Premium Only Content
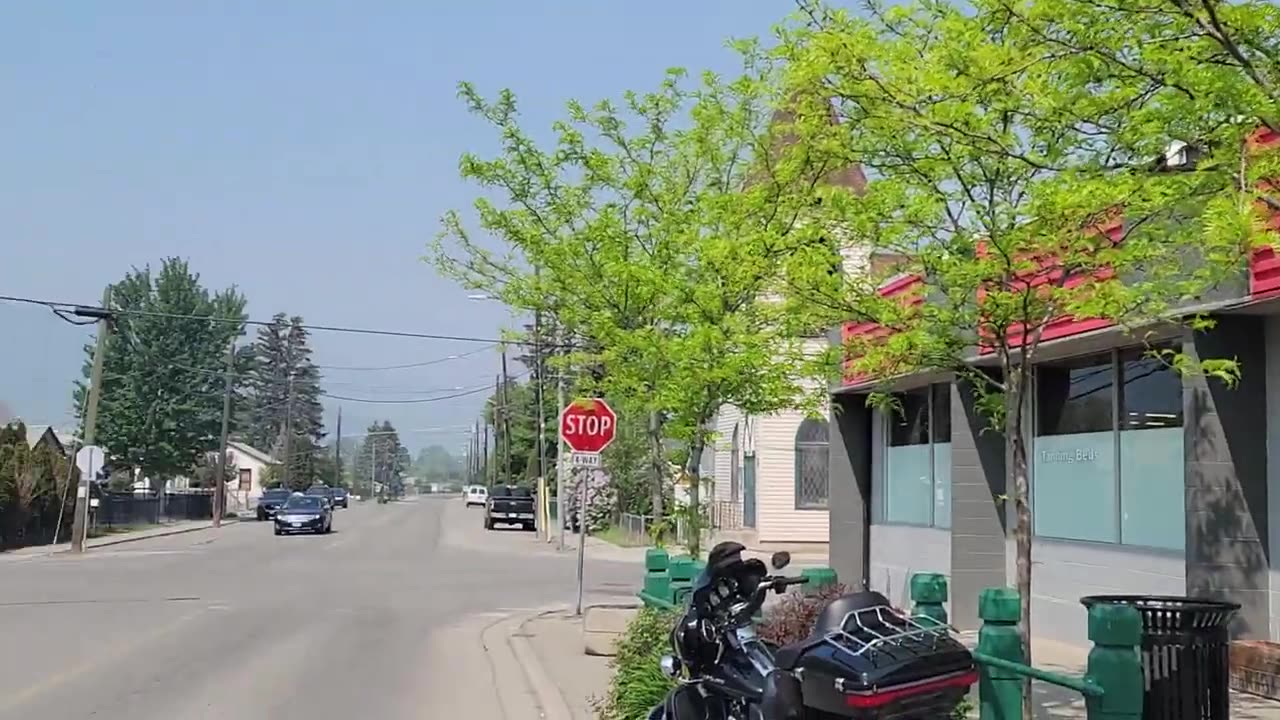

Smoke update in Merritt BC ! , Winds moving south west, Major Haziness thick like soup !
Smoke update in Merritt BC ! , Winds moving south west, Major Haziness thick like soup !
AI write up not me ! Tricking the Algo
Forest fires are catastrophic events that pose significant dangers to ecosystems, wildlife, human health, and property. In addition to the direct destruction caused by the flames, the thick smoke generated during these fires has far-reaching consequences, impacting air quality, climate change, and public health. This article explores the dangers associated with forest fires, with a focus on the hazards posed by thick smoke and the damages it can cause.
Forest fires cause extensive damage to ecosystems, destroying vast areas of trees, vegetation, and habitats. These fires can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to long-term consequences such as soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and alteration of natural processes. The direct destruction of forests not only affects the flora and fauna that rely on them but also disrupts the ecological services they provide, such as water filtration, carbon sequestration, and climate regulation.
Forest fires release massive amounts of smoke, composed of fine particles, gases, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The composition of smoke varies depending on the burned materials and the stage of combustion. Fine particles, known as PM2.5, are of particular concern due to their small size, allowing them to penetrate deep into the lungs when inhaled. The smoke also contains hazardous gases, including carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can have severe health implications.
Thick smoke from forest fires significantly degrades air quality, often extending hundreds or even thousands of kilometers from the fire source. The fine particles and gases released during combustion contribute to the formation of smog, reducing visibility and creating hazardous conditions for both humans and wildlife. Prolonged exposure to high levels of smoke can cause respiratory issues, aggravate existing respiratory conditions, and increase the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Forest fires play a crucial role in climate change. They release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming. The destruction of forests also reduces the Earth's capacity to absorb CO2, through photosynthesis, further exacerbating the problem, the release of black carbon (soot), from forest fires can deposit on ice and snow, reducing their reflectivity and accelerating ,the melting of glaciers and polar ice caps.
The thick smoke generated by forest fires poses significant risks to human health. Inhalation of fine particles and toxic gases can cause or exacerbate respiratory conditions, including asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The elderly, children, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable. Moreover, exposure to smoke can lead to eye and throat irritation, headaches, and fatigue. Prolonged exposure may also increase the risk of developing lung cancer and heart disease.
Forest fires have substantial economic consequences. The destruction of forests and the associated loss of timber resources impact industries such as logging and forestry. The tourism industry also suffers as popular destinations become engulfed in smoke and flames. Additionally, the costs of fire suppression efforts, property damage, and the rehabilitation of affected areas can be astronomical, placing a burden on local economies and governments.
-
 2:49
2:49
Mike Martins Channel
1 day ago $0.04 earnedwhat 20 Usd Bought me for Food in the Philippines 🇵🇭
1221 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Akademiks
3 hours agoICE MAN EPISODE 2 tonight. NEW NBA YOUNGBOY 'MASA' TONIGHT. BIG AKADEMIKS #2 MEDIA PERSONALITY 2025.
2,228 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
TimcastIRL
3 hours agoSouth Park Runs FULL FRONTAL Of Trump In Gross Parody After $1.5B Paramount Deal | Timcast IRL
8,598 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Quartering
2 hours agoOn To The Big Bosses! Act 2 Of Expedition 33
509 watching -
 1:24:56
1:24:56
Glenn Greenwald
5 hours agoGlenn Takes Your Questions on Tulsi's Russiagate Revelations, Columbia's $200M Settlement, and More | SYSTEM UPDATE #492
94.1K44 -
 LIVE
LIVE
megimu32
2 hours agoOTS: With Great Power: Every Spider-Man Movie Unmasked w/ @thisistheraygaming
129 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
WickedVirtue
1 hour agoSailing w/ The Crew
68 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Meisters of Madness
4 hours agoThe Finals with Redd
109 watching -
 1:27:11
1:27:11
Omar Elattar
9 hours agoThe Dating Expert: "I've Helped 4,000 Men Find LOVE!" - The #1 Alpha Trait Women Secretly Crave!
20K -
 LIVE
LIVE
VOPUSARADIO
9 hours agoPOLITI-SHOCK! "END THE FED, END THE LIES & END THE DEEP STATE ONCE AND FOR ALL"!
147 watching