Premium Only Content
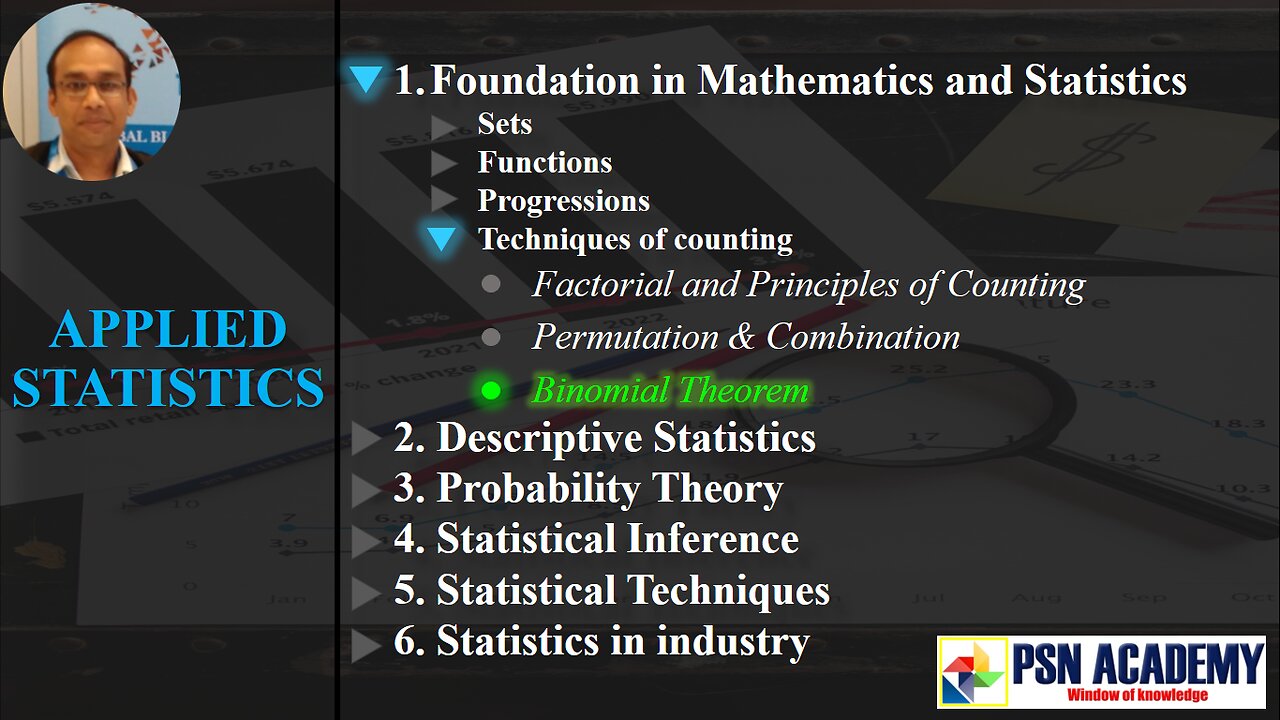
1.1.4.3 Binomial Theorem | Positive Integral Index | Negative Intetgral Index | Rational Index
In this video, you will get the idea of Binomial Theorem expansion with Positive Integral Index, Negative Intetgral Index and Rational Index.
1 term (monomial) : 16, 4𝑥, 3𝑥^7, 𝑎^4 𝑏
2 terms (binomial) : 𝑥+𝑦, 𝑝−𝑞, 𝑥^2−4𝑦, 7𝑎+3𝑏^2
3 terms (trinomial) : 𝑥+2𝑦−3𝑧, 𝑎−𝑏−𝑐, 2𝑥+3𝑦^4+6𝑧
4 or more terms (multinomial) : 𝑤+𝑥+5𝑦+𝑧, 2𝑎^3−𝑏−𝑐−𝑑^2+3𝑒
Binomial Theorem is a statement that describes this expansion of a binomial.
1. (_^𝑛)𝐶_0 , (_^𝑛)𝐶_1 . (_^𝑛)𝐶_2 ... (_^𝑛)𝐶_𝑛 are known as binomial coefficients.
2. Exponents of 𝑎: exponent of 𝑎 in the term with binomial coefficient (_^𝑛)𝐶_𝑟 will be 𝑛−𝑟.
3. Exponents of 𝑏: exponent of 𝑏 in the term with binomial coefficient (_^𝑛)𝐶_𝑟 will be 𝑟.
4. Sum of the exponents of 𝑎 and 𝑏 in each term: 𝑛
5. Total terms after expansion: 𝑛+1
6. Index: MUST be positive integer. When 𝒏 goes negative OR 𝒏 is rational, then this will not work.
N.B.: It is illeagal to download, distribute or display in public any part of this video production.
-
 19:39
19:39
James Klüg
1 day agoAnti-Trump Protesters Threaten To Pepper Spray Me For Trying To Have Conversations
15.7K16 -
 34:54
34:54
MattMorseTV
13 hours ago $26.01 earned🔴Trump just FIRED 154,000 FEDERAL WORKERS. 🔴
72.4K88 -
 2:03:32
2:03:32
Side Scrollers Podcast
21 hours agoMASSIVE Netflix Boycott + The TRUTH About Jimmy Kimmel’s Return + BIG Side Scrollers NEWS
35.6K15 -
 15:05
15:05
GritsGG
1 day agoFlawless Duos Victory w/ Most Winning Duo in Warzone History!
32.5K2 -
 1:53:52
1:53:52
FreshandFit
17 hours agoShe Was In 3 Domestic Violence Cases? Happy Birthday Fresh!!!
161K57 -
 2:03:22
2:03:22
Inverted World Live
9 hours agoThe Aliens Are Underwater | Ep. 117
78.8K29 -
 2:20:24
2:20:24
Badlands Media
17 hours agoDevolution Power Hour Ep. 394: The Long Game, Media Traps, and Military Signals
97.7K30 -
 2:08:38
2:08:38
TimcastIRL
11 hours agoNetflix Shares TANK, Elon Says BOYCOTT After Writer MOCKS Charlie Kirk Assassination
252K194 -
 8:48:01
8:48:01
SpartakusLIVE
13 hours agoI'M BACK || Quads w/ The Boys
95.4K9 -
 9:33
9:33
Ken LaCorte: Elephants in Rooms
16 hours ago $4.37 earnedWhy Do Black Men Love Big Butts?
38.4K26