Premium Only Content
Chapter-17, LEC-3 | Migration | #rumble #ethicalhacking #cybersport #cybersecurity #education
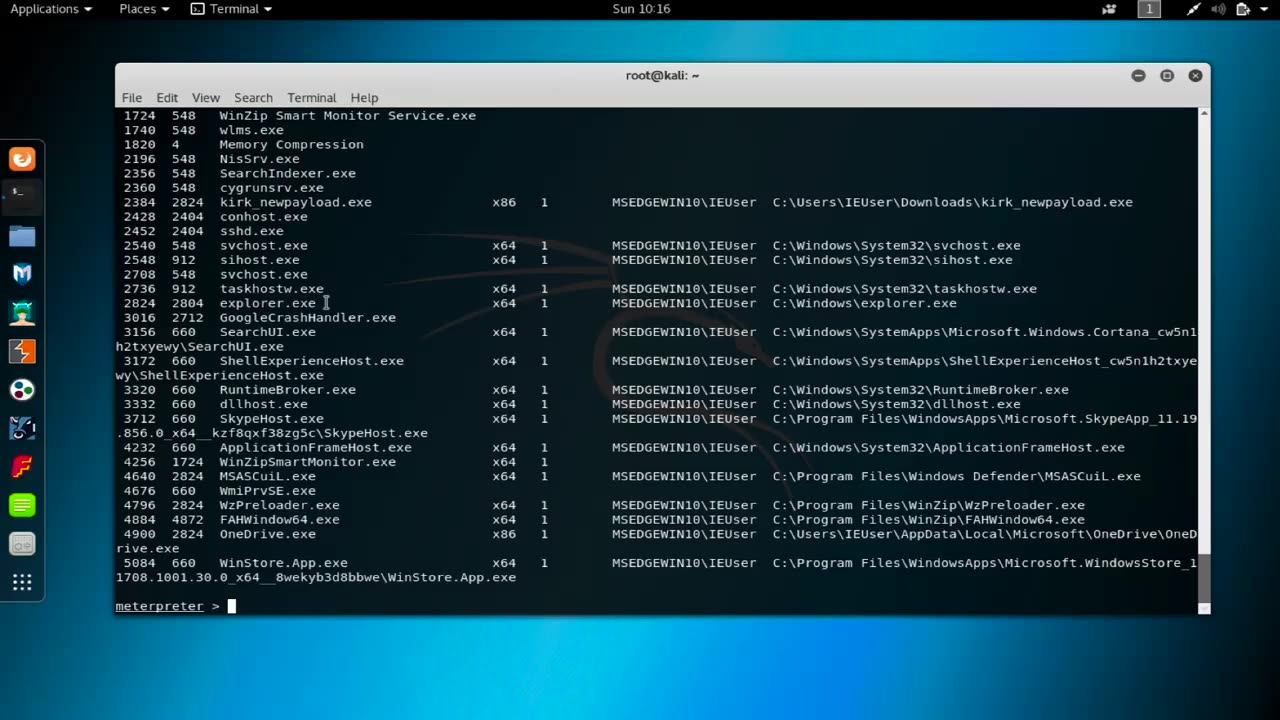
Migration is a critical post-hacking session that involves moving a compromised Meterpreter session to another process or system on the target network. The goal of migration is to maintain a persistent presence on the target network by evading detection and avoiding being terminated by security tools or system administrators.
When an attacker gains access to a system using a Meterpreter payload, they typically start with a low-privileged process or service, such as a web server or user-level process. However, these processes are often short-lived and can be terminated or restarted, which can result in the loss of access to the compromised system.
To maintain access, attackers use migration techniques to move the Meterpreter session to a more stable or privileged process, such as a system service or a process running with administrative privileges. This allows the attacker to maintain access to the compromised system even if the initial process or service is terminated.
There are various migration techniques available, depending on the operating system and network environment. For example, on Windows systems, attackers can use the "migrate" command in Meterpreter to move the session to a new process. On Linux systems, attackers can use tools like "pspy" or "lsof" to identify potential targets for migration.
Migration is a critical technique for maintaining access to a compromised system or network, but it's also a double-edged sword. If an attacker is careless or uses an inappropriate migration technique, they can potentially expose themselves to detection or trigger security alerts, making it easier for defenders to identify and remove their access. As such, migration is typically done by experienced and skilled attackers who have a deep understanding of the target network and security environment.
-
 1:19:42
1:19:42
Russell Brand
5 hours agoTHE LEFT’S NEW STAR — What Zohran Mamdani’s Victory Really Means - SF647
118K33 -
 1:42:32
1:42:32
vivafrei
10 hours agoLive w/ Stanislav Krapivnik - Military and Political Analyst on Russia, Europe & Beyond!
58.2K31 -
 LIVE
LIVE
LadyDesireeMusic
2 hours ago $0.01 earnedYour Daily White Pill- Music & Convo
157 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
StoneMountain64
6 hours agoBattlefield REDSEC UNSTOPPABLE WIN Squad
145 watching -
 1:40:36
1:40:36
The Quartering
6 hours agoKimmel Pulls Show Mysteriously, Youtube Collapse? & Much MOre
110K61 -
 LIVE
LIVE
cosmicvandenim
6 hours agoCOSMIC VAN DENIM | OFF CHARACTER | WARZONE PRACTICE
44 watching -
 2:08:06
2:08:06
The Robert Scott Bell Show
6 hours agoMike Adams, Brian Hooker, Live From Brighteon Studios in Austin Texas, Kids Triple Vaccinated, Blood Sugar and Autism, Candy Fed to Cows, Nutrition Reform - The RSB Show 11-7-25
41.5K10 -
 LIVE
LIVE
GritsGG
5 hours ago#1 Most Warzone Wins 3943+!
16 watching -
 1:15:58
1:15:58
DeVory Darkins
7 hours agoLIVE NOW: Democrats SABOTAGE GOP effort to reopen Government
114K62 -
 1:21:21
1:21:21
Tucker Carlson
6 hours agoThe Global War on Christianity Just Got a Whole Lot Worse, and Ted Cruz Doesn’t Care
70K273