Premium Only Content
Putin's war on Ukraine, explained
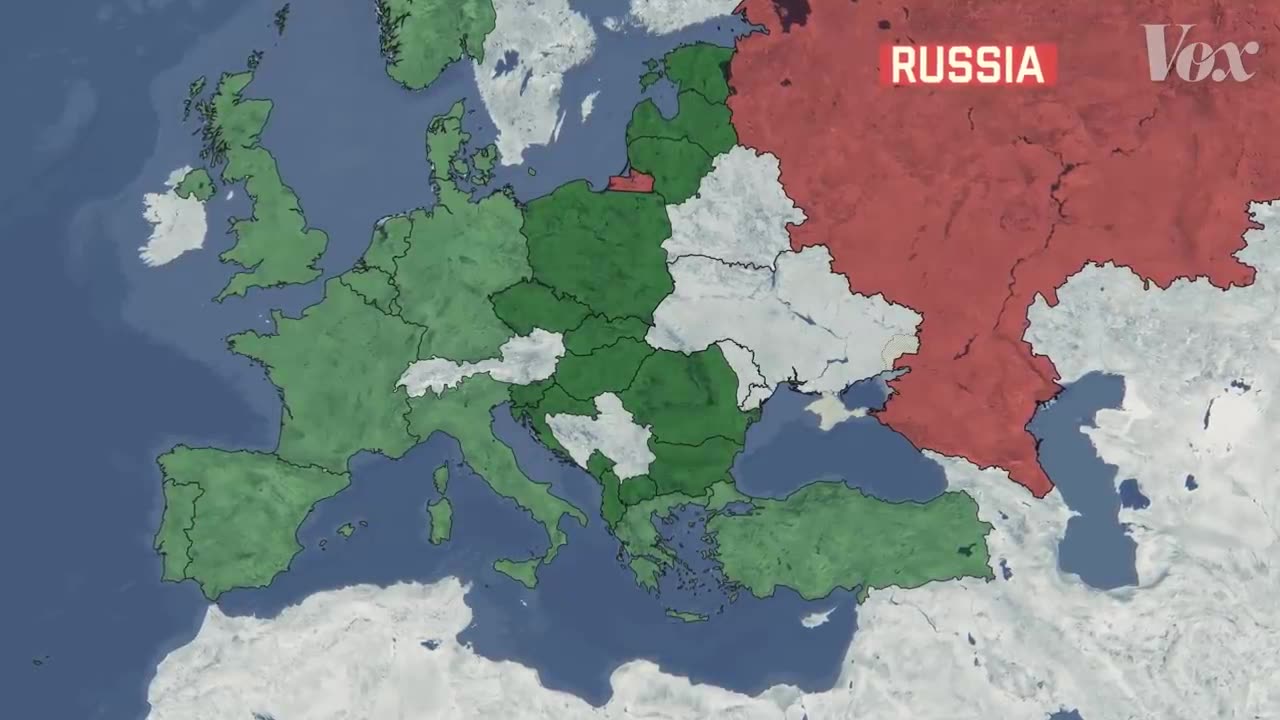
Putin's war on Ukraine refers to the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine, which began in 2014. The conflict erupted after Ukraine's political landscape shifted following the ousting of President Viktor Yanukovych, who was considered pro-Russian. This change in power led to tensions between Ukraine's pro-European and pro-Russian factions and resulted in Russia's military intervention in Crimea and eastern Ukraine.
The first major event in Putin's war on Ukraine was the annexation of Crimea in March 2014. Russian forces, without official insignia, occupied key government buildings and military bases in the region. A controversial referendum was held, resulting in Crimea being declared part of Russia. The international community widely condemned the annexation, viewing it as a violation of Ukraine's sovereignty and international law.
Following the annexation of Crimea, pro-Russian separatist movements emerged in eastern Ukraine, particularly in the Donbas region, consisting of Donetsk and Luhansk. These separatist groups, supported by Russia, declared independence and established self-proclaimed republics. The conflict escalated into a full-scale war, with Ukrainian government forces clashing with the separatists and Russian-backed troops.
Russia's involvement in the war on Ukraine is multifaceted. It includes the provision of military equipment, weapons, and troops to support the separatist forces. There have been numerous reports of Russian soldiers operating covertly in Ukraine, despite official denials from the Russian government. Russia has also been accused of fueling the conflict by providing financial and logistical support to the separatists.
The war on Ukraine has resulted in a significant loss of life and displacement of people. Thousands of combatants and civilians have been killed, and millions have been internally displaced or sought refuge in neighboring countries. The conflict has caused extensive damage to infrastructure, including homes, schools, hospitals, and vital services.
Efforts to resolve the war on Ukraine diplomatically have been ongoing but have had limited success. Multiple ceasefire agreements have been reached, such as the Minsk Protocol and the Minsk II agreement, but have been frequently violated. The conflict remains a major source of tension between Russia and Ukraine, with sporadic fighting and casualties continuing to this day.
The war on Ukraine has had profound geopolitical implications. It has strained relations between Russia and the West, leading to economic sanctions imposed on Russia by the United States, European Union, and other countries. The conflict has also fueled concerns among neighboring countries about Russia's intentions and territorial ambitions.
In conclusion, Putin's war on Ukraine is an ongoing conflict characterized by Russia's military intervention in Crimea and eastern Ukraine. The annexation of Crimea and support for separatist movements in the Donbas region have resulted in a protracted war with devastating humanitarian consequences. The conflict continues to pose significant challenges to Ukraine's sovereignty and stability, as well as to regional and international security.
-
 14:50
14:50
Russell Brand
11 hours agoJoe Rogan Goes Into SHOCK As Guest Exposes Government MIND CONTROL
62.4K86 -
 31:59
31:59
The Brett Cooper Show
12 days ago $7.83 earnedBernie Fights Oligarchy From His Private Jet & Prince Harry’s Biggest L Yet | Episode 30
43.8K29 -
 20:23
20:23
Exploring With Nug
15 hours ago $8.09 earnedI Found Something DISTURBING Thrown Off The Bridge!
211K9 -
 26:24
26:24
MYLUNCHBREAK CHANNEL PAGE
1 day agoMilitary Sites STOLE the Old World - Pt 1
154K72 -
 4:15:08
4:15:08
MissesMaam
7 hours agoRumblers Actin' Sus | Lockdown Protocol 💚✨
33.6K3 -
 4:09:19
4:09:19
GamerGril
9 hours ago☠ Doom Gal☠ | The Ages Aren't Dark Enough
82.5K18 -
 4:42
4:42
DecoyVoice
1 year agoPredictive AI is getting creepy
69.5K20 -
 4:16:28
4:16:28
SoundBoardLord
7 hours agoLockdown Protocol on a Sudbury Saturday Night!
38.1K3 -
 1:03:26
1:03:26
Tactical Advisor
13 hours agoUnboxing Tactical Gear/Hearing Protection Act | Vault Room LIve Stream 025
109K19 -
 5:00:00
5:00:00
Cripiechuccles
14 hours ago😁💚💙SHATTERDAY WITH CRIPIE💚💙RUMLUV ACTIVATE👌
34.9K4