the Earth's surface, atmosphere, and oceans. This accuracy can support informed decision-making.
Global Coverage: Satellites can monitor vast areas of the Earth, providing a global perspective that helps identify trends, patterns, and changes that might be difficult to observe on a local scale.
Timely Information: The real-time or near-real-time data provided by satellites can help communities respond swiftly to natural disasters, weather events, and other emergencies.
Long-Term Monitoring: Satellites enable continuous monitoring, which is essential for tracking long-term environmental changes and trends that could impact communities over time.
Weaknesses:
Cost: Developing, launching, and maintaining Earth science satellites can be expensive, which could limit the accessibility of this technology for some communities, especially those with limited resources.
Technical Expertise: Interpreting and utilizing satellite data require specialized knowledge and technical skills, which may not be readily available in all communities.
Data Interpretation: While satellites provide a wealth of data, interpreting and making sense of it can be challenging, potentially leading to misinformation or misinterpretation if not done correctly.
Opportunities:
Disaster Preparedness: Earth science satellites can aid in disaster preparedness by providing early warnings and real-time data to help communities respond effectively to natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods.
Environmental Monitoring: Satellite data can support monitoring of environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change impacts, helping communities make informed decisions to mitigate negative effects.
Urban Planning: Satellite data can be used for urban development planning, infrastructure design, and management of resources like water and energy, contributing to more sustainable and resilient communities.
Scientific Research: Satellite data can drive scientific research and innovation, enabling deeper insights into Earth's processes, weather patterns, and ecological changes.
Threats:
Privacy Concerns: The detailed monitoring capabilities of Earth science satellites could raise concerns about privacy, as they may inadvertently capture sensitive information.
Data Security: Satellite data transmission and storage could be vulnerable to cyberattacks, potentially compromising the integrity of the information.
Dependency: Overreliance on satellite data could lead to complacency in traditional observation methods or local data collection, diminishing the ability of communities to understand and manage their environments directly.
Equity Issues: Unequal access to satellite technology and data interpretation resources could exacerbate existing inequalities between communities.
In summary, using an Earth science satellite to help communities plan for a better future offers numerous benefits in terms of accurate data, global coverage, and timely information. However, challenges such as cost, technical expertise, and potential threats like privacy concerns should also be carefully considered. Effective implementation would require a balance between leveraging the strengths and opportunities while addressing weaknesses and threats to ensure the technology benefits all communities and contributes to sustainable development.
-
 1:10:58
1:10:58
vivafrei
2 hours agoBanning the Burning of the Flag? Raja Jackson Assault & Some Insanely Stupid Takes! NYC Chems & MORE
4.57K7 -
 LIVE
LIVE
LFA TV
5 hours agoLFA TV ALL DAY STREAM - TUESDAY 8/26/25
5,624 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Big Mig™
2 hours agoViolence & Burning The U.S. Flag, Democrats New Battle Cry
5,186 watching -
 27:39
27:39
Crypto.com
1 hour ago2025 Live AMA with Kris Marszalek, Co-Founder & CEO of Crypto.com
5.35K -
 LIVE
LIVE
The State of Freedom
2 hours ago#327 Digging Deeper into the Carbon Capture Scam w/ Brad LeBlanc
30 watching -
 38:39
38:39
VINCE
3 hours agoThis Is How The Media Spins The News | Episode 111 - 08/26/25
42.9K41 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Badlands Media
8 hours agoBadlands Daily: August 26, 2025
4,022 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
GritsGG
2 hours agoWin Streaking! Coloring Hair at End of Stream! Most Wins 3435+ 🧠
165 watching -
 1:56:45
1:56:45
Dear America
3 hours agoNO MORE BURNING FLAGS!! 🇺🇸 Trump Signs Order Making It ILLEGAL!! + Trump Is SUING NEWSOM!
73.8K58 -
 LIVE
LIVE
JuicyJohns
3 hours ago $0.64 earned🟢#1 REBIRTH PLAYER 10.2+ KD🟢
104 watching