Premium Only Content
Application of the Theory of Yin-yang in Chinese Medicine
The embodiment of Yin-yang is in every
aspect of Chinese medicine theory. It is used to explain the physiology and
pathology of the human body. It also serves as a principle
guide to clinical diagnosis. Chinese medicine believes
that the normal physiological function of the human body results from the unifying,
opposing, and coordinating relationships between Yin and Yang. Yin-yang are always in the state of
the dynamic union of the opposites. One of the classic theories of Chinese
medicine states "Yin preserve the Essence", where "Yang transforms the Qi". This refers to a Yin being involved
in the process of producing and preserving the life essence. While Yang is involved in the process
of decomposing substance and releasing energy. Physiological function
is based on substance. Without substance, including
the essence of life, Blood, and Fluids, there would be no source for function. If the Yin-yang mechanisms of the body
were to separate from each other and will not assist each other,
life will come to an end. If the normal function of Yin
preserving the Essence and Yang transforming the Qi
were to break down, the human body would be in an abnormal
state, resulting in the onset of disease. For example,
Yin of the heart will be depleted when structural parts of the heart
are damaged in a myocardial infarction. This will reduce the heart's
ability to pump, which can be understood as
the function of the Heart-yang. Because one of the basic pathogeneses of
a disease is the imbalance of Yin and Yang, any disease,
no matter how intricate and volatile its clinical manifestation, can
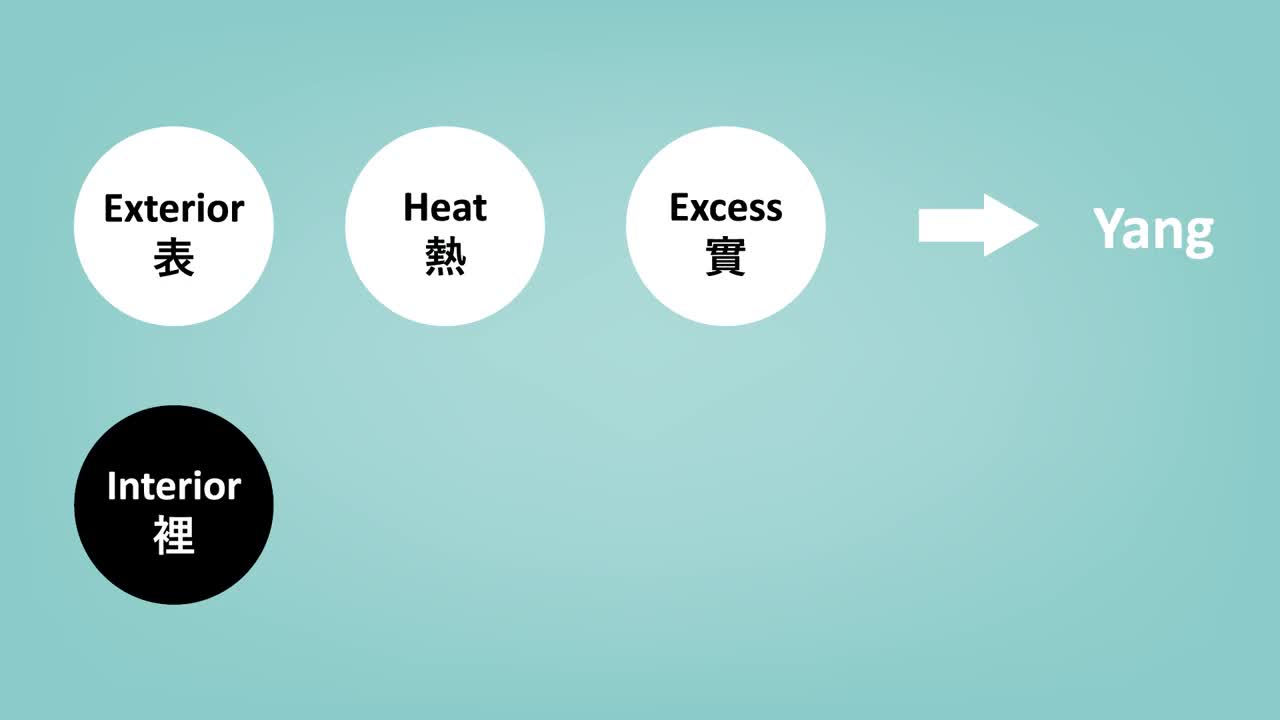
be diagnosed with the theory of Yin-yang. Diseases are classified as Exterior and
Interior according to their locations and as Cold, Heat, Deficiency, and
Excess according to their nature. As a result, when using the Theory
of Yin-yang, Exterior, Heat, and Excess are considered as Yang. Interior, Cold, and
Deficiency are considered as Yin. In Chinese medicine,
when making a diagnosis, the most important thing is to ascertain
whether the disease is Yin or Yang. For example, in a case where
Yang-Heat is exuberant and injures Yin-Fluids. The method of "Cooling what is Hot"
requires the use of medicinal substances that are Cold in nature to
reduce the surplus of Yang. For a case of excessive Yin-Cold,
injuring the Yang-Qi, the method of "Heating what is Cold"
requires the use of medicinal substances that are Hot in nature to
restrain excessive Yin. Because both syndromes
are both Excess syndromes, the therapeutic principles is called
"Treating Excess syndromes with purgation". For a case of hyperactivity of Yang due
to Yin-fluids failing to control Yang, or a case of exuberance of Yin due to
depleted Yang-Qi failing to control Yin. The treatment must include reinforcing
the deficiency of Yin or Yang. The therapeutic treatment principle
of restoring a relative balance between Yin and Yang is treating Yin for Yang
illness and treating Yang for Yin illness.
-
 2:12:28
2:12:28
Badlands Media
15 hours agoBaseless Conspiracies Ep. 144: NATO Narratives, Media Meltdowns & a Brightcore Boost with Kim Bright
114K16 -
 2:02:11
2:02:11
Inverted World Live
10 hours agoGiant Underground Blob Moving Toward NY | Ep. 85
51.8K20 -
 2:46:21
2:46:21
TimcastIRL
9 hours agoTexas GOP Greenlights ARREST WARRANTS For Dems Who FLED State | Timcast IRL
248K92 -
 3:16:50
3:16:50
Laura Loomer
9 hours agoEP137: EXPOSED: How Tucker Carlson Became Hunter Biden's Wingman
77.2K82 -
 4:22:34
4:22:34
Akademiks
8 hours agoNicki Minaj vs Dez Bryant. Trump Calls out Charlamagne. Diddy Denied Bail Again! ICEMAN soon?
62.1K3 -
 3:16:28
3:16:28
Nerdrotic
10 hours ago $10.69 earnedNerdrotic at Night 504
89.1K3 -
 8:20:30
8:20:30
Dr Disrespect
18 hours ago🔴LIVE - DR DISRESPECT - WARZONE - RANDOMLY GENERATED LOADOUTS EVENT
236K9 -
 1:36:07
1:36:07
Glenn Greenwald
12 hours agoTrump Admin Unleashes More Policies That Prioritize Israel Over American Citizens; The Smear Campaign Against Gaza Aid Whistleblower with Journalist Mel Witte | SYSTEM UPDATE #497
152K195 -
 58:14
58:14
MattMorseTV
11 hours ago $15.50 earned🔴Hakeem just lost EVERYTHING.🔴
88.2K63 -
 9:21:36
9:21:36
Rallied
14 hours ago $3.20 earnedWARZONE CHALLENGES WITH DRDISRESPECT & BOB
88.5K5