Premium Only Content
AC Parameters (Frequency, Effective Value - RMS, Peak-to-Peak Voltage, Alternans, and Cycle)
Hi guys! In our previous lesson, we examined the characteristics of alternative current, direct current and the differences between them. In this lesson, we will examine the parameters of sinusoidal wave in alternative current such as period, frequency, effective value (RMS), maximum value, peak-to-peak value, alternans, and cycle. There are not many parameters in DC, however, there are many parameters in AC as I said. We will have learned these at the end of this lesson.
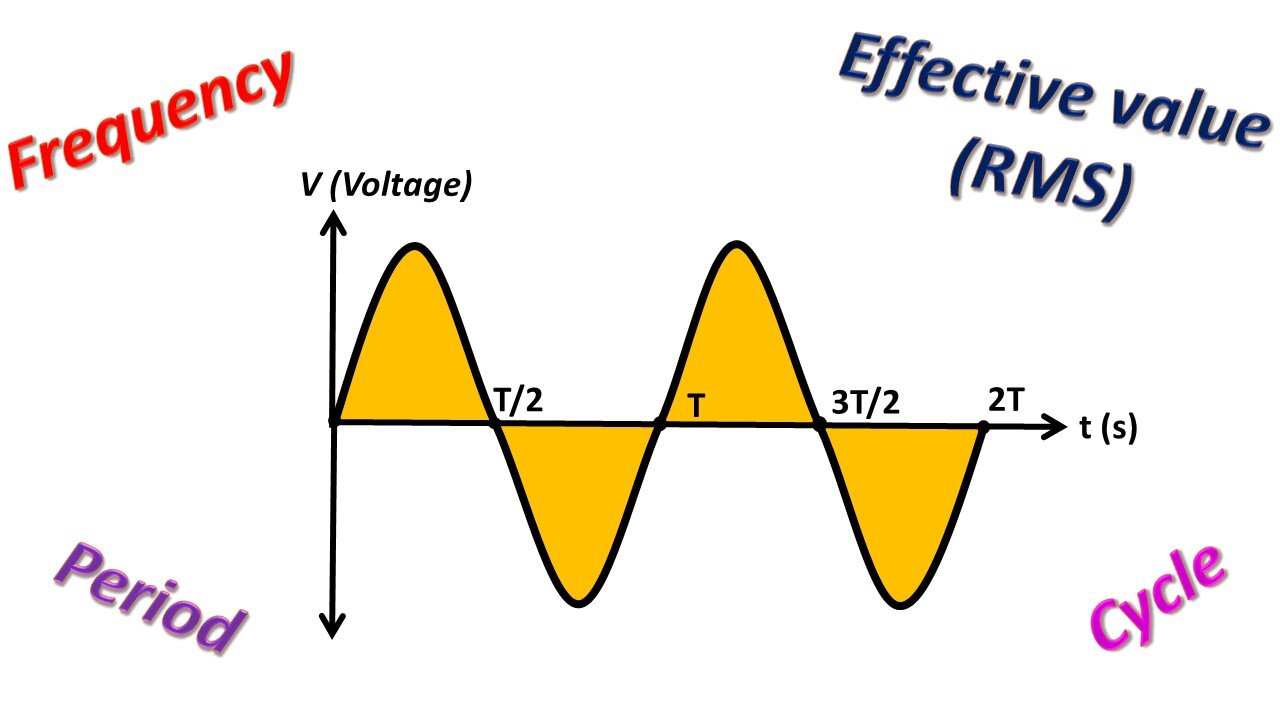
If the time axis is accepted as a reference in a sinusoidal signal, the portion of the signal above the time axis is called positive (+) alternans, and the portion below is called negative (-) alternans. The waveform formed by one full turn of the generator is called a cycle. In other words, when a cycle occurs, the generator makes a full 360-degrees turn. The time it takes for a cycle to occur is also called a period. The unit of the period is the second and is denoted by the letter "T". The number of repeated cycles of the signal in one second is called frequency. To talk about the frequency of an AC signal, that signal must have a period. In other words, if an AC signal repeats a certain cycle continuously, the frequency of that signal can be mentioned. Frequency is expressed as the mathematical inverse of the period. In this equation, f indicates the frequency of the signal and its unit is Hertz (Hz). E.g; The frequency of AC we use at home in the USA is 60Hz. In other words, 60 cycles of this sinusoidal waveform occur in one second.
We can think of it this way. If we light an incandescent lamp with a sinusoidal wave of 60 Hz, this lamp will flash 120 times per second. Because it will take 120 times maximum and zero values. But our eyes cannot detect more than 20 blinks per second. Therefore, we see the lamps as if they are always on. If we shoot a video of it and watch this by slowing down the speed, we can notice it.
The value at which the voltage is greatest is called the maximum value. It is denoted by Vm. The maximum value on the negative part of the graph would be –Vm. The amplitude value between the positive and negative maximum values is called the peak-to-peak voltage. The abbreviation Vpp, which is the initials of the words from peak to peak, is used for this. The equivalent of the work done by AC on a receiver to DC is also called effective value (RMS). For example, to obtain the amount of heat supplied by AC to a heater in a certain time interval, the value of DC, applied to the same heater for the same time, is the effective value of AC. The effective value is found by dividing the maximum value by √2.
We can explain better the effective value through this example. The time-dependent voltage values of the power supplies are given in the graphics below. On the left, a DC source with a constant voltage of 120V is connected to a heater. On the right, an AC source in the form of a sinusoidal wave with an effective value of 120V is connected to a heater. The energy that both heaters give us will be the same. In other words, we can say that the effective value is the value of the direct current corresponding to the alternative current. As a result, both power supplies do the same job.
Let's show these parameters on an instance. If we think according to the city network, that is, according to the electricity we use in the plug sockets at home, what are the values on the graph you see here? The frequency is 60Hz. Then the period will be equal to 1/f, i.e. 1/60, which is equal to about 0.017 seconds, or about 17ms. If we show the period on the graph, the time taken for a cycle to occur was 17ms in the mains. Meaning the rotor of the generator in the power plant completes one full revolution in 17ms. The effective value is 120V. Since the maximum value is √2xVRMS , √2x120 equals to 169V approximately. We can also show its location on the graph. Remember, Vpp is peak to peak value. Therefore, the value between the two peaks will be 338V from 2x169. The basic parameters of alternative current such as frequency, period, effective value, and maximum value used in the city network are as described above. The parameters of AC for the USA are like this, but these values may differ according to the countries. E.g; While 230V is used in European countries instead of 120V for the effective value, also the frequency is 50 Hz frequency instead of 60 Hz. You can calculate these parameters according to the values used by your own country.
The parameters of the AC sinusoidal wave are basically like this. I hope it was helpful and you liked it. Hope to see you in the next lesson. Goodbye.
These videos take a long time to make if you would like to buy me a coffee to say thanks, link below:
Buy Me a Coffe: https://www.buymeacoffee.com/eeapplications
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/eapplications
Paypal: paypal.eea@gmail.com
-
 8:09
8:09
Electrical Electronics Applications
2 years ago $0.01 earnedSeries and Parallel Combination Circuits Explained | How to Solve Any Series and Parallel Circuit?
193 -
 10:48
10:48
Nikko Ortiz
18 hours agoDont Watch These TikToks
58.1K11 -
 10:17
10:17
MattMorseTV
17 hours ago $12.71 earnedTrump's DOJ just DROPPED a NUKE.
72.8K79 -
 2:09:32
2:09:32
Side Scrollers Podcast
20 hours agoStreamer DIES Live On Air + Your Food is Poison + Xbox Announces $900 Handheld | Side Scrollers Live
25.2K11 -
 15:32
15:32
GritsGG
16 hours agoFull Auto ABR Sniper Support! Most Winning Quad Win Streaking!
13K3 -
 7:42
7:42
The Pascal Show
15 hours ago $0.89 earnedBREAKING! Police Provide UPDATE In Emmanuel Haro's Case! Is Jake's Lawyer Lying To Us?!
13.7K -
 2:29:46
2:29:46
FreshandFit
8 hours agoAfter Hours w/ Girls
117K80 -
 5:28
5:28
Zach Humphries
14 hours ago $1.73 earnedNEAR PROTCOL AND STELLAR TEAM UP!
20.8K2 -
 1:09:57
1:09:57
Brandon Gentile
1 day ago10,000 Hour BITCOIN Expert Reveals Why $13.5M Is Just The Start
26K3 -
 2:03:55
2:03:55
Badlands Media
8 hours agoDevolution Power Hour Ep. 382: DOJ Coverups, Clapper’s Team Sport & Trump’s Countermoves
138K24