Premium Only Content
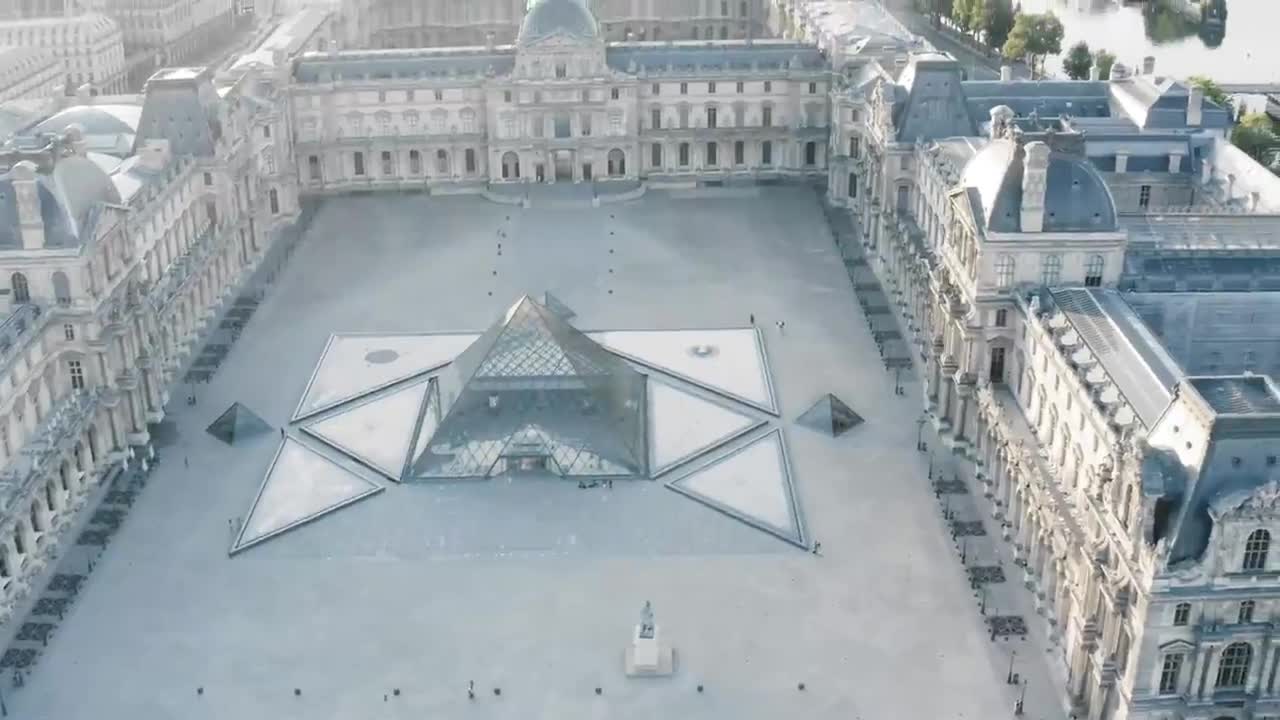

Drone Footage Captures The World's Most-Visited Museum, the Louvre Museum In Paris
Get The Best Drones Deals Here (Cheap Prices): https://bit.ly/3G0Dgvk
Get Drones Accessories Here: https://bit.ly/3WHBFRf
Get Drone BackPack Bags Here: https://bit.ly/3UFenJV
Get a Portable Power Station Here: https://bit.ly/3TvRzLO
Upgrade Your Photography Skills Here: https://bit.ly/3tgfZhr
Special Deals For Art Collectors Here: https://bit.ly/3Um7Ggb
===For Travelers===
Join TRAVEL + LEISURE CLUB here to save more with members-only savings deals: https://bit.ly/3UonkaK
The best way to obtain a travel visa to any country online with minimal effort and the highest approval rate, CLICK HERE: https://bit.ly/3teTqto
===The History of The Most Iconic Landmark In Paris, Louvre Museum===
When it was initially constructed, the Louvre museum in Paris served as a military outpost. In 1190 AD, French King Philippe II Auguste, also known as Philip the II of France (1165–1223, ruled after 1180), gave the order to erect a protective castle on the current site of the Louvre and a wall surrounding Paris.
As a result, the Louvre was initially utilised as a jail and an arsenal. Until Charles V (1338-1380, who ruled after 1364) had the fort converted into a royal home, the French royal family had their Paris residence on the Ile de la Cite in the Seine River (where the French Hall of Justice now sits). Charles V moved into the Louvre in 1369, not long after ascending to the throne as the King of Paris.
Therefore, the Louvre served as the French kings' residence in Paris from 1369 until 1422 and then again from 1527 to 1793. Of course, each French King had his own preferences for where to reside and which palace should serve as his main residence.
The Louvre palace was enlarged and embellished over time by the rulers. After 1515, King Francis I (1494–1547), who loved art, gathered a large number of Italian paintings and sculptures that he wished to exhibit in the Louvre. He assigned the task of rebuilding the palace to Pierre Lescot, a leading figure in the early French Renaissance. The sculptures' placement was the responsibility of Jean Goujon and Paul Ponce.
King Louis XIV moved his court to Versailles Palace in 1682, abandoning the Louvre as a major residence, despite the fact that it continued to be the royal palace for Paris. The Louvre palace was known around the world for its design and decoration by various masters of architecture.
The royal family was compelled to return to Paris and reside in the Louvre Palace during the French Revolution (more precisely, in 1791) by the revolutionaries, who also opted to use the Louvre Palace as a repository for all the scientific and artistic riches.
The Louvre changed its name to the Central Art Museum in 1793, two years later. Due to its extensive art holdings, the Louvre has now become a recognised museum around the world. The Louvre's remaining formal government departments (including the Finance Ministry) were relocated outside of the building in 1981, and the palace's usage as a museum afterwards took precedence.
The courtyard of the Louvre palace contains a huge glass pyramid. In French society, this arrangement was divisive and the topic of discussion. The French government commissioned Chinese-American architect Ieoh Ming Pei to create a structure for the bicentennial of the French Revolution during restorations in the 1980s.
This glass pyramid's design is in stark contrast to the Louvre's building style. Similar to how the Eiffel Tower concept sparked fears that an unsuitable structure would detract from Paris' artistic reputation, Pei's design also drew criticism.
The main entry to the exhibition sites is now this glass pyramid, whose multipurpose form better accommodates the growing number of visitors to the museum. Visitors are transported from the ancient Egyptian society to a tour of global art by the pyramid, which serves as a reminder of ancient Egypt.
The holdings of the Louvre museum include numerous treasures of art, including the Mona Lisa, Venus of Milo, Victoire de Samothrace, and many more old items. The museum's primary area of interest is the Renaissance through the classical Roman, Greek, and Egyptian periods.
Affiliate disclaimer:
Keep in mind that we may receive commissions when you click our links and make purchases. We are highly selective in products/services and try our best to keep things fair and balanced in order to help you make the best choice for you.
-

Sarah Westall
1 hour agoReal Intel: Power Struggles Fueled by Blackmail, Surveillance & Coercion w/ Dr. Dave Janda
7.95K4 -
 9:49
9:49
MattMorseTV
3 hours ago $0.44 earnedNewsom's CAREER just WENT UP IN FLAMES.
12.8K42 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Spartan
2 hours agoHalo for a bit, Octopath after maybe
120 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
sophiesnazz
3 hours ago $1.46 earned6kd in these lobbies !socials !specs
173 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Vedic compatability astrology
1 hour agoAbijit Shuckla: The Epic 8, 17, 25 Adventure!
40 watching -
 1:17:18
1:17:18
Jeff Ahern
4 hours ago $12.62 earnedThe Sunday Show with Jeff Ahern
33.2K5 -
 LIVE
LIVE
The Rabble Wrangler
4 hours agoSunday Shootouts in Battlefield 6 - Phantom Edition Giveaway!
110 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
Meisters of Madness
2 hours agoWuchang - Part 6
42 watching -
 34:55
34:55
Stephen Gardner
4 hours ago🔥Trump Admin FINALLY shutting it ALL DOWN!
40.1K84 -
 LIVE
LIVE
CassaiyanGaming
3 hours agoBattlefield 6 Open Beta Weekend!
31 watching