Premium Only Content
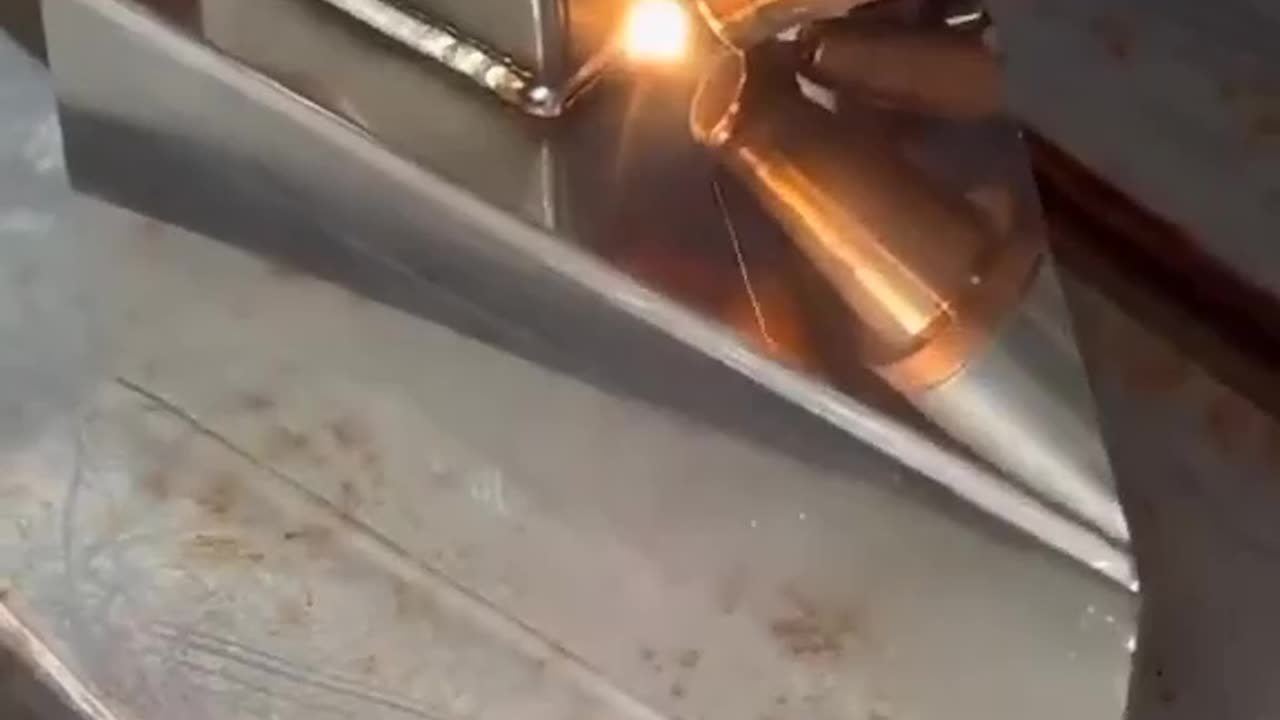

machinary
Machinery refers to a collection of mechanical devices, tools, and equipment designed to perform specific tasks or functions efficiently. These machines are essential components of various industries and play a crucial role in manufacturing, construction, transportation, agriculture, and many other sectors. Below, I'll provide a general description of machinery and some common examples:
Definition: Machinery encompasses a broad range of mechanical systems that use power sources to perform work. They often involve the conversion of energy from one form to another to achieve desired outcomes.
Types of Machinery: There are numerous types of machinery, each designed for specific purposes. Some common categories include:
a. Industrial Machinery: Used in manufacturing processes, such as lathes, milling machines, and conveyor systems.
b. Construction Machinery: Designed for construction tasks, including excavators, bulldozers, cranes, and cement mixers.
c. Agricultural Machinery: Used in farming operations, such as tractors, harvesters, plows, and irrigation systems.
d. Transportation Machinery: Including vehicles like cars, trucks, airplanes, ships, and trains.
e. Mining Machinery: Used for extraction and processing of minerals, like drills, crushers, and loaders.
f. Office Machinery: Includes copiers, printers, scanners, and other devices used in office environments.
g. Medical Machinery: Such as MRI machines, X-ray machines, and surgical equipment.
h. Robotics: Autonomous or semi-autonomous machines that can perform various tasks without human intervention.
Components of Machinery:
a. Power Source: Machines typically require a power source to function, which can be electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, or a combination of these.
b. Prime Mover: The component responsible for converting energy from the power source into mechanical motion. For example, an electric motor, internal combustion engine, or hydraulic motor.
c. Transmission System: Transfers the energy from the prime mover to various parts of the machine, often involving gears, belts, pulleys, or chains.
d. Working Components: These are the parts of the machine that carry out the intended task, such as cutting blades, conveyor belts, pistons, and drills.
e. Control System: For some machinery, control mechanisms are essential to regulate and monitor the operation of the machine. This can range from simple on/off switches to sophisticated computerized control systems.
f. Safety Features: Many machines include safety measures like emergency stops, protective guards, and sensors to prevent accidents and protect operators.
Importance: Machinery significantly improves productivity, efficiency, and accuracy in various industries, reducing manual labor and human errors. They allow us to undertake tasks that would be challenging or impossible to accomplish manually.
Maintenance and Safety: Regular maintenance and adherence to safety guidelines are crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of machinery while minimizing the risk of accidents.
Remember that machinery can vary significantly in complexity, size, and function, depending on the specific industry and application. The continuous advancement of technology leads to the development of more sophisticated and specialized machinery to meet the demands of modern industries.
-
 6:04:40
6:04:40
Akademiks
6 hours agoRoc Nation & Meg Thee Stallion did a 7 HOUR Deposition with me. Drake Secret Kid Finally Revealed.
27.7K1 -
 24:19
24:19
Stephen Gardner
2 hours ago🚨BREAKING: FBI Raid of John Bolton’s House Reveals THIS!
29.7K62 -
 8:31
8:31
MattMorseTV
4 hours ago $0.82 earnedTexas just did the IMPOSSIBLE.
27.6K56 -
 24:39
24:39
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
1 day agoInterdimensional Beings at Borobudur
38K18 -
 12:42
12:42
Scammer Payback
23 hours agoCalling Scammers who were Raided
9.46K10 -
 23:31
23:31
IsaacButterfield
15 hours ago $0.05 earnedThe Woke Mob Is Really CANCELLING Matt Rife For THIS…
16K14 -
 1:23
1:23
WildCreatures
8 days ago $0.97 earnedThis mother armadillo eating her palm nuts is truly adorable
14.4K16 -
 8:59
8:59
The Art of Improvement
10 hours ago $0.02 earnedHow to Build the Most Powerful Mindset for Success
13.1K2 -
 18:12:15
18:12:15
GritsGG
1 day ago36 Hour Stream! Most Wins 3420+ 🧠
237K11 -
 1:26:16
1:26:16
Michael Franzese
20 hours agoMenendez Brothers Denied Parole – Newsom Holds Their Fate
117K92