Premium Only Content
Chlamydia Infection - Causes, Risk Factors, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Chlamydia infection is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections around the world.
It is a bacterial infection, caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis.
Transmission of the disease can occur in several ways, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone with the infection;
From mother to baby during childbirth;
And children, by sexual abuse.
Risk factors for getting the infection include unprotected vaginal, anal, and oral sex, such as not using condoms;
Having multiple sex partners, which is common among commercial sex workers;
And males having sex with males.
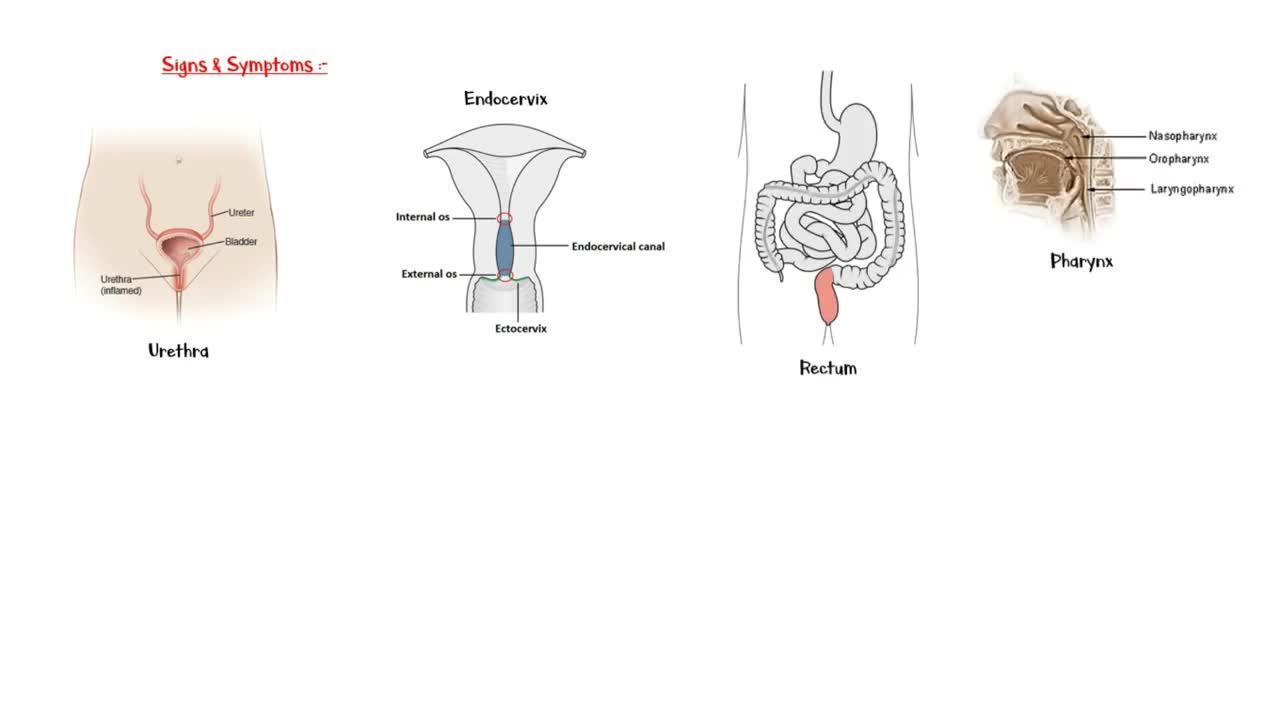
Signs and symptoms may vary according to the sex. Chlamydia infection commonly involves genital organs, such as urethra, and endo cervix.
However, it can involve other areas in the body as well. Including the rectum; Pharynx; And conjunctiva of the eye.
Up to 80% of the females & 50% of the males with the disease are asymptomatic. So, it is frequently unrecognized and therefore left untreated. In women, the initial most common site of infection is the cervix. This may cause signs and symptoms of cervicitis, such as mucopurulent vaginal discharge; and easily induced cervical bleeding.
Infection in the urethra can cause signs & symptoms of urethritis. These include polyuria; Painful urination; And frequent urination.
In men, chlamydia infection will manifest as urethritis with mucopurulent urethral discharge; Painful urination; And testicular tenderness, pain, & swelling.
Untreated chlamydia infection can lead to several complications. Spread of the infection to uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries can cause pelvic inflammatory disease, which leads to chronic pelvic pain; Infertility; Ectopic pregnancy; And fitz hugh Curtis syndrome, which is characterized by inflammation of the liver capsule, leading to adhesion formation. Chlamydia infection in pregnant mothers can lead to preterm delivery; And pneumonia and conjunctivitis of the newborn. Reactive arthritis is another complication of chlamydia infection. Finally, untreated chlamydia infection may increase the risk of HIV infection.
The mainstay of diagnosing chlamydia infection is nucleic acid amplification tests, which can be performed on urethral, endo cervical, oropharyngeal, and rectal specimens. If pelvic inflammatory disease is suspected, CT, or MRI scan is indicated.
Chlamydia infection can easily be treated with antibiotics. Azithromycin, and doxycycline are the first line agents for the treatment of chlamydia infection.
#Chlamydia #STI #STD
-
 1:01:56
1:01:56
BonginoReport
4 hours agoDems Scramble To Rebrand and it’s a BIG FAIL - Nightly Scroll w/ Hayley Caronia (Ep.114)
77.3K74 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Jimmy Dore Show
3 hours agoZelensky Wears SUIT to White House Meeting! MASSIVE Nationwide Protests In Israel! w/ Ryan Cristián
7,733 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Eternal_Spartan
19 hours agoEternal Spartan Plays Final Fantasy 7 Remake Pt. 5 | USMC Vet | Join the Best Chat on Rumble!
75 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
ZWOGs
5 hours ago🔴LIVE IN 1440p! - Kingdom Come Deliverance, Trying Off The Grid, and More! - Come Hang Out!
27 watching -
 1:10:27
1:10:27
Katie Miller Pod
7 hours ago $1.30 earnedEpisode 2 - Sage Steele | The Katie Miller Podcast
16.8K1 -
 6:32:18
6:32:18
MattMorseTV
9 hours ago $27.57 earned🔴Trump's meeting with Zelenskyy - LIVE🔴
114K81 -
 1:09:56
1:09:56
Kim Iversen
4 hours agoTrump Floats Sending U.S. Troops To Ukraine | Bill And Hillary Clinton Questioned Over Epstein Files
70.8K81 -
 10:02:30
10:02:30
GritsGG
11 hours agoWin Streaking! Most Wins 3390+ 🧠
23K5 -
 6:59:19
6:59:19
StoneMountain64
7 hours agoBattlefield 6 Roundup, and NEW MAP for Battlefield 2042 on the Road to BF6
84.8K2 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Spartan
3 hours agoOctopath 2 into Halo Infinite Ranked (Playing OP2 during infinite ranked queues, pun intended)
27 watching