Premium Only Content
"Liquidity Pools & Yield Farming - How Does It All Work?"
FoRGe Finance
358 subscribers
“Liquidity Pools” are reserves of tokens secured within a smart contract hosted by decentralized exchanges/protocols. They are the core technology behind the decentralized finance ecosystem.
“So what is a liquidity pool?”
First let’s make sure we understand the difference between centralized finance and decentralized finance.
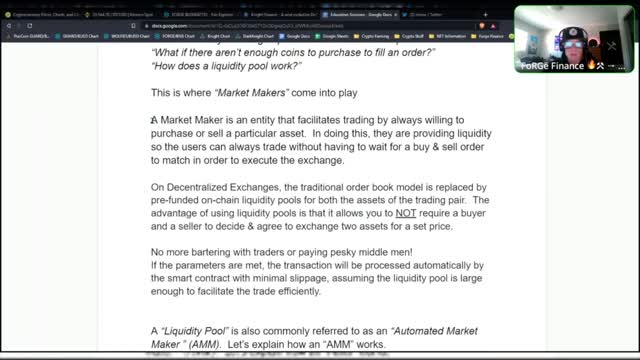
In centralized financial systems, such as the New York Stock Exchange, the NASDAQ, and various centralized exchanges like Coinbase & Binance, an “Order Book Model” is used to execute trades.
In this model, buyers and sellers come together and place their orders. Buyers attempt to purchase a specific asset for as low as possible, sellers try to sell the same asset for as high as possible.
For a trade to be executed, both the “buyers” and “sellers” must converge and agree on a set price. This can happen by a buyer bidding higher, or a seller lowering their selling price.
A “Liquidity Pool” is also commonly referred to as an “Automated Market Maker ” (AMM). Let’s explain how an “AMM” works.
Each token swap that a liquidity pool facilitates results in a price adjustment of the assets within the pair. The price of an asset is dictated by a deterministic pricing algorithm used by the liquidity pool. This algorithm is called a “Constant Product Market Maker” and is commonly represented by the equation Y x Z = K.
This gets complex, for the sake of time we will break it down further later.
The price you see on a data aggregator like “DexTools” or “PooCoin” is an estimate of this ratio updated in real time in a simple User Interface (UI).
To clarify, the assets in these liquidity pools are provided by other users, in order to facilitate trading & exchanges between the two assets in the pair.
These LPs (liquidity providers) earn passive yield via the trading fees associated with every exchange made between the two assets in the pair.
This is what we call “Liquidity Pool Mining”
When you provide liquidity for an asset pair, you receive “LP tokens” that are proportionate to your share of that liquidity pool.
The liquidity provider earns a percentage of the trading fees based on his/her percentage ownership of the liquidity pool.
“Alright I think I’m getting it now. So how does yield farming work then?”
Yield farming was created to further incentivize users to provide liquidity.
In order for a Decentralized Exchange (DEX) to function efficiently, large amounts of liquidity must be provided by the user base.
This allows the exchange to facilitate trades between many different assets with minimal slippage. In order to lure investors to provide liquidity for the DEX, the exchange provides high rates of return in their “native token”.
To do this, the DEX provides LP token pools called “Farms” for liquidity providers to deposit their LP tokens into. This allows the liquidity provider to earn the “native token” of the DEX in addition to the normal fees collected via liquidity pool mining.
-
 19:31
19:31
Liberty Hangout
3 days agoAnti-Trumpers Repeat CNN Talking Points
176K207 -
 19:53
19:53
Clintonjaws
2 hours ago $0.77 earnedThey Lied About Charlie Kirk - MAJOR UPDATE
9023 -
 LIVE
LIVE
Midnight In The Mountains™
10 minutes agoArc Raiders w/ The Midnights | THE BEST LOOT RUNS HERE
33 watching -
 DVR
DVR
ladyskunk
1 hour agoBorderlands 4 with Sharowen Gaming, Rance, and Sweets! - Part 8
3502 -
 LIVE
LIVE
S0lidJ
1 hour ago🟢Live -S0lidJ - Solos Arc Raiders
48 watching -
 LIVE
LIVE
TheItalianCEO
5 hours agoSunday is for chill games
86 watching -
 10:24
10:24
AlaskanBallistics
17 hours agoDiscovery Optics 1-8x28mm LPVO Riflescope Review
1.63K -
 2:08:24
2:08:24
Jeff Ahern
3 hours ago $7.20 earnedThe Sunday Show with Jeff Ahern
13.5K6 -
 27:41
27:41
DeVory Darkins
1 day agoMarjorie Taylor Greene STUNNED after Trump pulls her endorsement
37.8K316 -
 5:06:28
5:06:28
ttvglamourx
5 hours ago $0.73 earnedSUSSY SUNDAY !DISCORD
6.5K